The domains for adult assessment include physical, mental, and social health (see Table). “This is a very positive step in the overall approach to assess patient-reported outcomes”, Dr Deborah Miller (Cleveland Clinic, OH, USA) mentioned. “We are not only looking at the negative consequences of symptoms, but also at the positive results of improvements in patient functioning.”
Table. Domains for adult assessment in Neuro-QoL
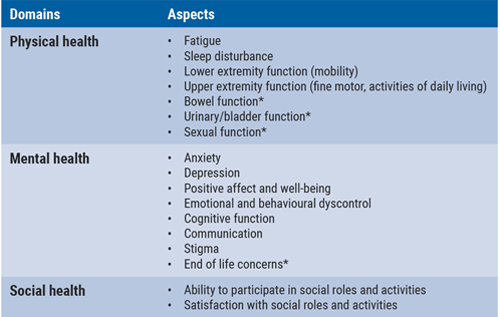
*untested item pools
Dr Miller emphasised the importance of HealthMeasures.net, the organisation which is responsible for the international implementation and modification of not only Neuro-QoL but also other measures: PROMIS®, NIH Toolbox®, and ASCQ-Me®. The website is developed and validated for common neurological conditions, using state-of-science methods which are psychometrically sound. All measures are designed to each be completed within 1 minute. They are also flexible regarding method of administration: there are pen-and-paper, web-based, or interviewer-based methods. Official translations are also available in Spanish and other languages. This set of measures is available without license, fee, or royalty. Neuro-QoL short forms and computerised adaptive test have been validated in MS [1,2].
MS-PATHS
Multiple Sclerosis Partners Advancing Technology and Health Solutions (MS-PATHS) is a technology-enabled network of MS centres through which researchers have access to patient data generated from a broad MS population. It functions as a learning health system. The aim is to better quantify the value of various treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes in MS. Dr Miller thinks that this is a very exciting concept. “At ECTRIMS, there has been a lot of relevant discussion about the importance of clinical practical trials. MS-PATHS is used both for clinical purposes, and for research.” Together with her team she studied symptoms of depression and use of anti-depressants in MS-PATHS patients (n=1,352). Around 40% were prescribed antidepressants and 23% met criteria of major mood disorder. “That suggests that we are doing a pretty good job in determining who has depression and who needs treatment. Unfortunately, we found that 31% of those prescribed antidepressants continued to meet the criteria for major mood disorder. This suggests that we are not paying enough attention to depression and that we are not adequately managing the consequences of depression in a vulnerable patient population.”
Next to Neuro-QoL, no other assessment platform provides unidimensional measures of MS symptoms and functions. There is growing evidence of international interest in the MS community to implement Neuro-QoL. The HealthMeasures organisation provides an infrastructure for an international collaboration to harmonise and optimise Neuro-QoL. The question of Neuro-QoL’s acceptance as tomorrow’s standard patient-reported outcome measure is up to the community of researchers.
Posted on
Previous Article
« pTMB is a feasible predictive biomarker for chemoimmunotherapy Next Article
Talazoparib + low-dose temozolomide seems promising in ES-SCLC »
« pTMB is a feasible predictive biomarker for chemoimmunotherapy Next Article
Talazoparib + low-dose temozolomide seems promising in ES-SCLC »
Table of Contents: ECTRIMS 2019
Featured articles
Towards a Comprehensive Assessment of MS Course
Cognitive assessment in MS
Late-breaking: Role for CSF markers in autoimmune astrocytopathies
Targeted therapies for NMOSD in development
Monitoring and Treatment of Progressive MS
Challenges in diagnosing and treating progressive MS
Risk factors for conversion to secondary progressive MS
Transplantation of autologous mesenchymal stem cells
Sustained reduction in disability progression with ocrelizumab
Late-breaking: Myelin-peptide coupled red blood cells
Optimising Long-Term Benefit of MS Treatment
Induction therapy over treatment escalation
Treatment escalation over induction therapy
Influence of age on disease progression
Exposure to DMTs reduces disability progression
Predicting long-term sustained disability progression
Treatment response scoring systems to assess long term prognosis
Safety Assessment in the Post-Approval Phase
Use of clinical registries in phase 4 of DMT
Genes, environment, and safety monitoring in using registries
Risk of hypogammaglobulinemia and rituximab
Determinants of outcomes for natalizumab-associated PML
Serum immunoglobulin levels and risk of serious infections
EAN guideline on palliative care
Pregnancy in the Treatment Era
The maternal perspective: when to stop/resume treatment and risks for progression
Foetal/child perspective: risks related to drug exposure and breastfeeding
Patient awareness about family planning represents a major knowledge gap
Late-breaking: Continuation of natalizumab or interruption during pregnancy
Related Articles
December 9, 2021
High-sensitive biomarker detection in MS via novel ELISA assay
December 20, 2022
Dimethyl fumarate reduces the risk of a first clinical event in RIS
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

