https://doi.org/10.55788/bc63e813
The FDA approval of ruxolitinib cream for vitiligo treatment was based on the results of the phase 3 TRuE-V1 (NCT04052425) and the TRuE-V2 (NCT04057573) trials [1]. According to Prof. John Harris (UMass Chan Medical School, MA, USA), this can be seen as a milestone in vitiligo therapy, but it is also interesting to see the long-term results [2].
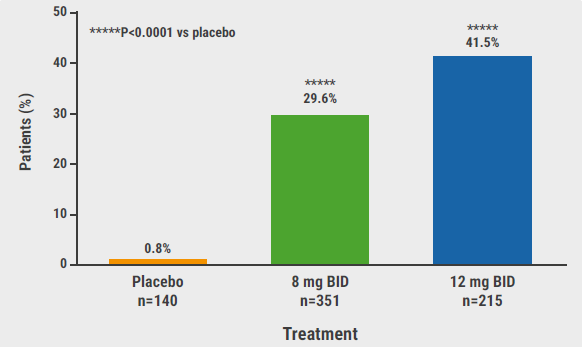
In 1 cohort of the long-term extension study (NCT04530344) of TRuE-V1 and the TRuE-V2 trials, 116 patients who had achieved a re-pigmentation of at least 90% in the face area were re-randomised to either continue twice-daily ruxolitinib cream 1.5% or withdraw from active treatment by switching to a vehicle. Prof. Harris’ maintenance analysis aimed to investigate the time span to relapse of vitiligo and the duration of maintenance.
At baseline (i.e. week 52 of TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2), participants with a facial vitiligo area scoring index (F-VASI) ≥90 had a median age of 42.0 years, more than half were women, and 31.9%, 30.2%, and 25.0% had the Fitzpatrick skin types 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Stable disease was present in 70.7%, while the rest had progressive vitiligo.
One year after withdrawal, 39.3% of the participants still had an F-VASI ≥75 response, while 28.6% experienced a relapse defined as F-VASI ≤75. The relapses happened within the first 4 months in half of the cases. Interestingly, 21.4% of the participants in the withdrawal arm and 61.8% who continued on ruxolitinib cream had a sustained F-VASI ≥90 response over 1 year, with a median duration of F-VASI ≥90 response of 195.0 days on vehicle only. Re-starting active treatment in case of relapse in the withdrawal group, resulted in 75% of participants achieving a F-VASI ≥75 scoreover a median period of 12 weeks. An F-VASI ≥90 response was regained in 68.8% of the participants after a median of 15 weeks.
In general, ruxolitinib cream was well tolerated with only mild and moderate treatment-related adverse events. No incidence of application-site acne or pruritus was reported.
“There is a population that really maintains response. If patients lose pigment, put them back on [ruxolitinib] and they will regain it in most cases,” Prof. Harris concluded.
- Rosmarin D, et al. N Engl J Med 2022;387(16):1445–1455.
- Harris JE. Relapse and maintenance of clinical response in the randomised withdrawal arm of the TRuE-V long-term extension phase 3 study of ruxolitinib cream in vitiligo. S025, AAD 2023 Annual Meeting, 17–21 March, New Orleans, USA.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Nemolizumab decreases lesions and itch in prurigo nodularis Next Article
Delgocitinib shows promise as topical therapy for chronic hand eczema »
« Nemolizumab decreases lesions and itch in prurigo nodularis Next Article
Delgocitinib shows promise as topical therapy for chronic hand eczema »
Table of Contents: AAD 2023
Featured articles
New Developments in Dermatology
Delgocitinib shows promise as topical therapy for chronic hand eczema
Vitiligo patients maintain re-pigmentation after ruxolitinib cream withdrawal
Nemolizumab decreases lesions and itch in prurigo nodularis
Lichen planus: a future indication for baricitinib?
Atopic Dermatitis: State of the Art
As-needed ruxolitinib shows successful long-term symptom control in AD
Dupilumab: a viable option for atopic hand and foot eczema
Topical roflumilast beneficial in atopic dermatitis
IL-22 receptor blocker reduces itch and skin lesions in AD
Psoriasis: New Developments
Switching to risankizumab successful in IL-17 inhibitor non-responders
Novel, selective TYK2 inhibitor shows promise for psoriasis
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: What You Need to Know
Izokibep shows remarkably high grades of clinical response in HS
Bimekizumab could be the new up-and-comer for HS treatment
Pearls of the Posters
Biologics in psoriasis: can they prevent joint involvement?
JAK inhibitor deuruxolitinib shows encouraging hair re-growth in alopecia areata
Biomarkers predicting response of different CSU treatments in children
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy