Dose-related use of NSAIDs together with TNFi in AS patients has a synergistic effect in slowing radiographic progression. The greatest effect is seen in those using both high-dose NSAIDs and TNFi. Of all NSAIDs, celecoxib appears to confer the greatest benefit in decreasing progression with effect at both 2 and 4 years. According to Dr Gensler (University of California San Francisco Medical Center, US), the potential of TNFi and/or NSAIDs to reduce radiographic progression in AS was uncertain.
Until now, causal effects of both exposures on radiographic progression have not been convincingly demonstrated. In addition, no study has evaluated whether effects are comparable among different NSAIDs in this setting. Therefore, Gensler et al. explored the causal effects of TNFi on radiographic progression in AS and determined whether the NSAID dose and type impact this relationship.
A total of 519 adult patients from the Prospective Study of Outcomes in Ankylosing Spondylitis (PSOAS) cohort who met the modified New York criteria were included with at least 4 years of clinical and radiographic follow-up. Clinical and medication data were collected every 6 months and radiographs were performed at baseline and every 2 years. Longitudinal targeted maximum likelihood estimation was used to estimate the causal effect of TNFi and NSAIDs (using the NSAID index) on radiographic progression as measured by the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) at 2 and 4 years, accounting for time-varying covariates.
The researchers adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, education, disease duration, enrolment year, number of years on TNFi, disease duration at time of TNFi start, NSAID use, TNFi use, days since last mSASSS measurement, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP), smoking status, and missed visit status. The majority of patients was male (75%) and Caucasian (81%); the baseline mean age was 41.4 years and symptom duration was 16.8 years. Baseline mean mSASSS was 14.2. At baseline, 70% of patients used NSAIDs, TNFi were used by 46% of patients at baseline, and 15% used DMARDs. Patients using TNFi and high-dose NSAIDs showed less progression at 4 years, with the least progression observed at both 2 and 4 years in those using TNFi plus celecoxib (see Figure).[2]
Figure: TNFi users on celecoxib have less mSASS progression at 2 and 4 years [2]
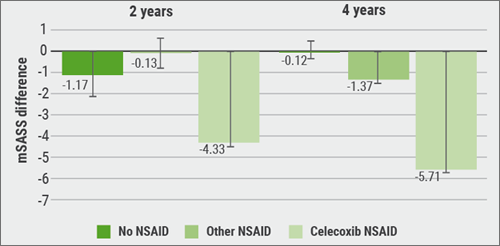
Celecoxib users had higher NSAID index in comparison to other NSAID users and after controlling for NSAID dosages, no change in mSASSS difference was seen. Dr Gensler added that it seemed that celecoxib use, and not the dose of celecoxib, confers benefit in the setting of TNFi.
It was concluded that in this study TNFi prevented radiographic progression in AS patients. This was especially evident when patients were also exposed to NSAIDs at a higher dose at 4 years and with a greater effect in the setting of celecoxib at 2 and 4 years. TNFi and NSAIDs may have a synergistic effect. However, Dr Gensler warned that despite the statistical approach taken in this trial, which addresses many of the biases in observational research, unmeasured confounders are still a possibility. It may be the case that celecoxib users on TNFi rather have different patient characteristics, than there is a drug-specific effect of the combined use of celecoxib with TNFi.[2]
- Gensler LS, et al. Abstract OP0198. EULAR 2018.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Switching to biosimilar bDMARDs is safe and efficacious Next Article
Promising results rituximab in systemic sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus classification criteria »
« Switching to biosimilar bDMARDs is safe and efficacious Next Article
Promising results rituximab in systemic sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus classification criteria »
Table of Contents: EULAR 2018
Featured articles
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Switching to biosimilar bDMARDs is safe and efficacious
No significant differences when tapering TNF blockers versus csDMARDs
Confirmation of long-term safety profile adalimumab across indications
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Clinical effect of vedolizumab on articular manifestations spondyloarthritis associated with IBD
Synergistic effect NSAIDs plus TNFi in slowing radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis patients
Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Promising results rituximab in systemic sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus classification criteria
Related Articles
August 14, 2020
Anifrolumab achieves rapid and durable BICLA-response
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

