https://doi.org/10.55788/32a0f49f
High-intensity statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACEi/ARBs), and sodium‐glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have been shown to improve outcomes for patients with T2D and ASCVD. Yet, “these therapies are highly underused in clinical practice: 37.4% use none and only 2.7% take all 3,” said study presenter Prof. Neha Pagidipati (Duke University Hospital, NC, USA) [1].
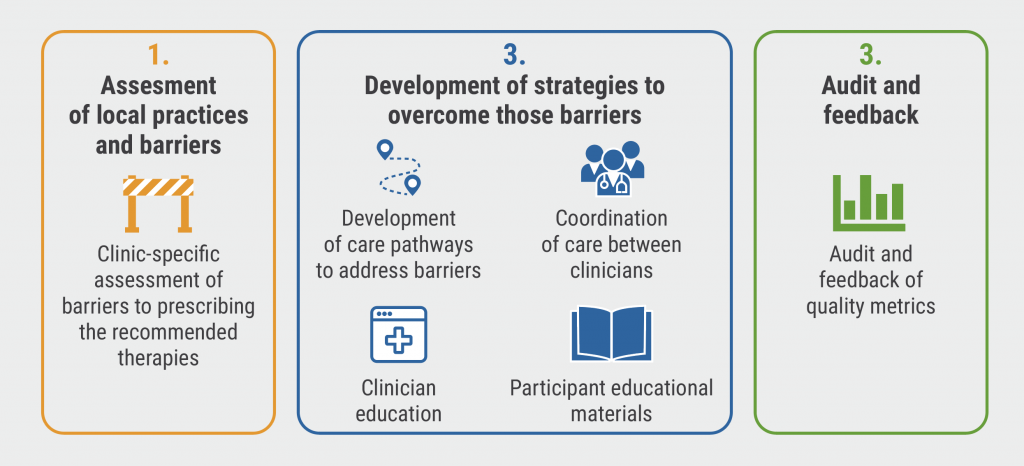
The COORDINATE-Diabetes study (NCT03936660) evaluated the effect of a clinic-level intervention that incorporated assessment, education, and feedback on the prescription of high-intensity statins, ACEi or ARBs, and SGLT2i and/or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs). Clinics in the intervention group collaborated to develop a multifaceted intervention (see Figure).
Figure: The multifaceted intervention of COORDINATE–Diabetes [1]
The study enrolled 1,049 patients, 459 of whom were treated in clinics in the intervention group and 590 received usual care. The mean age was 70 years, and 32% were women. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients prescribed all 3 groups of therapies at 6 to 12 months after enrolment.
The primary endpoint was reached by 173 out of 457 (37.9%) in the intervention group and 85 out of 588 (14.5%) in the control group; an absolute difference of 23.4% (adjusted OR 4.38; 95% CI 2.49– 7.71; P<0.001). Dr Pagidipati said this difference was primarily driven by a large increase in prescriptions for SGLT2i and GLP1RAs.
She added that the composite secondary outcome of all-cause death or hospitalisation for myocardial infarction, stroke, decompensated heart failure, or urgent revascularisation was reached by 5% in the intervention group and 6.8% in the control group (adjusted HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.46–1.33). “This difference is not statistically significant, but it is in line with what we would expect based on previously published data,” said Prof. Pagidipati. “The next step is to scale this intervention across cardiology practices to deliver high-quality care more broadly.”
- Pagidipati N, et al. Coordinating Cardiology Clinics Randomized Trial Of Interventions To Improve Outcomes (COORDINATE) - Diabetes: Primary Results. Session 409-16, ACC Scientific Session 2023, 4–6 March, New Orleans, USA.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Bempedoic acid benefits statin-intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk Next Article
Statins associated with reduced heart dysfunction from anthracyclines »
« Bempedoic acid benefits statin-intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk Next Article
Statins associated with reduced heart dysfunction from anthracyclines »
Table of Contents: ACC 2023
Featured articles
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Sotatercept improves exercise capacity in patients with PAH
Fixed-dose macitentan plus tadalafil superior to either agent alone in PAH
Coronary Revascularisation
Immediate complete revascularisation non-inferior to staged complete revascularisation
RENOVATE-COMPLEX-PCI results support intravascular-guided PCI for complex lesions
Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy
No need to restrict vigorous exercise in selected HCM patients?
No difference in CV outcomes between PET or CMR and SPECT
Interventional and Structural Cardiology
Benefits of MitraClip sustained to 5 years in COAPT trial
Transcatheter repair for patients with tricuspid regurgitation
Minimally invasive versus conventional sternotomy for mitral valve repair
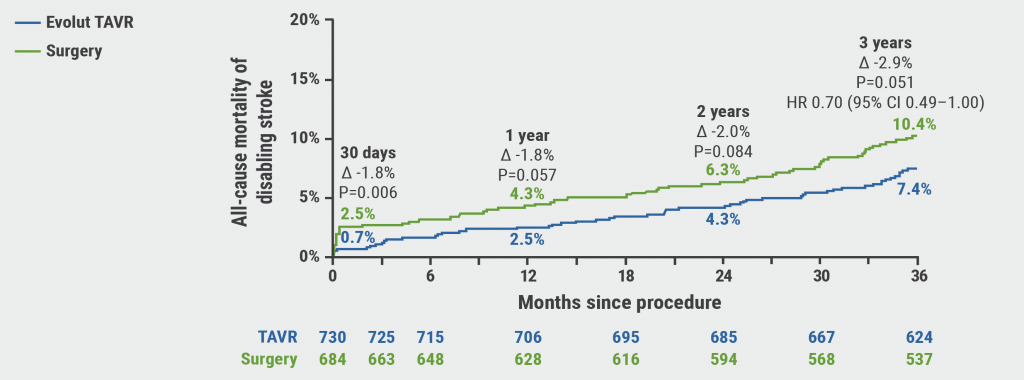
Durable benefits of TAVR versus surgical aortic valve replacement in aortic stenosis patients
PCI not better than GDMT in severe ischaemic cardiomyopathy
Prevention
Anticoagulation in non-critically ill hospitalised COVID patients
Statins associated with reduced heart dysfunction from anthracyclines
Multifaceted strategy improves prescription of therapies for diabetes and ASCVD
Dyslipidaemia
Bempedoic acid benefits statin-intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk
Evolocumab improves coronary plaque morphology in stable CAD
Inflammation stronger predictor of MACE than cholesterol levels
Oral PCSK9 inhibitor significantly lowers LDL-C
Miscellaneous
Baxdrostat in patients with uncontrolled hypertension
Hormone therapy for gender dysphoria associated with increased CV risk
Pulsed-field ablation appears safe and effective for atrial fibrillation
Key correlates of incident dementia identified in the MESA study
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com