Standard treatment for patients with stage III (cT3-4aN0M0 or cT1-4aN1-3M0) urothelial cancer is cisplatin-based chemotherapy followed by radical surgery. However, a substantial number of patients is unfit for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Results from NABUCCO cohort 1 (NCT03387761) showed promising efficacy (46% pathological complete response) of neoadjuvant immunotherapy with ipilimumab/nivolumab [1]. Dosing in this cohort was: ipilimumab 3 mg/kg at day 1 and day 22, and nivolumab 3 mg/kg at day 43. Recent data in pre-operative trials for other cancer types suggests that a lower dose of ipilimumab has equal activity and is better tolerated [2]. NABUCCO cohort 2 compared efficacy and safety of alternative adjuvant dosing regimens. Patients in cohort 2A (n=15) were treated with ipilimumab 3 mg/kg and nivolumab 1 mg/kg at day 1 and day 22, and nivolumab 3 mg/kg at day 43. Patients in cohort 2B (n=15) were treated with ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg at day 1 and day 22, and nivolumab 3 mg/kg at day 43. Primary endpoint was pathologic complete response (pCR) rate. Secondary endpoints included feasibility (resection within 12 weeks) and grade 3/4 immune-related adverse events. Dr Jeroen van Dorp (Netherlands Cancer Institute, the Netherlands) presented the first results [3].
A total of 26/30 (87%) patients received all 3 treatment cycles; these 26 patients underwent radical surgery, 24 within 12 weeks after start of treatment. Four patients missed one or more cycles of therapy due to immune-related adverse events. Response was evaluable in 28 patients. In cohort 2A, 6/14 (43%) patients had a pCR; 8/14 (57%) had a pCR or ypTisN0. In cohort 2B, 1/14 (7%) had a pCR whereas 3/14 (21%) had a pCR or ypTisN0. Grade 3/4 immune-related adverse events were observed in 5/15 (33%) patients in cohort 2A, and in 3/15 (20%) patients in cohort 2B.
“In contrast to what was observed in other malignancies, neoadjuvant ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg was less efficacious than ipilimumab 3 mg/kg and nivolumab 1 mg/kg,” concluded Dr van Dorp. Further translational work is currently ongoing.
- Van Dijk N, et al. Nat Med. 2020;26:1839–1844.
- Rozeman EA, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:948–960.
- Van Dorp J, et al. High- vs low-dose pre-operative ipilimumab and nivolumab in locoregionally advanced urothelial cancer (NABUCCO cohort 2). Abstract LBA31, ESMO Congress 2021, 16–21 September.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Better survival with neoadjuvant dose-dense MVAC regimen in MIBC Next Article
Modified ipilimumab schedule reduces risk of grade 3/4 adverse events »
« Better survival with neoadjuvant dose-dense MVAC regimen in MIBC Next Article
Modified ipilimumab schedule reduces risk of grade 3/4 adverse events »
Table of Contents: ESMO 2021
Featured articles
Breast Cancer
Trastuzumab deruxtecan triples PFS
Novel conjugate meets primary endpoint
Longest survival benefit from first-line CDK4/6 inhibitor
Meta-analysis shows 6-months adjuvant trastuzumab is optimal
Double-positive results for triple-negative metastatic breast cancer
Survival after neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab-lapatinib plus chemotherapy
