β-thalassemia is an inherited haemoglobinopathy characterised by impaired haemoglobin (Hb) production, chronic anaemia, and iron overload that affects survival and quality of life. Tailored red blood cell transfusions and novel therapies target key pathophysiologic mechanisms in transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia (TDT) and NTDT. Patients with NTDT do not require lifelong regular transfusion for survival; however, they may require occasional transfusions during pregnancy, surgery, or infection [1].
The Hb level significantly correlates with morbidity-free survival in NTDT: an Hb increase of <8 g/dL to >10 g/dL in steps of 1 g/dL dramatically decreases the development of morbidities [2]. This highlights the need for effective management options for anaemia in NTDT, which are currently unavailable.
Therefore, the BEYOND study (NCT03342404) aimed to determine the safety and efficacy of luspatercept in adult patients with NTDT. Luspatercept is an ActRIIB/IgG1 Fc recombinant fusion protein that has been approved for the treatment of anaemia in adult patients with TDT. Participants were randomised to either 1 mg/kg subcutaneous luspatercept (n=100) or placebo (n=50) every 3 weeks for a duration of at least 48 months. The study was followed by an open-label treatment period and post-treatment follow-up. The primary endpoint was ≥1.0 g/dL mean Hb increase from baseline, in the absence of transfusions, over a 12-week interval from weeks 13 to 24.
Prof. Ali Taher (American University of Beirut Medical Center, Lebanon) presented the first results. The primary endpoint was met: 77.1% of participants treated with luspatercept achieved a mean Hb increase of ≥1.0 g/dL from baseline (P<0.0001), regardless of the baseline being <8.5 or ≥8.5 g/dL and regardless of patient subgroup (see Figure), whereas none of the participants treated with placebo achieved this endpoint. Moreover, 52.1% of participants in the luspatercept arm achieved a mean Hb increase of ≥1.5 g/dL from baseline.
Figure: Subgroup analysis of mean change in Hb from baseline to weeks 13-24 [1]
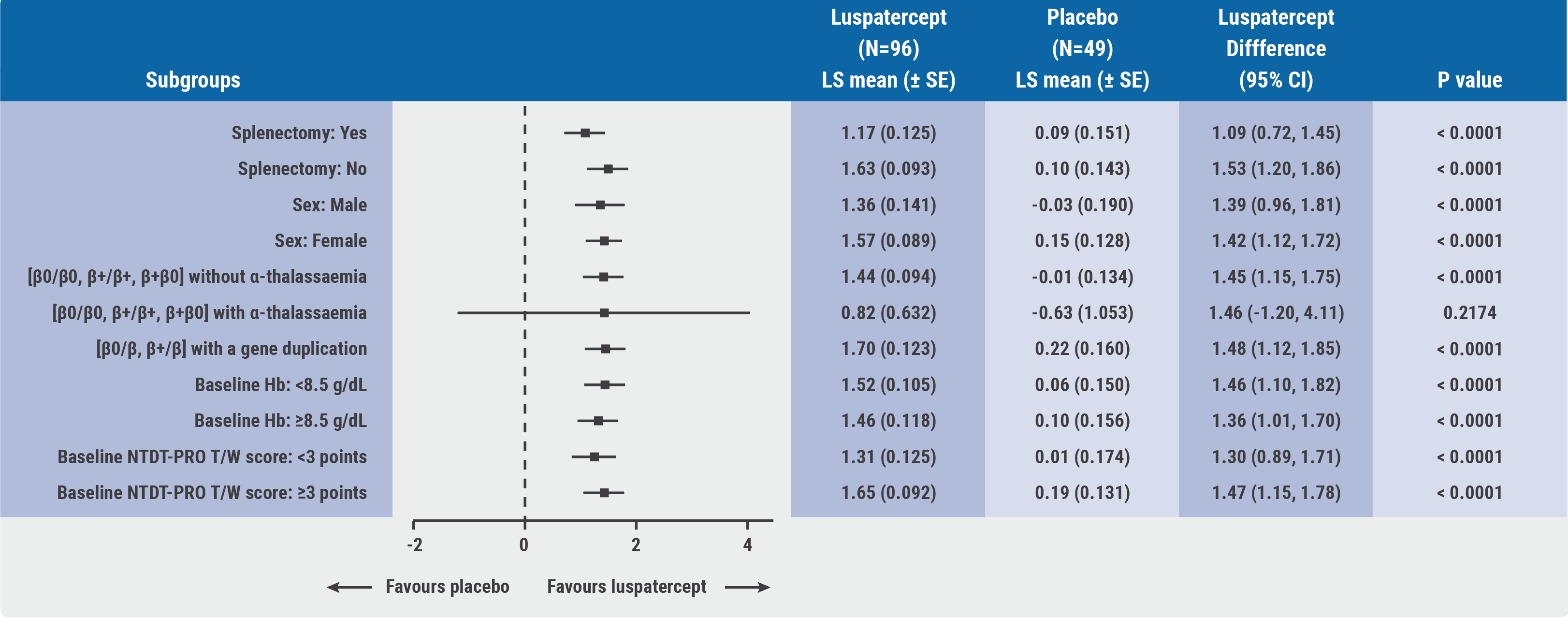
A key secondary endpoint was improvement in quality of life as assessed in NTDT–patient-reported outcomes (PRO) in the domains of tiredness and weakness (T/W) scores from baseline, which occurred more frequently in patients receiving luspatercept and was consistently improving through week 78. The improvement in NTDT-PRO T/W score was significantly correlated with Hb increase (R= -0.29; P<0.0001). The safety outcomes were similar in both arms; no deaths, malignancies, or thromboembolic events were reported.
Prof. Taher summarised, “The clinical benefit of luspatercept treatment, previously observed in patients with TDT through significant reduction in red blood cell transfusion burden, has now also been observed in patients with NTDT, as measured by meaningful improvement of anaemia.”
- Taher AT, et al. The BEYOND study: results of a phase 2, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study of luspatercept in adult patients with non-transfusion dependent beta-thalassemia. P204-2, EHA 2021 Virtual Congress, 09–17 June.
