https://doi.org/10.55788/2e1c8f3f
The phase 3 SYMPATICO trial (NCT03112174) randomised 267 participants with R/R MCL 1:1 to the combination therapy of ibrutinib plus venetoclax or to monotherapy of ibrutinib plus placebo. Participants received the allocated therapy for 24 months. Hereafter, single-agent ibrutinib was administered. The primary endpoint was PFS and the primary results were presented by Prof. Michael Wang (University of Texas, TX, USA) [1].
At a median follow-up of 51.2 months, the primary endpoint was met: the median PFS in the experimental arm was 31.9 months, significantly outperforming the control arm (median PFS 22.1 months; HR 0.65; 95% CI 0.47–0.88; log-rank P=0.0052). This result was consistent across pre-defined subgroups. Also, the duration of response was prolonged in the experimental arm (see Figure). Moreover, the time-to-next-therapy was significantly longer in participants who were treated with the combination therapy (not reached vs 35.4 months; HR 0.60; 95% CI 0.40–0.89; P=0.0096). “For overall survival, only a numerical benefit of the combination therapy over the monotherapy could be observed at this interim analysis (44.9 vs 38.6 months; HR 0.85; 95% CI 0.62–1.19; P=0.35),” said Dr Wang.
Figure: Duration of response of ibrutinib plus venetoclax or monotherapy of ibrutinib plus placebo [1]
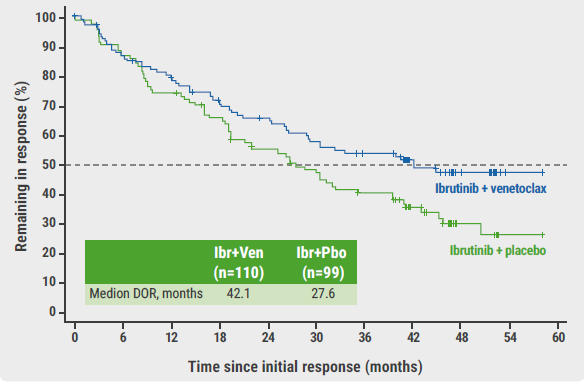
DOR, duration of response; Ibr, ibrutinib; Mo, months; Pbo, placebo; Ven, venetoclax.
The safety profile of the combination regimen was consistent with the known safety profiles of each respective single agent. The rate of adverse events (AEs) leading to dose reductions was higher in the combination therapy arm than in the monotherapy arm (36% vs 22%) and the most common grade ≥3 AEs in the experimental arm were neutropenia (31%), pneumonia (13%), and thrombocytopenia (13%). The atrial fibrillation rate was 5% in both arms.
In conclusion, the addition of venetoclax to ibrutinib resulted in a favourable benefit-risk profile in participants with R/R MCL.
- Wang M, et al. Ibrutinib combined with venetoclax in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: primary analysis results from the randomized phase 3 SYMPATICO study. Abstract LBA-2, 65th ASH Annual Meeting, 9–12 December 2023, San Diego, CA, USA.
Copyright ©2024 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« KdD outperforms Kd in R/R MM also in participants with poor renal function Next Article
Primary phase 2 efficacy and safety results of M-Pola in relapsed/refractory LBCL »
« KdD outperforms Kd in R/R MM also in participants with poor renal function Next Article
Primary phase 2 efficacy and safety results of M-Pola in relapsed/refractory LBCL »
Table of Contents: ASH 2023
Featured articles
Meet the Trialist: Prof. Jeff Sharman on ELEVATE-TN
Leukaemia
FLT3-ITD-specific MRD assessment useful for clinical management of AML
MRD status rather than FLT3-ITD co-mutation is linked to the benefit of CR1-allo in NPM1-mutated AML
Promising results for quizartinib, venetoclax, and decitabine in FLT3-ITD mutated AML
AUGMENT-101: Excellent results for revumenib in R/R KMT2Ar leukaemia
Blinatumomab reduces toxicity in the consolidation phase in paediatric high-risk B-cell ALL
Promising results for olverembatinib in combination with venetoclax for Ph+ ALL
Undetectable MRD on maintenance venetoclax, acalabrutinib, and obinutuzumab in the majority of R/R CLL participants
Lymphoma
Is allogeneic stem cell transplantation a solid option in R/R LBCL or R/R T-cell lymphoma?
Encouraging results for the addition of acalabrutinib to lenalidomide and rituximab in follicular lymphoma
Can ibrutinib ameliorate outcomes in R/R ABC-DLBCL undergoing autoSCT?
Primary phase 2 efficacy and safety results of M-Pola in relapsed/refractory LBCL
SYMPATICO: Ibrutinib plus venetoclax boosts PFS in R/R mantle cell lymphoma
Multiple Myeloma
KdD outperforms Kd in R/R MM also in participants with poor renal function
IsKia: Novel treatment regimen for MM delivers high MRD-negativity rates
Novel standard-of-care in newly diagnosed MM
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
TRANSFORM-1: High spleen volume reduction rates for navitoclax plus ruxolitinib in myelofibrosis
Momelotinib beats controls regarding transfusion outcomes in myelofibrosis
DALIAH: Peginterferon-α head-to-head against hydroxyurea in MPN
Non-Malignant Haematology
Long-term efficacy and safety of iptacopan in PNH with anaemia
ADVANCE IV: Swift responses on efgartigimod in ITP
Favourable QoL and bleeding outcomes for rilzabrutinib in ITP
Novel risk assessment model acts on increasing hospital-acquired venous thromboembolism rates among children
Miscellaneous Topics
Axatilimab may present a new therapeutic strategy in chronic GvHD
Pomalidomide may become the first approved therapy for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
Ancestry-specific study into CH delivers new leads
Featured Interviews
Interview: Sandwich treatment model shows promise for mantle cell lymphoma
Meet the Trialist: Prof. Jeff Sharman on ELEVATE-TN
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy