Mixed evidence exists on the risk of serious infections in elderly patients with RA treated with bDMARDs compared with csDMARDs. Moreover, the relation between JAK inhibitors and serious infections has not been investigated in elderly patients with RA. The current prospective cohort study collected data from the German RABBIT register to assess whether bDMARD and JAK inhibitor recipients are at an increased risk of serious infections compared with csDMARD-treated patients. Between 2007 and 2020, RA patients >70 years of age who had at least 1 follow-up appointment were included in the study. Dr Anja Strangfeld (German Rheumatism Research Centre Berlin, Germany) shared the results of the study.
In total, 2,274 elderly RA patients (mean age 76.0) were included and 616 serious infections in 425 patients were reported. Crude rates of serious infections per 1,000 patient-years were 61.5 for csDMARDs, 72.8 for TNF inhibitors, 58.4 for abatacept, 73.8 for rituximab, 54.4 for IL-6 inhibitors, and 72.1 for JAK inhibitors. No significantly increased or reduced risks of serious infections were associated with bDMARD or JAK inhibitor use compared with csDMARD use (see Figure). Disease activity, represented by DAS28 erythrocyte sedimentation rate (HR 1.11), and physical capacity (HR 0.93) were significantly associated with the risk of serious infections. After stratifying for disease activity, glucocorticoid use was no longer significantly associated with an increased risk of serious infections. COPD (HR 1.79), chronic kidney disease (HR 1.50), and diabetes mellitus (HR 1.33) were also significantly associated with an increased risk of serious infections in this population of elderly RA patients. Overall, the data is very reassuring in relationship to the sleuth of new RA-targeting DMARDS in the last 20 years and infection risk in older subjects.
Figure: Hazard ratios for serious infections associated with rheumatic treatments [1]
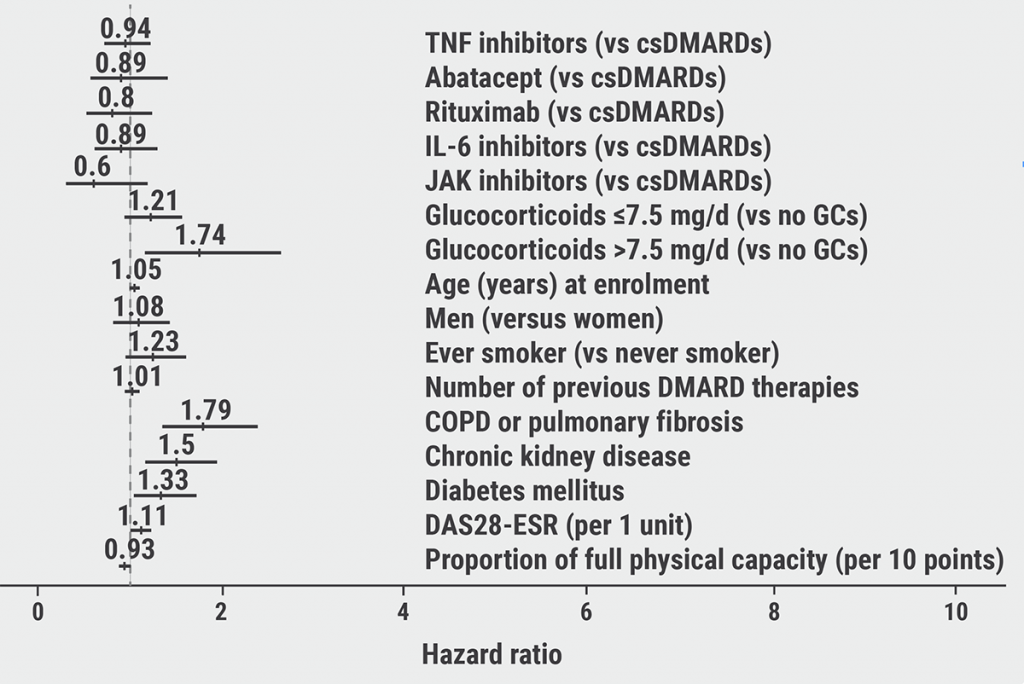
- Strangfeld A, et al. Elderly patients are not at increased risk of serious infections when receiving bDMARDs or JAK inhibitors compared to csDMARD treatment. OP0116, EULAR 2021 Virtual Congress, 2–5 June.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Rituximab or JAK inhibitors increase the risk of severe COVID-19 Next Article
Perioperative SOX protocol bests adjuvant CapOx in locally advanced gastric cancer »
« Rituximab or JAK inhibitors increase the risk of severe COVID-19 Next Article
Perioperative SOX protocol bests adjuvant CapOx in locally advanced gastric cancer »
Table of Contents: EULAR 2021
Featured articles
COVID-19 Update
Rituximab or JAK inhibitors increase the risk of severe COVID-19
Updates on COVID-19 vaccines in patients with rheumatic disease
Immunomodulatory therapies for severe COVID-19: literature update
New Developments in Rheumatoid Arthritis
JAK inhibitors and bDMARDs not associated with increased risk of serious infections in RA
Remote management of RA is a feasible alternative for outpatient follow-up
TOVERA: Ultrasound is a promising biomarker of early treatment response
The risks of polypharmacy in RA
ABBV-3373: A potential new therapeutic agent for RA
JAK inhibitors and bDMARDs show comparable effectiveness
Spondyloarthritis: Progression in Therapies
SELECT-AXIS: 64-week results of upadacitinib in active ankylosing spondylitis
Guselkumab efficacious in PsA patients with inadequate response to TNF inhibition
Faecal microbiota transplantation not effective in active peripheral PsA
Risankizumab meets primary and ranked secondary endpoints in PsA
Prognostic factors for minimal disease activity in early psoriatic arthritis revealed
Imaging in Large-Vessel Vasculitis
PET/CT is a reliable measure of disease activity in LVV, but does not predict future relapses
Ultrasound is useful for disease monitoring in giant cell arteritis
Prevention in Rheumatic Diseases
Air pollution predicts decreased response to biological treatment in rheumatic diseases
Passive smoking associated with an increased risk of RA
Gene-Environment Interaction in Gout
Gene-diet and gene-weight interactions associated with the risk of gout
What Is New in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Intensified treatment regimen of anifrolumab for lupus nephritis is promising
Systemic lupus erythematosus: increased risk of severe infection
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Emerging therapies and future treatment directions in osteoarthritis
Related Articles
December 1, 2023
Repeat steroid injection in knee osteoarthritis possibly beneficial
July 31, 2023
Methotrexate lowers pain in inflammatory hand OA
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

