https://doi.org/10.55788/3480eb23
JNJ-77242113 is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively and potently blocks IL-23 signalling and downstream inflammatory cytokine production. Its strength and gastrointestinal stability allow for systemic IL-23 pathway blockade when administered orally. “Our study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral JNJ-77242113 in treating patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis,” explained Dr Robert Bissonnette (Innovaderm Research, Canada) [1].
FRONTIER 1 (NCT05223868) was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study with 255 participants randomised into 6 groups. The participants received different dose regimens of JNJ-77242113 25 mg daily (n=43), 50 mg daily (n=43), 100 mg daily (n=43), 25 mg twice daily (n=41), and 100 mg twice daily (n=42), or placebo (n=43) through to week 16. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving a ≥75% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI75) at week 16. Additionally, PASI90, PASI100, Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of clear or almost clear skin (0/1), IGA score 0, and scalp-specific (ss)-IGA score of 0/1 with ≥2-grade improvement from baseline at week 16 were assessed.
At week 16, the results showed a significant dose-dependent response, with all JNJ-77242113 doses demonstrating significantly higher response rates for PASI75, PASI90, PASI100, IGA scores, and ss-IGA scores compared with the placebo group (P<0.05). The proportions of participants achieving PASI75 ranged from 37.2% (in the 25 mg once daily group) to 78.6% (100 mg twice daily group), which significantly exceeded the 9.3% in the placebo group. Furthermore, those reaching PASI90 and PASI100 at week 16 in the JNJ-77242113 groups ranged from 25.6 to 59.5% and 9.8 to 40.5%, respectively, whereas in the placebo group, only 1 patient achieved PASI90 and none attained PASI100. Response rates for scalp psoriasis were also significantly higher in all doses of JNJ-77242113 compared with placebo with up to 75% of participants achieving an ss-IGA score of 0/1 with ≥2-grade improvement from baseline (see Figure).
Figure: JNJ-77242113 response rates for scalp psoriasis were significantly higher than placebo [1]
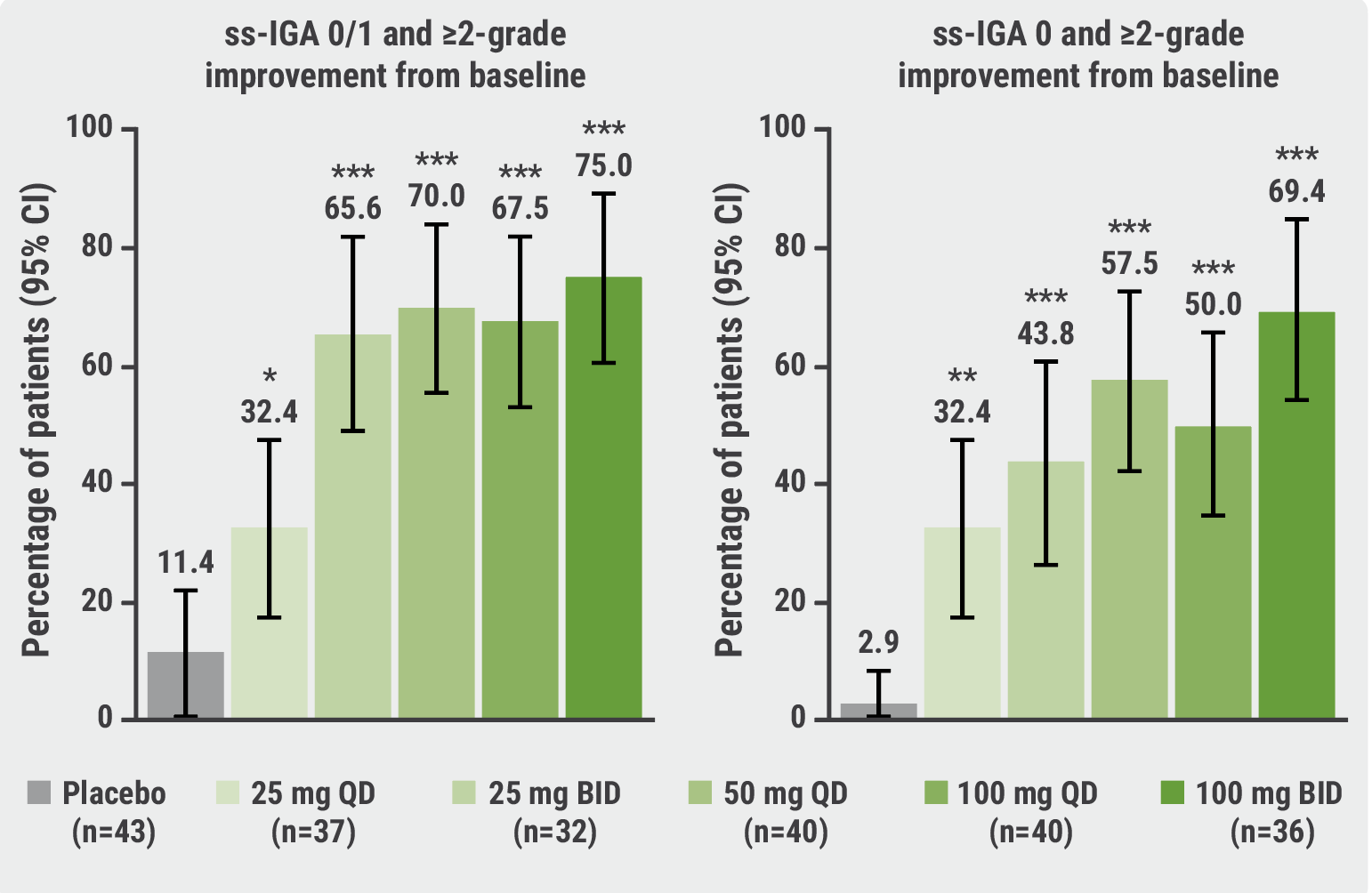
Importantly, adverse event rates were similar between the JNJ-77242113 and placebo groups, with COVID-19 and nasopharyngitis frequently reported but showing no dose-dependent trends.
"JNJ-77242113 is an excellent first-in-class oral IL-23R antagonist peptide that has proven high efficacy in treating moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis including scalp psoriasis," Dr Bissonnette concluded.
