Dr Geu-Ru Hong (Yonsei University College of Medicine, South Korea) presented the results of the open-label, parallel group, randomised Korean ENAVLE study, which aimed to explore the efficacy of edoxaban in patients after mitral valve repair or bioprosthetic valve implantation [1]. Dr Hong pointed out that 3 months of warfarin administration after surgical or transcatheter valve therapy is common practice in Korea. The problem is that a Korean diet typically includes high levels of vitamin K that can interfere with the efficacy of warfarin. Thus, the investigators in this trial sought to identify an alternative among the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the occurrence of thromboembolic and any thrombus at repaired ring or bioprosthetic valves at week 12. Patients (n=220) were randomised, 5 to 9 days after surgical aortic or mitral valve replacement or repair, to receive edoxaban (60 mg or 30 mg once daily; n=110) or warfarin for 3 months (standard care; n=110). Baseline characteristics were well balanced; both arms had similarly high levels of hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, and/or atrial fibrillation. Outpatient clinic visits occurred at 2, 4, and 12 weeks. Echocardiography and CT scans were performed during the final visit at 12 weeks.
In total, 4 patients from the warfarin group and 0 patients in the edoxaban group experienced a primary outcome event. Additionally, there were 3 ISTH bleeds with edoxaban versus 1 with warfarin. Dr Hong noted that a higher risk for gastrointestinal bleeding was observed in the edoxaban group, which may warrant further consideration. Session co-moderator Dr Martin Leon (New York Presbyterian Hospital, USA) summarised: “If we are going to change the guideline recommendation and begin using a DOAC post-valve therapy, we need more data. We need larger numbers of patients to be assured of safety, and to be at least somewhat confident that there really is an efficacy benefit relevant to no therapy, which is generally the standard in the United States.”
Table: Efficacy outcomes in the intention-to-treat cohort [1]
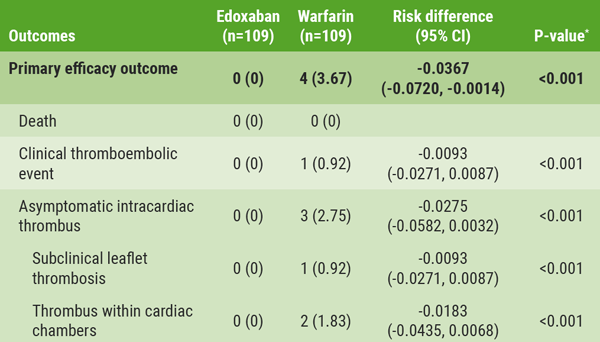 * P for non-inferiority.
* P for non-inferiority.- Hong GR, et al. Abstract 412-14. ACC/WCC 28-30 March 2020.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Bleeding reduction post-TAVI with OAC alone vs OAC + clopidogrel Next Article
TAILOR-PCI misses endpoint but still provides valuable insights »
« Bleeding reduction post-TAVI with OAC alone vs OAC + clopidogrel Next Article
TAILOR-PCI misses endpoint but still provides valuable insights »
Table of Contents: ACC/WCC 2020
Featured articles
Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies
Mavacamten shows promising results in non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Vericiguat shows beneficial effects in a very high-risk HF population
No role for sodium nitrite in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Vascular Medicine and Thromboembolism
Rivaroxaban and aspirin effective and safe for PAD patients
TAILOR-PCI misses endpoint but still provides valuable insights
Edoxaban: alternative to warfarin after surgical aortic or mitral valve procedures?
Bleeding reduction post-TAVI with OAC alone vs OAC + clopidogrel
Apixaban offers new perspective for cancer patients in need of anticoagulation
Rivaroxaban superior to enoxaparin in preventing VTE in non-major orthopaedic surgery
Interventional Cardiology
TAVR safe and effective in low-risk bicuspid aortic stenosis patients
TAVR model reveals differences in hospital outcomes
2-year results show non-significant outcomes TAVR vs surgery in severe aortic stenosis
Renal denervation better than sham for blood pressure
Infusion of ethanol in the vein of Marshall for persistent AF
Atrial Fibrillation/Acute Coronary Syndrome
Fewer adverse events with ticagrelor monotherapy after 3 months DAPT
TWILIGHT sub-study: same outcomes for diabetes patients
TWILIGHT sub-study: complex PCI patients
LAAO Watchman registry data positive
Apixaban in AF patients with recent ACS/PCI: Drop aspirin after 30 days
Genetics and Prevention
Homozygous FH responds to alirocumab
Evinacumab significantly reduces LDL-C in homozygous FH patients
Higher serum levels of eicosapentaenoic acid correlate with reduced CV events
Quit smoking: vaping + counselling helps
Related Articles
September 8, 2020
Homozygous FH responds to alirocumab
September 8, 2020
TAVR safe and effective in low-risk bicuspid aortic stenosis patients
September 8, 2020
PCI and CABG are equal in left main CAD
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

