A subset of patients with CLL treated with both a covalent BTK inhibitor and venetoclax will still develop progressive disease. Dr Meghan Thompson (Memorial Sloan Cancer Center, NY, USA) explained that data is limited regarding therapy efficacy in these double-exposed patients. Therefore, practice patterns vary.
The current international, retrospective, multicentre study compared the efficacy of in USA available approved options (i.e. CIT or PI3K inhibitors) with investigational options (i.e. non-covalent BTK inhibitors, CAR T-cell therapy, or allogeneic SCT) in double-exposed patients with CLL (n=125). The primary endpoint was the investigator-assessed overall response rate.
The overall response rate was 85.7%, 76.5%, and 75.0% in patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy (n=7), allogeneic SCT (n=17), or non-covalent BTK inhibitors (n=43), respectively. In contrast, patients who received PI3K inhibitors (n=24) or CIT (n=23) achieved response rates of 40.9% and 31.8%, respectively. In addition, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3 months and 5 months in patients treated with CIT or PI3K inhibitors, whereas patients treated with allogeneic SCT achieved a median PFS of 11 months. The subset of patients that received non-covalent BTK inhibitors had not yet reached median PFS (see Table).
Table: Therapy responses [1]
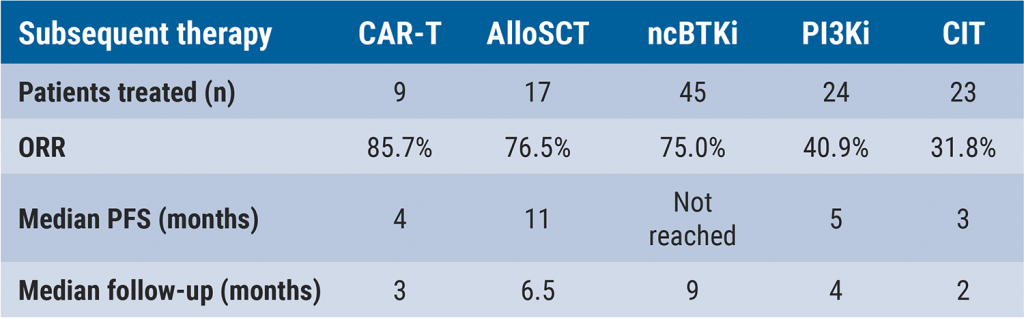 AlloSCT, allogeneic stem cell transplantation; CAR T, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy; CIT, chemo+/-immunotherapy; ncBTKi, non-covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor; ORR, overall response rate; PI3Ki, PI3K inhibitor.
AlloSCT, allogeneic stem cell transplantation; CAR T, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy; CIT, chemo+/-immunotherapy; ncBTKi, non-covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor; ORR, overall response rate; PI3Ki, PI3K inhibitor.The results showed that CIT or PI3K inhibitors yield poor outcomes compared with non-covalent BTK inhibitors, allogeneic SCT, or CAR T-cell therapy. Dr Thompson argued that the results suggest that the use of CIT and PI3K inhibitors is questionable in double-exposed patients with CLL and that treatment with allogeneic SCT or non-covalent BTK inhibitors should be considered in these patients. The administration of CAR T-cell therapy in this population should be further explored, according to Dr Thompson.
- Thompson MC, et al. Addressing a New Challenge in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Outcomes of Therapies after Exposure to Both a Covalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor and Venetoclax. Abstract 2628, ASH 2021 Annual Meeting, 11–14 December.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« GRIFFIN: Sustained responses of daratumumab plus RVd in MM Next Article
Most re-hospitalisations within first month from CAR T-cell infusion »
« GRIFFIN: Sustained responses of daratumumab plus RVd in MM Next Article
Most re-hospitalisations within first month from CAR T-cell infusion »
Table of Contents: ASH 2021
Featured articles
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
New Interfant protocol includes blinatumomab for KMT2A-r ALL
Persistent disparities in ALL health outcomes
EWALL-INO: Inotuzumab ozogamicin promising as first-line therapy for BCP-ALL
UKALL 2003: Therapy de-escalation safe in low-risk MRD patients with ALL
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
AMLSG 16-10: Long-term benefits of midostaurin for FLT3-ITD-mutated AML
Comparable effectiveness of CPX-351 and venetoclax plus HMA in older AML patients
Promising frontline triplet regimen for TP53-mutated AML
Encouraging results of novel triplet combination for AML
Heavily pre-treated FLT3-mutated AML population may benefit from novel triplet regimen
Benefits of eprenetapopt plus azacitidine for TP53-mutant MDS and oligoblastic AML
Improved risk stratification in MDS via gene-based scoring system
Chronic Leukaemia
CAPTIVATE: Ibrutinib plus venetoclax shows ongoing efficacy in CLL
SEQUOIA: Zanubrutinib meets primary endpoint for treatment-naïve CLL/SLL
Investigational therapies superior to standard-of-care in double-exposed CLL
Multiple Myeloma
GRIFFIN: Sustained responses of daratumumab plus RVd in MM
MajesTEC-1: Teclistamab efficacious in heavily pre-treated MM
iStopMM: Smouldering MM highly prevalent in general population
Mechanisms of D-KRd treatment failure in MM identified
TRIMM-2: Favourable results of talquetamab plus daratumumab for MM
Lymphoma
Second-line tisa-cel similar to standard-of-care for R/R aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Axi-cel improved event-free survival in R/R DLBCL
Axi-cel more effective but tisa-cel less toxic in DLBCL
POLARIX: Novel regimen superior to R-CHOP in DLBCL
Novel non-invasive biomarker ctDNA shows value in CNS lymphoma
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Mechanisms behind TP53 mutations revealed in myeloproliferative neoplasms
JAK2V617F variant allele frequency prognostic of venous events in polycythaemia vera
Immune Thrombocytopenia
Promising results of tacrolimus plus dexamethasone for ITP
Sustained remission after TPO-RA discontinuation in chronic ITP
Haemophilia
Fitusiran meets primary endpoint in ATLAS-A/B trial
ATLAS-INH: Impressive results of fitusiran for haemophilia with inhibitors
rFVIIIFc establishes rapid tolerisation in haemophilia A with inhibitors
Clonal Haematopoiesis
Reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease in CHIP carriers
Lifelong patterns of clonal haematopoiesis revealed
Related Articles
February 4, 2022
Reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease in CHIP carriers
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

