The 156-week, phase 3 SPIRIT-P2 study included patients who met the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) and had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or 2 TNFi. Although there was a placebo group through week 24, this data was derived only from patients in the intent-to-treat population randomised to ixekizumab at baseline. The 244 participants were randomised to 80 mg subcutaneous ixekizumab every 2 (Q2W; n=123) or 4 weeks (Q4W; n=122) after they received a 160 mg starting dose. Their baseline characteristics are outlined in the Table.
Table: Baseline characteristics [1]
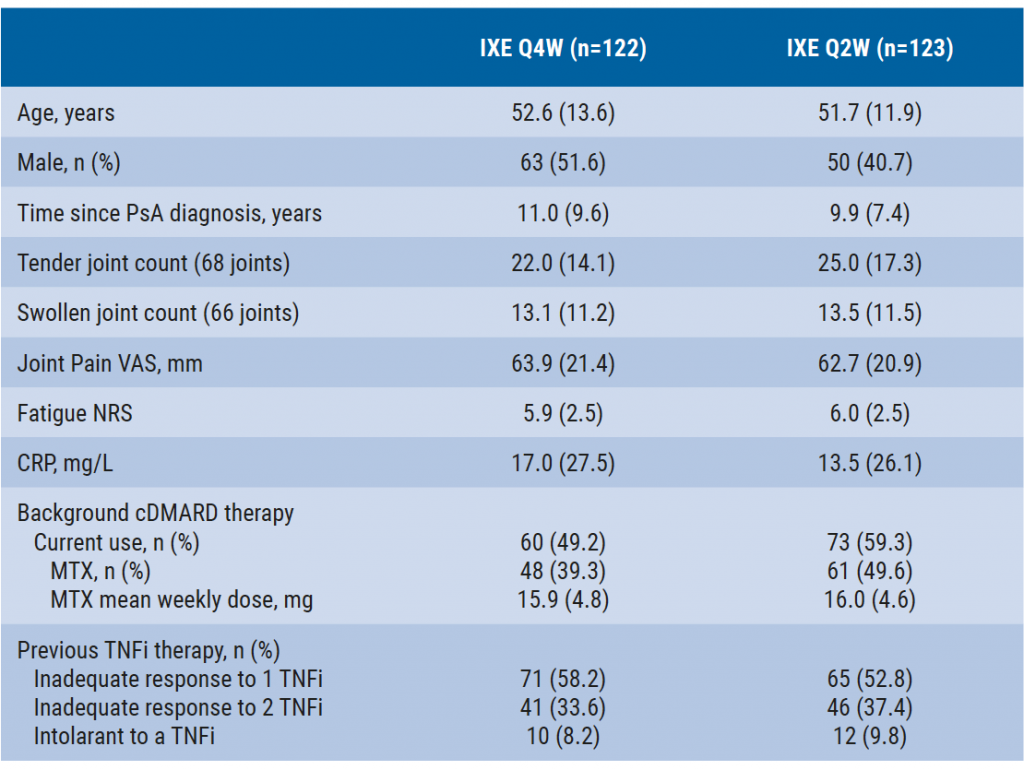 Mean (standard deviation) unless stated otherwise.
Mean (standard deviation) unless stated otherwise.Participants self-rated their symptoms using the Joint Pain Visual Analog Scale (Joint Pain VAS; ranging from 0 [none] to 100 [worst imaginable]), the Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36; ranging from 0 [worst] to 100 [best]), and the Fatigue Severity Numeric Rating Scale (Fatigue NRS; 0 [none] to 10 [worst imaginable]). The minimum clinically important difference (MCID) cut-offs were ≥10 for Joint Pain VAS, ≥5 for SF-36 domains, and ≥3 for Fatigue NRS.
The 156 weeks of treatment was completed by 57.4% of patients in the ixekizumab Q4W group and 44.7% of those in the ixekizumab Q2W group. At week 156, mean change from baseline for the Joint Pain VAS was -28.9 (ixekizumab Q4W) and -25.3 (ixekizumab Q2W). Clinically meaningful improvement of joint pain was reported by 51.8% of patients on ixekizumab (56.1% ixekizumab Q4W and 47.5% ixekizumab Q2W) at week 156. Patients reported an 18-point mean improvement in the SF-36 bodily pain domain. Patients also reported improvements in fatigue up to week 156, with 35.0% of patients achieving the MCID on the Fatigue NRS (39.4% ixekizumab Q4W and 30.6% ixekizumab Q2W). Improvement in fatigue was supported by a 14-point mean improvement in the vitality domain of the SF-36 at week 156.
The researchers concluded that improvements regarding pain and fatigue in patients with psoriatic arthritis with an inadequate response or intolerance to TNFi were sustained through 3 years of ixekizumab treatment in both the Q2W and Q4W treatment groups.
- Orbai A-M, et al. Abstract FRI0357. EULAR E-Congress, 3-6 June 2020.
- Kavanaugh A, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(4):566-574.
- Turkiewicz A, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(S9):2577.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Adalimumab added to methotrexate yields better results in PsA than methotrexate escalatio Next Article
Positive effect denosumab on fall risk »
« Adalimumab added to methotrexate yields better results in PsA than methotrexate escalatio Next Article
Positive effect denosumab on fall risk »
Table of Contents: EULAR 2020
Featured articles
COVID-19 and inflammatory rheumatic disease: some key issues
Secukinumab monotherapy as efficient as adalimumab
AxSpA real-life remission rates higher on biologics
Olokizumab significantly improves RA features and patient-reported outcomes
Rheumatoid Arthritis
New nanoparticle promising future agent in RA
Olokizumab significantly improves RA features and patient-reported outcomes
Low DAS at 4 months predicts sustained DMARD-free remission
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Reduced maintenance dose of certolizumab pegol can be used in axSpA
Worse response axSpA patients to second TNFi versus first TNFi
AxSpA real-life remission rates higher on biologics
Certolizumab pegol reduces acute anterior uveitis in axial spondyloarthritis
TNF-α inhibitors improve bone mineral density in AS patients
Psoriatic Arthritis
Ixekizumab shows sustained improvements in pain and fatigue at 3 years
Adalimumab added to methotrexate yields better results in PsA than methotrexate escalatio
Upadacitinib provides fast onset of improvement in psoriatic arthritis
Secukinumab monotherapy as efficient as adalimumab
Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
Higher mortality risk with tramadol versus NSAIDs for osteoarthritis patients
Hydroxychloroquine not effective in patients with hand osteoarthritis
Positive effect denosumab on fall risk
Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Anifrolumab achieves rapid and durable BICLA-response
Subclinical myocardial involvement progresses in SSc patients
Composite endpoint CRESS for primary Sjögren’s syndrome
COVID-19
COVID-19 and inflammatory rheumatic disease: some key issues
Related Articles
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