Postmenopausal breast cancer: extended letrozole reduces recurrence
Asian women also benefit from palbociclib plus letrozole
No PEARLs of survival with palbociclib plus endocrine therapy compared with capecitabine, but QoL better
Gastrointestinal Cancer
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy potential alternative to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in LARC
Immune chemo-sensitisation looks promising in microsatellite-stable mCRC
Adagrasib shows promising clinical activity in heavily pretreated KRAS-mutated CRC
Automated detection of microsatellite status on unstained samples in early colon cancer
Consistent benefit of anti-PD-1 therapy for oesophageal and gastric cancer
HIPEC in gastric cancer with peritoneal metastases
ctDNA highly predictive in HER2-positive, advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer
Lung Cancer
Robust anticancer activity of trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-mutated NSCLC
Nivolumab/ipilimumab continues to provide survival benefit in unresectable MPM
Adjuvant atezolizumab lowers relapse rate in resected NSCLC
Three-year OS follow-up from CASPIAN trial
TCR clonality predicts pembrolizumab response in NSCLC
Melanoma
Adjuvant immunotherapy reduces risk of disease recurrence in stage II melanoma
IFN-γ signature predicts response to immunotherapy
Updated results of SECOMBIT trial
Combining T-VEC and pembrolizumab does not significantly improve survival in advanced, unresectable melanoma
Durable intracranial responses with nivolumab/ipilimumab
Genitourinary Cancer
TKI drug-free interval strategy not detrimental to conventional continuation strategy in RCC
Modified ipilimumab schedule reduces risk of grade 3/4 adverse events
Optimal neoadjuvant dose ipilimumab/nivolumab in stage III urothelial cancer
Better survival with neoadjuvant dose-dense MVAC regimen in MIBC
PARP inhibitor rechallenge improves PFS in ovarian cancer
Pembrolizumab prolongs survival in persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer
Pembrolizumab has durable effect in previously treated MSI-H/dMMR advanced endometrial cancer
HRR mutational status is prognostic and predictive biomarker olaparib activity
Haematological Cancer
Mutational analyses are predictive in malignant lymphomas
Low numbers of M2 macrophages in tumour microenvironment associated with superior response to immunotherapy in Hodgkin lymphoma
COVID-19
Adequate response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in cancer patients
Cancer patients more likely to die from COVID-19 when hospital admittance is required
Third global survey of the ESMO Resilience Task Force
High COVID-19 mortality in Swiss cancer patients
Basic Science & Translational Research
Neutrophils negatively correlate with response to anti-PD-1 monotherapy in dMMR tumours
Tetraspecific ANKETs harnesses innate immunity in cancer therapies
Early ctDNA reduction in metastatic uveal melanoma correlates better with OS than RECIST response
Gut microbiota as a potential predictive biomarker
Related Articles
November 19, 2021
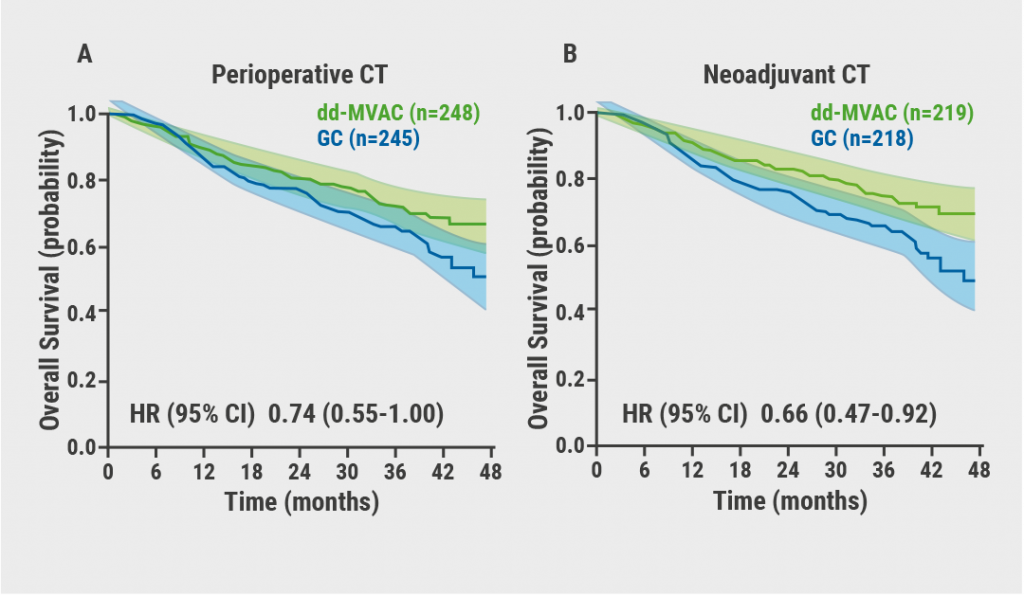
Better survival with neoadjuvant dose-dense MVAC regimen in MIBC
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

