https://doi.org/10.55788/8e93d6b0
The splanchnic bed is the main blood volume reservoir of the body. Since the activation of the sympathetic nervous system recruits blood from this reservoir into the central circulating volume, which leads to elevated filling pressures, ablation of the GSN may redistribute this blood to the periphery and relieve the symptoms of patients with HFpEF.
Prof. Marat Fudim (Duke Cardiology Clinic, NC, USA) presented the preliminary 1-month observations from the single arm roll-in cohort (n=18) [1,2].
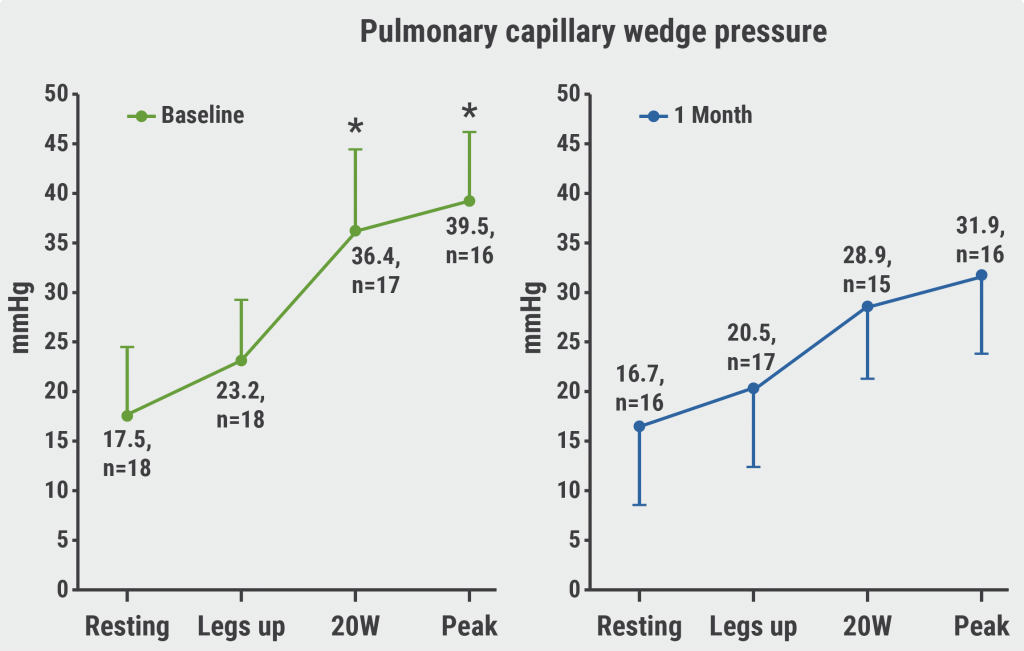
One month post-GSN ablation, the mean PCWP was significantly lower relative to baseline during 20W exercise (36.4 mmHg vs 28.9 mmHg; P<0.007) and peak exercise (39.5 vs 31.9; P<0.013). No significant difference was measured between the mean resting state PCWP at baseline and 1 month (17.5 vs 26.7; P=0.417) or with legs up (23.2 vs 20.5; P=0.066; see Figure). Notably, New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class had improved by at least 1 class in 33% of the participants after 1 month, and Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) overall score increased by an average 22.1 points (P<0.05). The 6 minute walk test and NT-proBNP levels did not change after the ablation procedure.
Figure: Haemodynamic outcomes in the REBALANCE-HF trial [1]
Concerning safety, 3 non-serious device-related adverse events were reported, with 1 case of acute HF decompensation, 1 case of transient hypertension during the procedure, and 1 participant experiencing back pain after ablation.
Although these preliminary results are promising, more data is needed before this approach can be applied in the real world. The randomised part of REBALANCE-HF will provide more information on the efficacy and safety of this ablation procedure in patients with HFpEF.
The multicentre, prospective REBALANCE-HF study (NCT04592445) is currently randomising patients with HFpEF to right-sided GSN ablation or a sham procedure to analyse to efficacy and safety of this procedure. The primary endpoint is the change in PCWP at 1 month, in rest, with legs up, and during 20W and peak supine exercise intensity.
- Fudim M, et al. REBALANCE-HF Roll in Cohort. LBT Devices, Heart Failure 2022, 21–24 May, Madrid, Spain.
- Fudim M, et al. Eur J Heart Fail, May 22, 2022. DOI:10.1002/ejhf.2559.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« DAPA-HF: Dapagliflozin is safe and efficacious in frail patients Next Article
Cardiac contractility modulation therapy promising for patients with HFpEF »
« DAPA-HF: Dapagliflozin is safe and efficacious in frail patients Next Article
Cardiac contractility modulation therapy promising for patients with HFpEF »
Table of Contents: HFA 2022
Featured articles
Phase 3 and 4 Trials
GALACTIC-HF: Omecamtiv mecarbil as option for HFrEF patients with low SBP
HELIOS-A: Vutrisiran meets exploratory endpoints
Patiromer helps HFrEF patients to optimise RAAS inhibitors without hyperkalaemia
FIDELITY: Cardiorenal benefits of finerenone, regardless of LVH status
DAPA-VO2: Rapid effect of dapagliflozin on peak VO2 in stable HFrEF
Phase 1/2 Trials
Significant improvement in BP from istaroxime, a novel non-adrenergic agent
SERENADE: Macitentan fails in HFpEF plus PAH
Combination of filgrastim and dutogliptin appears safe in STEMI
Therapeutic Devices
Cardiac contractility modulation therapy promising for patients with HFpEF
REBALANCE-HF: Encouraging observations for splanchnic nerve ablation in HFpEF
Updates on SGLT2 Inhibitors
DAPA-HF: Dapagliflozin is safe and efficacious in frail patients
EMPEROR-Preserved: Empagliflozin stable across age groups
EMPULSE: Empagliflozin delivers rapid and clinically meaningful decongestion
Dapagliflozin performs consistently across LVEF in HF
Miscellaneous Topics
Cardiac wasting relevant for clinical outcomes in cancer
Urocortin-2 a potential treatment target for HFpEF
Should ATTR-CM be added to the differential diagnosis of patients with HF?
Delayed initiation of novel GDMTs associated with adverse outcomes in HF patients
Related Articles

October 30, 2023
Heart failure: the 2023 update
January 18, 2022
Speech analysis can link voice changes to heart failure status
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

