The selective IL-23 blocker guselkumab demonstrated efficacy in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in the two phase 3 trials DISCOVER-1 (NCT03162796) and DISCOVER‑2 (NCT03158285) [1]. Dactylitis and enthesitis are both key PsA clinical manifestations that can be difficult to treat and increase the disease burden. In a pooled analysis of the DISCOVER-1 and -2 trials including 1,100 patients, relationships between improvements in dactylitis or enthesitis and other PsA domains in patients with dactylitis or enthesitis at baseline were assessed.
At baseline, 42% of the pooled patients had dactylitis (assessed in a total score 0-60) and 65% had enthesitis (assessed in the Leeds Enthesitis Index). At week 24, guselkumab in both doses significantly improved dactylitis (see Figure) and enthesitis scores compared with placebo. Rates of dactylitis or enthesitis resolution by week 24 were consistently significantly associated with ACR20/50/70 and PASI75/90 response (P<0.001). At week 24, significant correlations were observed between dactylitis change scores and PASI. As Prof. Dennis McGonagle (University of Leeds, UK) pointed out during the presentation, improvement in dactylitis by guselkumab was also associated with improved mental health. Likewise, improvements in enthesitis index score correlated with improved physical function.
Figure: Pooled DISCOVER-1 & 2: Improvement/resolution of dactylitis through week 24 among patients with dactylitis at baseline [1]
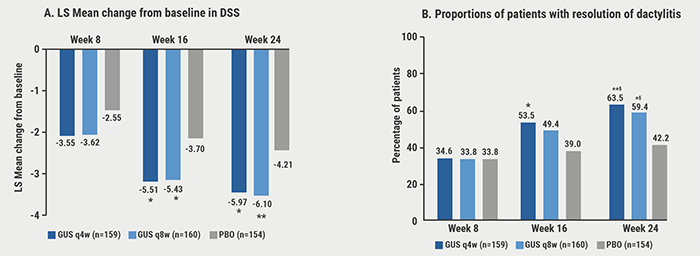
Unadjusted (nominal) *P<0.01, **P<0.001 versus placebo
- McGonagle D, et al. Effects of guselkumab, a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19-subunit of interleukin-23, on dactylitis and enthesitis in patients with active psoriatic arthritis: pooled results through week 24 from two phase 3 studies. 0895, ACR Convergence 2020, 5-9 Nov.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Promising novel treatment option for psoriatic arthritis Next Article
Artificial intelligence can help in the diagnosis of axSPA »
« Promising novel treatment option for psoriatic arthritis Next Article
Artificial intelligence can help in the diagnosis of axSPA »
Table of Contents: ACR 2020
Featured articles
Late-Breaking News
Gout treatment with febuxostat: no higher cardiovascular mortality
New agent with great potential for the treatment of giant cell arteritis in the pipeline
Autotaxin inhibitor successful in the first trial in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
JAK inhibition as a treatment option for ankylosing spondylitis
Spotlight on Rheumatoid Arthritis
Persuasive long-term results for JAK inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis: new EULAR treatment guidelines
Rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: a deadly combination
COVID-19 – What Rheumatologists Need to Know
COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic disease: most report mild disease
Poor disease control: a risk factor for severe COVID-19
No heightened outcome risk for rheumatic patients with COVID-19
What Is Hot in Lupus Nephritis?
Lupus nephritis biomarkers: moving toward an omic-driven approach
Lupus nephritis: new therapies on the horizon in 2020
Spondyloarthritis – The Beat Goes On
Artificial intelligence can help in the diagnosis of axSPA
Resolution of dactylitis or enthesitis is associated with improvements in joint and skin symptoms
Promising novel treatment option for psoriatic arthritis
How to Diagnose Large Vessel Vasculitis: Promises and Pitfalls
How to choose imaging modalities in large vessel vasculitis
Diagnosis of large vessel vasculitis with imaging
Osteoarthritis – Novel Developments
Knee osteoarthritis patients with indicators of inflammation could profit from methotrexate
Anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonist is associated with risk of knee and hip replacement
Osteoporosis – New Data
Bisphosphonate use: Asian American women have a smaller treatment benefit
Inflammatory disease as a risk factor for fractures
Best of the Posters
No progression of osteoarthritis with corticosteroid injections
Hydroxychloroquine use: no indication for arrhythmias in RA and SLE patients
Children with rheumatic disease have no greater risk of a COVID-19 infection
Insufficient antimalarial supply for rheumatic disease treatment in the early COVID-19 pandemic
Related Articles
January 18, 2021
No heightened outcome risk for rheumatic patients with COVID-19
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

