https://doi.org/10.55788/a0db58a9
Patients with resected stage IIA/B/C melanoma face a 5-year risk of recurrence of 24–43% [1]. The phase 3 CheckMate76K study (NCT04099251) evaluated the efficacy and safety of adjuvant nivolumab for 12 months in patients with resected stage IIB/C melanoma. Recently published results showed that adjuvant nivolumab significantly increased recurrence-free survival (RFS; HR 0.42; P<0.0001) [2].
In addition, Prof. Georgina Long (University of Sydney, Australia) and colleagues performed an exploratory biomarker analysis to determine patient subgroups that have a high risk of recurrence (prognostic biomarkers) and to understand the benefit of adjuvant nivolumab treatment in biomarker-defined subgroups of patients (predictive biomarkers) [3].
In CheckMate76K, 790 patients were randomised 2:1 to adjuvant nivolumab or placebo. Baseline biomarkers were obtained from serum (i.e. CRP) and primary tumour biopsy (i.e. IFNγ signal, tumour mutation burden [TMB], BRAFv600 status, percentage CD8 T cells, PD-L1 expression, and tumour mitotic rate [TMR]). Analyses were performed within each treatment arm and comparing nivolumab with placebo treatment.
Within the nivolumab arm, a higher IFNγ signal, TMB, and CD8 T cell count, and lower serum CRP were associated with improved RFS. Within the placebo arm, none of the biomarkers tested was prognostic for RFS.
In addition, a higher IFNγ signal, TMB, CD8 T cell count, and lower serum CRP were predictive of the benefit of nivolumab versus placebo. For example, patients with a high IFNγ signal had more benefit from nivolumab versus placebo (HR 0.29) compared with patients with a low IFNγ signal (HR 0.44).
In a multivariate analysis, tumour stage and CRP level at baseline proved to be the strongest independent prognostic biomarkers in this population. TMB and IFNγ signalling were the strongest independent predictive biomarkers (see Figure).
Figure: Multivariate analysis of biomarkers with prognostic and predictive value [3]
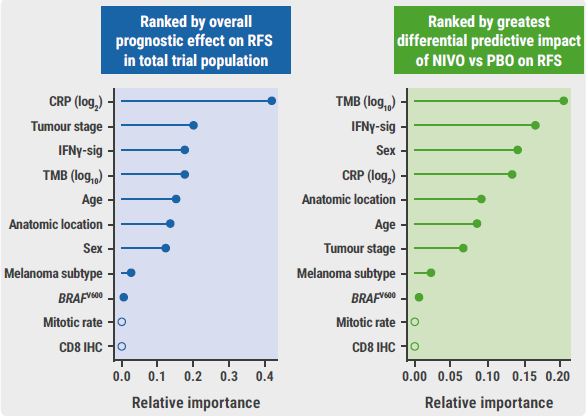
CRP, c-reactive protein; NIVO, nivolumab; PBO, placebo; RFS, recurrence-free survival; TMB, tumour mutation burden.
Based on these results, Prof. Long concluded that “among all the biomarkers tested, TMB and IFNγ signalling had the largest independent effect of the relative benefit of nivolumab over placebo.”
- Garbe C, et al. J Clin Oncol.2022;32:3741–3749.
- Long GV, et al. SMR Annual Meeting 2022, 17–20 October, Edinburgh, Scotland.
- Long GV, et al. Association of biomarkers with efficacy of adjuvant nivolumab vs placebo in patients with resected stage IIB/C melanoma (CA209-76K). Abstract 9504, ASCO Annual Meeting 2023, 2–6 June, Chicago, USA.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Combining PARP inhibition and androgen receptor-signalling inhibition improves radiographic progression-free survival in HRR-deficient mCRPC Next Article
Response-directed treatment personalisation in stage III melanoma »
« Combining PARP inhibition and androgen receptor-signalling inhibition improves radiographic progression-free survival in HRR-deficient mCRPC Next Article
Response-directed treatment personalisation in stage III melanoma »
Table of Contents: ASCO 2023
Featured articles
Real-world data support new SOC in patients with SCLC
What can real-world evidence teach us about atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in HCC?
Colorectal Cancer
7-year outcomes of PRODIGE 23 trial
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be viable option in locally advanced colon cancer
De-escalation of neoadjuvant treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer is non-inferior
Breast Cancer
SONIA: No survival benefit with first-line versus second-line CDK4/6 inhibition in metastatic breast cancer
Adjuvant ribociclib improves invasive DFS in early breast cancer
Gene expression profiles predict benefit of neoadjuvant immune checkpoint therapy in triple-negative breast cancer
Lung Cancer
Adding pembrolizumab to perioperative chemotherapy improves EFS in early-stage NSCLC
TTFields therapy: a new treatment modality for metastatic NSCLC
Adding chemotherapy to EGFR TKI does not improve OS in advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC
Upper GI Cancer
No improved OS in pancreatic cancer after neoadjuvant mFOLFIRINOX
AI detects gastric cancer with high accuracy in common blood tests
Melanoma
Response-directed treatment personalisation in stage III melanoma
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in patients with resected stage IIB/C melanoma
GU Cancers
Combining PARP inhibition and androgen receptor-signalling inhibition improves radiographic progression-free survival in HRR-deficient mCRPC
Erdafitinib outperforms chemotherapy in FGFR-altered advanced urothelial cancer
Probiotic CBM588 seems to improve clinical effect cabozantinib/nivolumab in mRCC
Exploratory analysis of IMvigor130 trial finds no OS benefit from atezolizumab in subgroups
Miscellaneous
Immune checkpoint inhibition improves PFS in non-BRCA-mutated ovarian cancer
First-line nivolumab-AVD improves PFS both in adult and paediatric patients with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma
Vorasidenib successfully targets IDH1/2-mutated glioma
ASCO Interviews
IMbrave050: Adjuvant atezolizumab plus bevacizumab provides landmark recurrence-free survival for HCC
What can real-world evidence teach us about atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in HCC?
Related Articles

November 25, 2020
Lorlatinib outperforms crizotinib in ALK-positive advanced NSCLC
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

