https://doi.org/10.55788/f811f2b0
Zolbetuximab is a first-in-class chimeric, IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting CLDN18.2 and inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) [1,2]. In a phase 2b trial, this agent, in combination with epirubicin + oxaliplatin + capecitabine (EOX), improved the survival in patients with increased expression of CLDN18.2 in their tumour cells [3]. This result led to the development of the SPOTLIGHT study.
SPOTLIGHT (NCT03504397) is a global phase 3 trial randomising newly diagnosed patients with CLDN18.2-positive/HER2-negative, locally advanced, mG/GEJ adenocarcinoma (n=565) 1:1 to mFOLFOX6 plus zolbetuximab or to mFOLFOX6 plus placebo [4]. Over 38.5% of assessable patients were CLDN18.2 positive, defined as moderate to strong CLDN18.2 staining in ≥75% of tumour cells. PFS was the primary endpoint of the study and Dr Kohei Shitara (National Cancer Center Hospital East, Japan) presented the primary findings.
After a median follow-up of 12.9 months, the median PFS was significantly higher if patients were treated with zolbetuximab compared with mFOLFOX6 only (10.61 months vs 8.67 months; HR 0.75; 95% CI 0.59‒0.94; P=0.0066, see Figure). The corresponding 24-month PFS rates were 24% and 15%, respectively. The OS results confirmed the benefit of the addition of zolbetuximab to mFOLFOX6 with a median OS of 18.2 months compared with 15.5 months for patients who received mFOLFOX6 only (HR 0.75; 95% CI 0.60‒0.94; P=0.0053).
Figure: Higher PFS for patients on zolbetuximab compared with mFOLFOX6 only [4]
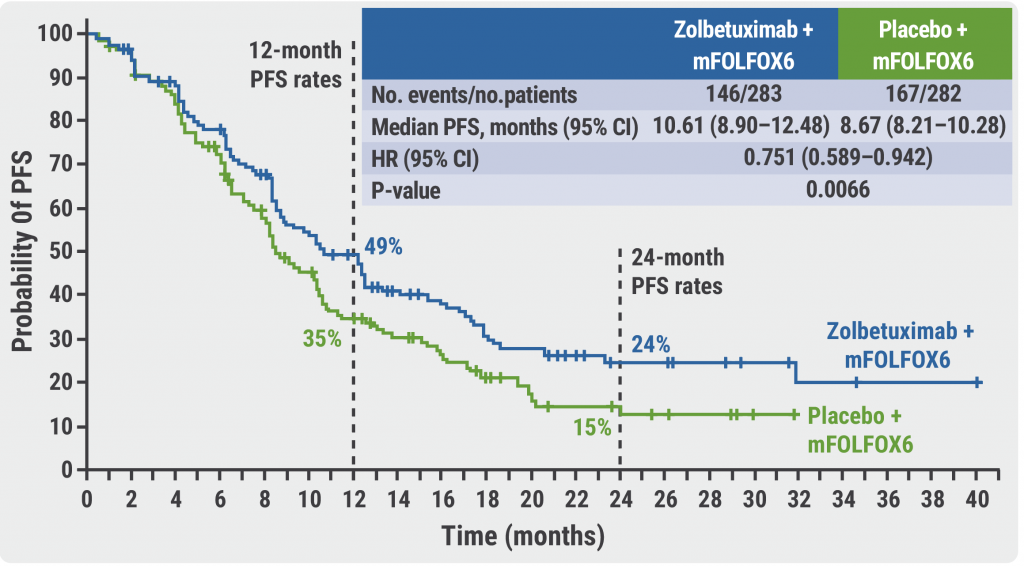
PFS, progression-free survival; mFOLFOX6, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin.
According to the authors, the safety profile of zolbetuximab and mFOLFOX6 was acceptable. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was comparable for the 2 treatment arms, but grade 3 or higher nausea (16.1% vs 6.5%) and vomiting (16.1% vs 5.8%) were more common in the zolbetuximab arm. Dr Shitara commented that these events mostly occurred in the first cycle of zolbetuximab and that they were manageable with treatment adjustments. In total, 13.6% of the patients discontinued zolbetuximab due to treatment-related adverse events compared with 2.2% of the patients in the placebo arm.
In conclusion, zolbetuximab plus mFOLFOX6 candidates as a new standard-of-care therapy for patients with CLDN18.2-positive/HER2-negative, locally advanced, mG/GEJ adenocarcinoma. It is the first moleculary targeted therapy to show a statistically significant survival benefit since trastuzumab.
- Sahin U, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2018;100:17–26.
- Rohde C, et al. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019;49:870–876.
- Sahin U, et al. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:609–619.
- Shitara K, et al. Zolbetuximab + mFOLFOX6 as first-line (1L) treatment for patients (pts) with claudin-18.2+ (CLDN18.2+) / HER2− locally advanced (LA) unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction (mG/GEJ) adenocarcinoma: Primary results from phase 3 SPOTLIGHT study. Late-breaking abstract 292, ASCO GI, 19–21 January, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Regorafenib offers survival benefit for patients with pre-treated gastric cancer Next Article
Can we improve total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer? »
« Regorafenib offers survival benefit for patients with pre-treated gastric cancer Next Article
Can we improve total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer? »
Table of Contents: ASCO GI 2023
Featured articles
Oesophageal and Gastric Cancer
Zolbetuximab plus mFOLFOX6 successful in CLDN18.2-positive subgroup of gastric cancer
Regorafenib offers survival benefit for patients with pre-treated gastric cancer
Radiotherapy or not in locally advanced oesophageal or junctional cancer?
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy is safe and efficacious in a phase 2 gastric cancer trial
S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy: 4 or 8 courses in stage 2 gastric cancer?
LATG/LAPG demonstrates excellent long-term efficacy in stage 1 gastric cancer
3-year follow-up data confirms benefits of nivolumab plus chemotherapy
Long-term results for nivolumab plus chemotherapy and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in oesophageal cancer
Promising phase 2 results for HER-Vaxx in gastric cancer
Anal and Colorectal Cancer
IMbrave 151 missed primary endpoint in advanced BTC
Combination botensilimab plus balstilimab demonstrates promising activity in heavily pre-treated MSS CRC
Mutation-based selection to identify patients suitable for panitumumab treatment
Fucoidan associated with quality-of-life benefits in patients with rectal cancer receiving CCRT
ctDNA appears useful in monitoring patients with anal cancer undergoing CRT
SUNLIGHT trial meets primary endpoint in refractory metastatic CRC
Does cell-free DNA influence MRD testing in post-operative colon cancer?
OPERA: surgery may be avoided with adequate therapy in rectal cancer
Can we improve total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer?
Hepatobiliary Cancer
Palliative radiation therapy improves hepatic pain in HCC and liver metastasis
Improved survival following postoperative sorafenib plus TACE in HCC
Quality-of-life benefits for tislelizumab in uHCC
Stereotactic body radiation therapy beneficial for patients with locally advanced HCC
SWOG 1815, first-ever phase 3 trial in BTC, fails
Acceptable safety profile and encouraging efficacy of nanvuranlat in BTC
Pancreatic Cancer
First-line NALIRIFOX superior to standard treatment in mPDAC
Novel approach delivers quality-of-life benefits for patients with pancreatic cancer
Related Articles
March 12, 2021
Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: phase 2 results

© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

