https://doi.org/10.55788/2c05af95
SELECTIONLTE (NCT02914535) is an ongoing, open-label extension trial of the JAK inhibitor filgotinib which has already been approved as a treatment for UC [1]. “The aim of this interim analysis, based upon approximately 4 years of therapy, was to assess the safety and efficacy over the longer term,” Dr Brian Feagan (University of Western Ontario, Canada) outlined the topic of the presented investigation. The analysis included data up to week 144 from 148 participants who completed the SELECTION trial (NCT02914522) and who responded to induction therapy with filgotinib and entered SELECTIONLTE after completing the maintenance part. It also included results up to week 192 from 372 patients who did not respond to induction and were directly changed to open-label filgotinib.
Looking at safety first, overall treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE) were reported at an exposure-adjusted incidence rate of 111.5 per 100 patient-years. TEAE of at least grade 3 happened at 9.8 per 100 patient-years. Special focus was placed on specific issues noted in association with JAK inhibitor therapy. This included herpes zoster, malignancies, major adverse cardiovascular events and, venous thromboembolisms with rates of 1.5, 0.5, 0.2, and 0.1 per 100 patient-years, respectively.
The efficacy results were more favourable in the subgroup of completers than in the induction non-responders. Dr Feagan highlighted that up to 144 weeks, preservation is seen of the absolute changes in the partial Mayo Clinic Score from approximately 6 to 2 in approximately 70–80% of patients over time (see Figure).
Figure: Mean change in the Mayo Clinic Score over time in SELECTION and SELECTIONLTE among completers treated with filgotinib 200 mg during both studies [1]
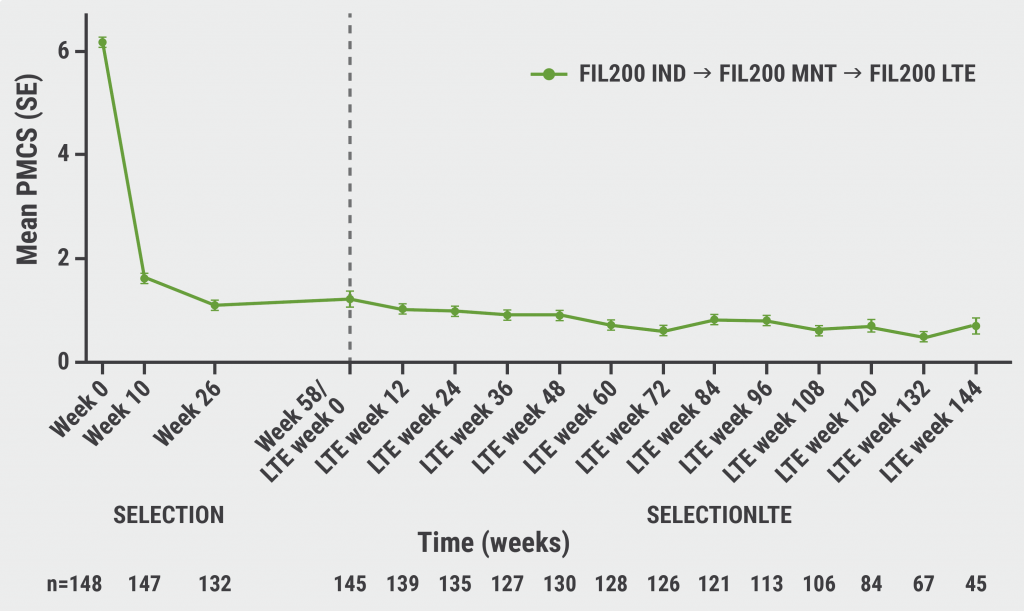
N, number of patients with available data; pMCS, partial Mayo Clinic Score defined as the sum of Mayo rectal bleeding, stool frequency, and physician’s global assessment subscores; FIL200, filgotinib 200 mg; IND, induction; LTE, long-term extension; MNT, maintenance.
Notably, in the initial non-responders, the scores continued to improve up to week 192. As for health-related quality-of-life, over 90% of responders and over 60% of non-responders achieved a minimal clinically important difference that was defined as an increase of ≥16 points on the inflammatory bowel disease questionnaire score. Clinical remission, represented by ≥170 points in the same score, was seen in more than 80% of completers at week 144 and in over 70% of primary non-responders at week 192.
“In the collective assessment of the data, this indicates that filgotinib as a long-term treatment shows a consistent and established safety profile and is effective for the management of these patients,” Dr Feagan summarised.
- Feagan BG. Efficacy and safety outcomes up to ~4 years of treatment with filgotinib 200 mg among patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Results from the SELECTIONLTE study. OP35, ECCO 2023, 01–04 March, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Surgery saves lives in patients with oesophageal fistula Next Article
Upadacitinib successful in the management of both CD and UC »
« Surgery saves lives in patients with oesophageal fistula Next Article
Upadacitinib successful in the management of both CD and UC »
Table of Contents: ECCO 2023
Featured articles
What Is New in Biologic Therapy?
Beneficial effect of early, post-operative vedolizumab on endoscopic recurrence in CD
Long-term data supports the established efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in UC
Anti-TNF withdrawal may be a safe option in stable IBD
Intensified drug therapy leads to better stricture morphology in CD
Small Molecules in IBD: State of the Art
Continued efficacy of long-term ozanimod as UC treatment
Upadacitinib successful in the management of both CD and UC
Solid results for long-term therapy of UC with filgotinib
Paediatric IBD: What You Need To Know
Perinatal period is crucial for the risk of developing CD
Early-life antibiotic exposure: a risk factor for paediatric-onset IBD
Paediatric patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease harbour a heightened cancer risk
Risk Factors and Complications of IBD
Checking kidney function is important during the course of IBD
Diabetes therapy with GLP-1-based drugs does not elevate the risk of IBD
Surgical Approaches: New Developments
Long-term resection potentially better than anti-TNF treatment in CD
Early, post-operative complications in CD reduced by pre-operative enteral nutrition, irrespective of biologic exposure
Pearls of the Posters
Drop in overall IBD procedures during the pandemic
Proton pump inhibitors associated with worse outcomes in CD
Poor sleep in CD linked to low levels of vitamin D
Novel AI tool assessing mucosal inflammation achieves high correlation with histopathologists
Related Articles
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

