This is the first comparative real-world data study assessing long-term safety of tofacitinib which is an important consideration given the cardiovascular safety of anti-TNF agents. Dr Joel Kremer (Albany Medical College, New York, USA) et al. evaluated 5-year adverse event incidence rates in patients starting tofacitinib versus bDMARDs using cohorts from the US Corrona RA registry, during November 2012, the month when tofacitinib received US marketing approval, through December 2017 [1].
Data were obtained from RA patients in the registry who were treated with either tofacitinib (n=1,544) or biologics (n=7,083). The safety assessment focused on the combined rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including myocardial infarction, stroke or transient ischaemic and fatal events; the incidence of serious infection events; herpes zoster (HZ) regardless of severity; and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
The results showed that patients treated with tofacitinib had slightly more than double the rate of HZ events (adjusted HR 2.12; 95% CI 1.22-3.66), compared with patients on biologics, a finding consistent with prior reports that found tofacitinib treatment to be linked with an almost 3-fold increased rate of HZ when compared with placebo-treated patients [2]. “None of the HZ activations identified in the registry patients on tofacitinib were rated as “serious,” said Dr Kremer. Patients treated with tofacitinib had a 42% lower rate of MACE, compared with patients who received a bDMARD, although the difference was not statistically significant. Both subgroups had virtually identical rates of all serious infections. VTE analysis showed a rate of 0.19/100 patient-years with tofacitinib treatment, and 0.33/100 patient-years with other biologicals, a difference that was not statistically significant. “It is an important finding because of prior concerns raised about VTE in patients taking tofacitinib or another JAK inhibitor,” said Dr Kremer. Adjusted analysis of VTE is expected within another couple of years. Comparison of the rates of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis were each not statistically different between the two treatment subgroups. These findings are very reassuring for the long-term use of this JAK inhibitor -and possibly the JAK class in general- in the real-world setting. Obviously, further studies are needed.
- Kremer JM et al. Abstract OP0028. EULAR 2019
- Winthrop KL, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Oct;66(10):2675-84.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Switching upadacitinib and adalimumab is beneficial in refractory RA Next Article
Short methotrexate stop is safe in patients with RA »
« Switching upadacitinib and adalimumab is beneficial in refractory RA Next Article
Short methotrexate stop is safe in patients with RA »
Table of Contents: EULAR 2019
Featured articles
Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab versus adalimumab in patients with PsA
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Cohort study shows improvement during 25 years of RA treatment
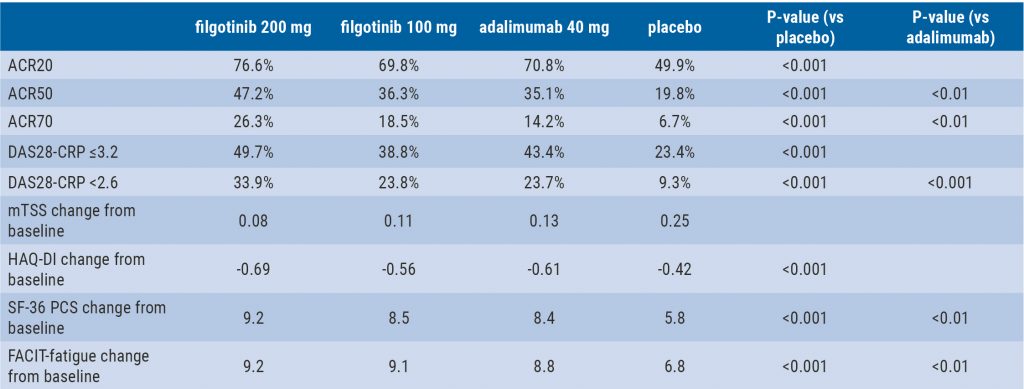
Filgotinib in RA patients with inadequate response or naïve to methotrexate
Clinical effectiveness of fenebrutinib in RA patients with methotrexate or TNFi failure
Short methotrexate stop is safe in patients with RA
Tofacitinib is safe according to real-world data analysis
Tapering of prednisone in RA patients who achieved low disease activity or remission with tocilizumab
Efficacy and safety of E6011 in RA patients with inadequate response to methotrexate
Preliminary efficacy and safety data of RG6125 in RA patients with an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors
Integrated 10-year analysis confirms safety profile abatacept
Switching among multiple infliximab biosimilars does not cause immunogenicity
Switch to sarilumab from adalimumab is efficacious and safe
Axial Spondyloarthritis
Treat-to-target approach emerging in axial spondyloarthritis
NSAIDs consumption is linked to patient-assessed disease activity and decreases with use of TNF inhibitors
Psoriatic Arthritis
Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab versus adalimumab in patients with PsA
Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in patients with active PsA
Filgotinib is efficacious and safe in PsA
Ixekizumab improves signs and symptoms in TNFi-naïve PsA patients
Etanercept and methotrexate as first-line treatment in PsA
Unacceptable pain is common in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis
Miscellaneous
Interstitial lung disease in rheumatic diseases and systemic sclerosis
Emapalumab in patients with macrophage activation syndrome
Support for tocilizumab use in giant cell arteritis
Related Articles
September 4, 2019
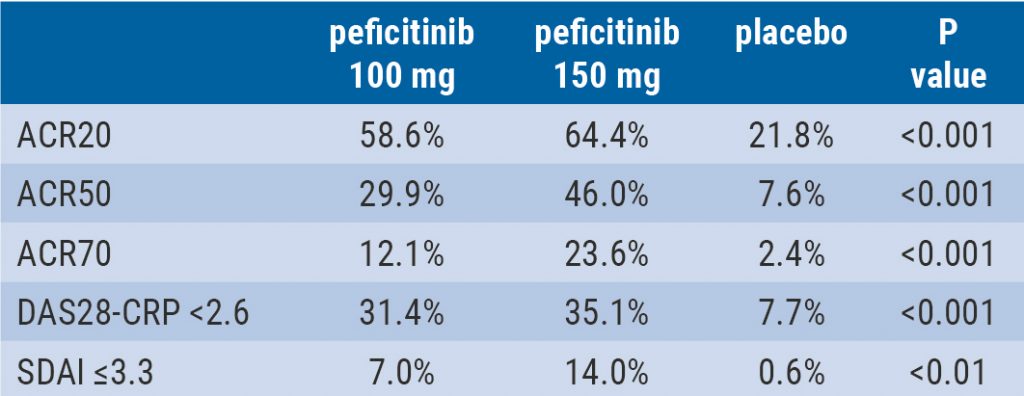
Peficitinib likely efficacious and safe
September 4, 2019
Switch to sarilumab from adalimumab is efficacious and safe
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

