Featured video: Phase III study assessing the efficacy of adjuvant use of targeted agent osimertinib in patients with localized non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR mutation after complete tumor resection and adjuvant chemotherapy.
Adjuvant osimertinib demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit for patients with stage IB, II, or IIIA EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with complete tumour resection in the phase 3 ADAURA trial, presented by Prof. Roy Herbst (Yale Cancer Center, USA) [1].
Osimertinib is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with demonstrated efficacy as a frontline agent for metastatic NSCLC with confirmed EGFR mutation [2]. The phase 3 ADAURA clinical trial attempted to assess whether this agent is also effective in earlier stages of metastatic disease characterised by EGFR mutation, namely as an adjuvant therapy after complete surgical resection of stage IB, II, or IIIA disease.
Oral osimertinib (80 mg once daily) was compared with placebo for a treatment duration of up to 3 years or until disease recurrence. The primary endpoint was disease-free survival (DFS), and the key secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Other secondary endpoints include DFS at 2, 3, and 5 years; patient health-related quality of life and symptoms; and plasma concentrations.
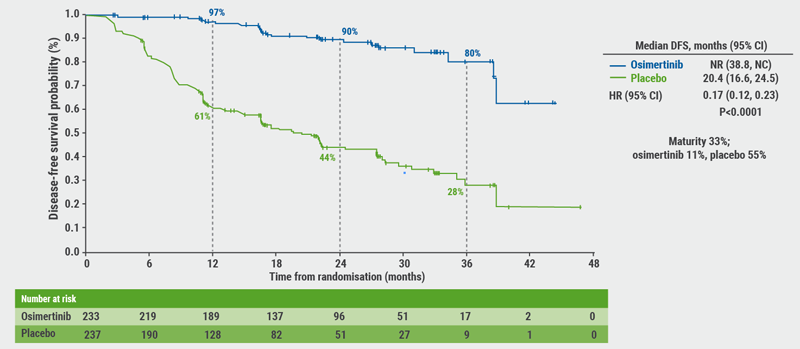
The study was unblinded early under the recommendation from an Independent Data Monitoring Committee due to efficacy, Prof. Herbst described the unplanned interim analysis. At the time of the unblinding, all patients had been enrolled and randomised (n=682) and all patients had been followed up for at least 1 year. For the primary endpoint in stage II-III patients, the DFS curves separated early on and showed an 83% reduced risk of disease recurrence for the osimertinib arm (HR 0.17; 95% CI 0.12-0.23; P<0.0001, see Figure). Adding in the early-stage IB patients to the overall population did not change this trend (HR 0.21; 95% CI 0.16-0.28; P<0.0001), indicating that osimertinib benefits early stage patients as well. DFS across all subgroups in the overall population (i.e. age, gender, smoking status, Asian vs non-Asian, EGFR mutation, adjuvant chemotherapy) favoured osimertinib.
Figure. Primary endpoint: DFS in patients with stage II-IIIA disease [1]
The median duration of exposure was 22.3 months (range 0-43) for the osimertinib arm, and 18.4 months (range 0-48) for the placebo arm. Osimertinib was well tolerated with a safety profile consistent with its known safety profile (diarrhoea, paronychia, dry skin, and pruritis being the most common). There were no adverse events leading to death in the osimertinib arm. The rate of grade 3-4 adverse events was low. Interstitial lung disease was reported in 10 (3%) patients in the osimertinib arm and in 0 patients in the placebo group; cardiac QTc prolongation was reported in 22 patients (7%) in the osimertinib arm and 4 patients (1%) in the placebo arm.
In conclusion, adjuvant osimertinib is the first targeted agent in a global randomised trial to show a significant and clinically meaningful improvement in DFS in patients with stage IB/II/IIIA EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Overall, there was a 79% reduction in the risk of disease recurrence or death with osimertinib. Osimertinib versus placebo DFS rates at 2 years were 89% vs 53%, respectively. A consistent improvement was observed in DFS regardless of prior adjuvant chemotherapy. The safety profile was beneficial. In short, adjuvant osimertinib provides a highly effective, practice-changing treatment for patients with stage IB/II/IIIA EGFR-mutant NSCLC after complete tumour resection.
- Herbst RS, et al. ASCO Virtual Meeting, 29-31 May 2020, Abstract LBA5.
- Soria JC, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113‐125.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Quit smoking: vaping + counselling helps Next Article
Higher serum levels of eicosapentaenoic acid correlate with reduced CV events »
« Quit smoking: vaping + counselling helps Next Article
Higher serum levels of eicosapentaenoic acid correlate with reduced CV events »
Table of Contents: ASCO 2020
Featured articles
COVID-19 & Telemedicine
COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium Registry: initial results
Oncology hospital-at-home model reduces hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and costs
Nurse-led telephone triage system reduces hospitalizations, helps patients manage symptoms at home
Melanoma
Adjuvant pembrolizumab: durable RFS for stage III melanoma
Adjuvant pembrolizumab: durable RFS for stage III melanoma
Pembrolizumab plus low-dose ipilimumab well tolerated after progression on PD1 antibody therapy
Toripalimab plus axitinib effective in metastatic mucosal melanoma
Breast & Ovarian Cancer
Advanced breast cancer: locoregional therapy does not improve OS
T-DM1 does not improve safety or efficacy in HER-2 positive early breast cancer; favorable iDFS reported
Maintenance olaparib improves OS in relapsed ovarian cancer with BRCA1/2 mutation
Combination pembrolizumab/chemo improves PFS in metastatic TNBC
Effect of veliparib with or without cisplatin in breast cancer: results of SWOG S1416
PHOEBE, a phase 3 trial comparing pyrotinib and lapatinib in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
BYLieve demonstrates efficacy of PIK3CA-directed treatment post CDK4/6-ihibition
Strategies emerge for chemotherapy de-escalation in HER2-positive breast cancer
Multiple Myeloma
Carfilzomib: no PFS benefit for multiple myeloma
Lung Cancer
ES-SCLC: tremelimumab + durvalumab + chemotherapy misses endpoint
Adjuvant osimertinib in NSCLC: practice changing ADAURA trial
ES-SCLC: pembrolizumab KEYNOTE-604 data
Second-line gemcitabine plus ramucirumab significantly improves overall survival
Tiragolumab and atezolizumab: ORR in NSCLC
MET-amplified advanced NSCLC responds well to MET inhibitor capmatinib
Genitourinary Cancer
Urothelial cancer: avelumab works as maintenance therapy
ARAMIS final OS and nmCRPC safety outcomes
Final survival results from phase 3 SPARTAN trial
Novel drug for kidney cancers/VHL patients
Primary analysis from IMvigor010, adjuvant atezolizumab in high risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
First randomised trial of Lu-PSMA in mCRPC progressing after docetaxel
Gastrointestinal Cancer
HER2-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer: trastuzumab deruxtecan
REGOMUNE: a phase 2 study combining regorafenib and avelumab
Cardiotoxicity: consider switching to S-1
Perioperative chemotherapy for resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Real-world data of sequential sorafenib followed by regorafenib in unresectable HCC
Paediatric Cancer
Sustained improvements in quality of life with larotrectinib
Promising first immunotherapy trial in placental trophoblastic tumours
Precision medicine for poor-prognosis paediatric patients
Related Articles
September 17, 2020
Perioperative chemotherapy for resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
September 17, 2020
REGOMUNE: a phase 2 study combining regorafenib and avelumab
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

