https://doi.org/10.55788/f0a84142
Despite new additional treatment options like CDK4/6 inhibitors, endocrine resistance in patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer eventually develops. For endocrine-resistant disease, sequential single-agent chemotherapy is standard-of-care, however, this treatment is associated with low response rates, poor outcomes, and declining quality-of-life [1]. Sacituzumab govitecan is a first-in-class Trop-2-directed antibody-drug conjugate that has demonstrated significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in pre-treated, endocrine-resistant HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients in the phase 3 TROPiCS-02 trial (NCT03901339) [2]. Prof. Hope Rugo (Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Centre, CA, USA) presented the first OS results from the TROPiCS-02 trial [3].
This randomised, phase 3 trial included 543 participants with locally advanced/metastatic, inoperable HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, who’s tumours progressed after at least 1 endocrine therapy, taxane, and CDK4/6 inhibitor in any setting, and who received at least 2 but not more than 4 lines of chemotherapy for metastatic disease. Participants were 1:1 randomised to receive sacituzumab govitecan (10 mg/kg, days 1 and 8, every 21 days) or TPC. OS was the key secondary endpoint.
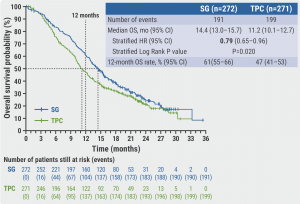
In the second interim analysis median OS for participants treated with sacituzumab govitecan was 14.4 months versus 11.2 months for TPC patients (HR 0.79; P=0.020, see Figure). The OS rate at 12 months was 61% (sacituzumab govitecan) versus 47% (TPC). The overall response rate was 57% versus 38% and the main duration of response was 8.1 months versus 5.6 months for sacituzumab govitecan and TPC, respectively. The median time-to-deterioration was 4.3 months (sacituzumab govitecan) versus 3.0 months (TPC). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were observed in 74% versus 60% of patients for sacituzumab govitecan and TPC, respectively.
Based on these results, Prof. Rugo concluded that “the statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit of sacituzumab govitecan over TPC supports the use of sacituzumab govitecan as a novel therapy for patients with pre-treated HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.”
- Burstein HJ, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(35):3959–3977.
- Rugo HS, et al. J Clin Oncol. DOI: 0.1200/JCO.22.01002.
- Rugo HS, et al. Overall survival (OS) results from the phase III TROPiCS-02 study of sacituzumab govitecan (SG) vs treatment of physician's choice (TPC) in patients (pts) with HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (mBC). Abstract LBA76, ESMO Congress 2022, 09–13 September, Paris, France.
Figure: Sacituzumab govitecan treatment improves overall survival probability and overall survival rate of HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients, as per 2nd interim analysis [3].
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Deep learning models predict the risk of relapse and the mutational profile in GIST Next Article
OS benefit of abemaciclib in HR-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer not (yet) statistically significant »
« Deep learning models predict the risk of relapse and the mutational profile in GIST Next Article
OS benefit of abemaciclib in HR-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer not (yet) statistically significant »
Table of Contents: ESMO 2022
Featured articles
Letter from the Editor
Colorectal Cancer
High pathological responses to neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibition in locally advanced dMMR colon cancer
Fruquintinib: a potential new treatment for patients with refractory mCRC
Second-line avelumab is effective in patients with MSI-H/dMMR mCRC
Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer
Deep learning models predict the risk of relapse and the mutational profile in GIST
Addition of pembrolizumab to lenvatinib does not improve OS in advanced HCC
New, highly selective inhibitor of FGFR2 driver alterations and resistance mutations
Chemo-immunotherapy in gastric cancer is more effective when administered in parallel
Breast Cancer
Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes identify patients with immunogenic triple-negative breast cancer
OS benefit of abemaciclib in HR-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer not (yet) statistically significant
OS benefit of sacituzumab govitecan in pre-treated HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer
Lung Cancer
A pathway from air pollution to lung cancer in non-smokers identified
Selective KRASG12C inhibitor sotorasib demonstrates superior PFS and ORR compared to docetaxel in previously treated patients with NSCLC
Promising clinical activity of tepotinib plus osimertinib in NSCLC with MET amplification after progression on first-line osimertinib
High pathological responses in borderline resectable NSCLC patients after induction with dual immunotherapy and concurrent chemoradiotherapy
Melanoma
Treatment with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes for advanced melanoma outperforms ipilimumab
Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab outperforms adjuvant pembrolizumab in resectable stage III–IV melanomas
Survival-benefit of neoadjuvant T-VEC maintained over 5 years of follow-up
Baseline ctDNA predicts survival in resected stage III–IV melanoma
Genitourinary Cancer – Prostate Cancer
Overall survival benefit of abiraterone in mHSPC is maintained for 7 years
Limited benefit of adding long-term ADT to post-operative radiotherapy in prostate cancer
Intensified ADT benefits biochemical progression-free survival in biochemically relapsed prostate cancer
Genitourinary Cancer – Non-Prostate Cancer
Adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab does not improve survival in patients with localised RCC at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy
Triple therapy improves progression-free survival in patients with advanced RCC versus dual therapy
Adjuvant atezolizumab does not improve outcomes for patients with RCC and increased risk of recurrence
Gynaecological cancers
OS benefit for advanced ovarian cancer patients treated with maintenance olaparib
Maintenance tegafur-uracil does not improve survival in locally advanced cervical cancer
Head and Neck Cancer
Adding first-line pembrolizumab to CRT in locally advanced HNSCC does not significantly prolong survival or event-free survival
5-FU-free chemotherapy combination as an alternative for first-line treatment of recurrent or metastatic HNSCC
Epstein Barr virus-specific autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes do not improve survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Related Articles
November 16, 2022
Baseline ctDNA predicts survival in resected stage III–IV melanoma
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