- Musallam KM, et al. Ann Hematol 2021;Feb 11. DOI: 1007/s00277-020-04370-2.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Personalising treatment for sickle cell disease Next Article
Letter from the Editor »
« Personalising treatment for sickle cell disease Next Article
Letter from the Editor »
Table of Contents: EHA 2021
Featured articles
Lymphoma
Immuno-oncology agents are effective in treating classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma
MATRix with ASCT: best long-term survival for primary CNS lymphoma
Naratuximab emtansine + rituximab safe and effective in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
The journey ahead for CAR T-cell therapy in r/r follicular lymphoma
ZUMA-5 vs SCHOLAR-5: Axicabtagene ciloleucel significantly improves FL outcome
Promising chemo-free treatment options in r/r DLBCL
Leukaemia
Sabatolimab achieved durable responses in patients with high-risk MDS and AML
Final analysis of EURO-SKI: primary endpoints met in chronic myeloid leukaemia
Favourable outcomes with zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib in patients with r/r CLL
Oral azacitidine improves overall survival in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia
Reduced-intensity conditioning ASCT is effective in older patients with AML
ELEVATE-TN: Acalabrutinib shows long-term efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
ELEVATE-RR: Acalabrutinib demonstrates similar efficacy and better safety versus ibrutinib
Fixed 12 cycles and MRD-guided venetoclax consolidation effective in CLL
GLOW: Ibrutinib + venetoclax showed superior PFS as first-line CLL treatment
Myeloma and Myelofibrosis
Novel targets in myelofibrosis: overview of emergent therapies
Immune therapy of multiple myeloma
MAIA results confirm superior efficacy of daratumumab with standard-of-care
ANDROMEDA: Addition of daratumumab showed superior efficacy in patients with AL amyloidosis
Thrombotic and Thrombocytopenic Disorders including COVID-19 related
Acquired TTP: new treatments and updated guidelines
Maternal screening to prevent foetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia
Fostamatinib effectively increased platelet counts in immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Physiopathology of coagulopathy in haematological malignancies and COVID-19
Haemostatic abnormalities are associated with mortality in COVID-19
Mechanisms of COVID-19 vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia
COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia: discovery and diagnosis
Haemoglobinopathies
Luspatercept improved anaemia in patients with non-transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia
Personalising treatment for sickle cell disease
Gene therapy: A promising approach for hereditary haemoglobinopathies
Related Articles
August 9, 2019
New sickle cell drug voxelotor boosts levels of haemoglobin
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