- Bissonnette R, et al. A Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Dose-ranging Study of Oral JNJ-77242113 for the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Efficacy of Overall and Scalp Psoriasis Responses from FRONTIER 1. FC08.9, EADV Congress 2023, 11-14 October, Berlin, Germany.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Skin tape stripping allows a novel precision medicine approach in HS Next Article
IL-23 blockers may lower the risk of developing inflammatory and psoriatic arthritis »
« Skin tape stripping allows a novel precision medicine approach in HS Next Article
IL-23 blockers may lower the risk of developing inflammatory and psoriatic arthritis »
Table of Contents: EADV 2023
Featured articles
Tapinarof on course to become a new topical treatment in AD
AD and Eczema in 2023
Tapinarof on course to become a new topical treatment in AD
Upadacitinib provides sustained skin clearance in adolescents and adults with AD
Sustained deep clinical and itch responses with novel IL-13 inhibitor
IL-13 inhibitor shows potential in atopic dermatitis
Encouraging results for amlitelimab in atopic dermatitis
Chronic hand eczema: patients share similar molecular signatures regardless of AD status
Severe hand eczema: dupilumab could be a future treatment
Psoriasis News
Dual IL-17 blockade yields efficacy on joints and skin
High-dose subcutaneous spesolimab prevents GPP flares up to week 48
Drug survival of guselkumab and risankizumab seems superior to other biologics
IL-23 blockers may lower the risk of developing inflammatory and psoriatic arthritis
First-in-class oral IL-23 inhibitor safe and effective for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: End of the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Draught
Skin tape stripping allows a novel precision medicine approach in HS
Nanobodies: A novel way to treat HS
Anti-IL17 blockade leads to maintained pain reduction in patients with HS
Vitiligo: Novel Treatment Options
JAK1 inhibition: a promising forthcoming treatment option in vitiligo
Vitiligo: Continuation of topical ruxolitinib successful in many initial non-responders
Alopecia Areata: Novel Developments
JAK3/TEC inhibition achieves clinically meaningful responses in AA
Alopecia areata: remarkable regrowth rates with deuruxolitinib
Botanical drug solution improves hair regrowth in children and adolescents with AA
What’s New in Other Disease Entities
Nemolizumab shows high success rates in prurigo nodularis
Remibrutinib reduces itch, sleep problems, and activity impairment in patients with CSU
Innovative wound gel reduces frequency of painful dressing changes in epidermolysis bullosa
Best of the Posters
Women with psoriasis face increased adverse effects with systemic therapy
Improved AI tool shows high sensitivity rates in skin cancer detection
Dermoscopy training combined with AI significantly improves skin cancer detection
Related Articles
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

