The VOYAGER PAD trial (NCT02504216) showed a significant reduction of major cardiovascular events in patients with CLTI or claudication after LER who were treated with rivaroxaban compared with placebo (HR 0.86; P=0.0086) [2]. The current subanalysis analysed the consistency of these results across the different patient conditions (i.e. claudication or CLTI). Furthermore, the study described haemodynamic and patient-reported outcomes, and the risk profile of major adverse events in patients with claudication after LER. In total, 5,031 patients with claudication were assessed. The primary outcome was a composite score of major cardiovascular events, and the 3-year results were presented by Prof. Marc Bonaca (University of Colorado, CO, USA).
The primary endpoint was met: there was a significant risk reduction of major cardiovascular events in patients with claudication who were treated with rivaroxaban after LER (HR 0.86) compared with placebo. In addition, no interaction effect was observed between patients with claudication and patients with CLTI who underwent LER (P=0.94; see Figure).
Figure: Primary efficacy endpoint of rivaroxaban in claudication and CLTI
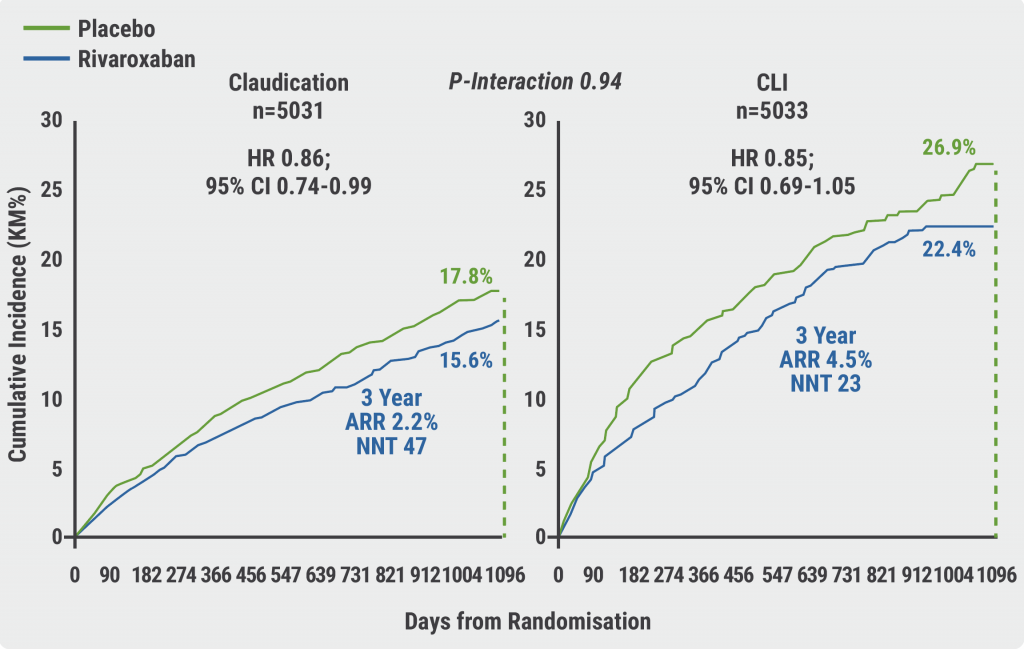
ARR, absolute risk reduction; CI, confidence interval; CLI, critical limb-threatening ischaemia; HR, hazard ratio; NNT number needed to treat.
Patients with claudication (both rivaroxaban and placebo pooled) showed an improved walking function 1 month after LER. Pre-LER, 38% of participants indicated in the Walking Impairment Questionnaire that they were able to walk 2 blocks compared with 82% of participants post-LER. This effect was durable over approximately 2–3 years regardless of surgical approach.
At 3 years after LER, the unplanned index limb revascularisation rate was 22%. In addition, major adverse limb events occurred with a rate of 8.5% per 3 years, and thus a high risk in patients with claudication following LER. Rivaroxaban consistently reduced these risks in those with claudication and CLI.
A risk-benefit analysis of rivaroxaban after LER for patients with claudication showed that a net value of 22 major cardiovascular events was prevented by the treatment at the expense of 5 major bleeding events. Moreover, a net value of 16 unplanned limb revascularisations was prevented by the treatment.
- Bonaca MP, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rivaroxaban in Patients with PAD Undergoing Lower Extremity Revascularization for Claudication. FS06, AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, 13–15 November.
- Bonaca MP, et al. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1994–2004.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« LIBERTY 360 shows quality-of-life improvements after peripheral vascular intervention Next Article
External support device for SVG grafts in CABG surgery shows promise »
« LIBERTY 360 shows quality-of-life improvements after peripheral vascular intervention Next Article
External support device for SVG grafts in CABG surgery shows promise »
Table of Contents: AHA 2021
Featured articles
The scope of remote healthcare in hypertension and hyperlipidaemia
Atrial Fibrillation
New developments in remote diagnostics and monitoring of AF
Head-to-head: Efficacy of dabigatran versus warfarin on cognitive impairment
Posterior left pericardiotomy safe and effective in reducing atrial fibrillation
LAA ligation did not reduce recurrent atrial arrhythmias in persistent AF
Equal benefits of early rhythm control in AF subtypes
CVD Risk Reduction
Remote healthcare programme improves hypertension and lipid control
Novel oral PCSK9 inhibitor shows promising results for hypercholesterolaemia
REVERSE-IT: Interim analysis shows promising effect of bentracimab on ticagrelor reversal
No significant effect of aspirin on reducing cognitive impairment
Milvexian phase 2 data supports safety and efficacy for VTE prevention after total knee replacement
Network meta-analysis observes no clear effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on CV outcomes
Heart Failure
Empagliflozin efficacious in HF patients with preserved ejection fractions ≥50%
EMPULSE: Empagliflozin improves outcomes of acute heart failure
CHIEF-HF: Canagliflozin improves health status in heart failure
DREAM-HF: MPC therapy for HFrEF did not meet primary endpoint
Therapeutic approaches in heart failure with diabetes
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Ticagrelor cessation: early CABG non-inferior to delayed surgery
Distinguishing patients before AMI based on plaque morphology
Vascular Diseases: PVD
Rivaroxaban regimen beneficial after revascularisation for claudication
LIBERTY 360 shows quality-of-life improvements after peripheral vascular intervention
Deficient treatment outcomes after PVI in Black and low-income adults with PAD
REDUCE-IT: Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl in PAD
Vascular Diseases: CAD
Long-term reduced risk of CV events with ticagrelor plus aspirin after CABG
Early surgery outperforms conservative management in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis
External support device for SVG grafts in CABG surgery shows promise
COVID-19 & the Heart
Blood pressure control disrupted during the pandemic
Icosapent ethyl did not reduce the risk of hospitalisation in COVID-19
Neutral effect of P2Y12 inhibitors in non-critical COVID-19 hospitalisations
COVID-19 mRNA vaccination benefits outweigh the risk for myocarditis
Other
2021 Guideline for Chest Pain: Top 10 takeaways
Accurate ejection fraction assessment in paediatric patients via artificial intelligence
Concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty reduces treatment failure in moderate tricuspid regurgitation
Related Articles
January 14, 2022
Therapeutic approaches in heart failure with diabetes
January 14, 2022
Distinguishing patients before AMI based on plaque morphology
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

