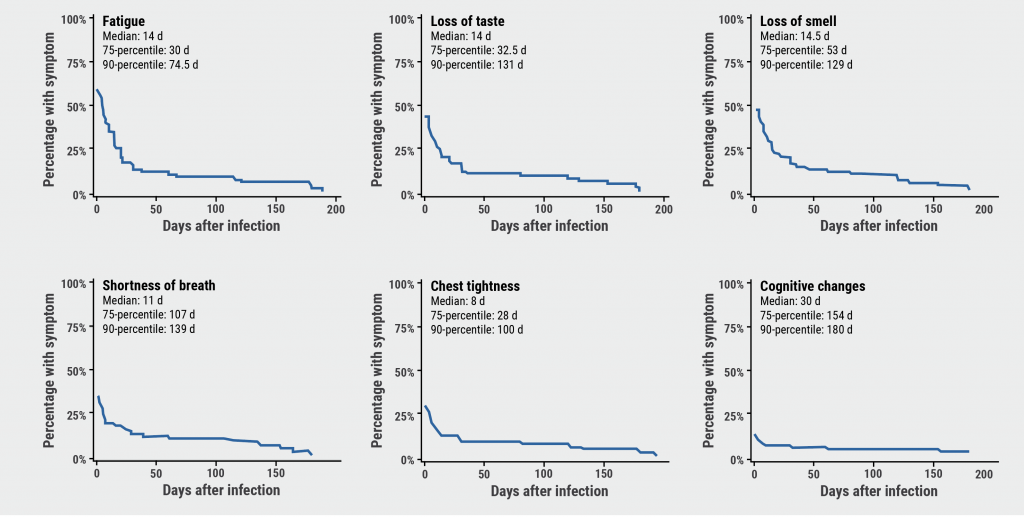
Complement activation (C5a) has been shown to play an important role in severe COVID-19 [1] and vilobelimab is a first-in-class anti-C5a monoclonal antibody that leaves the membrane attack complex (MAC) intact. Since it has been shown that C5a levels are high in patients with severe COVID-19 and related to disease severity [2], Prof. Alexander Vlaar (Amsterdam UMC, the Netherlands) and co-investigators deemed it reasonable to assess C5a inhibition in patients with severe COVID-19.
After the successful results of the PANAMO phase 2 study [3], the PANAMO phase 3 study (NCT04333420) was initiated [4]. This study randomised 368 critically-ill, intubated patients with COVID-19 1:1 to vilobelimab plus standard-of-care or to placebo plus standard-of-care. All-cause mortality after 28 days was the primary outcome.
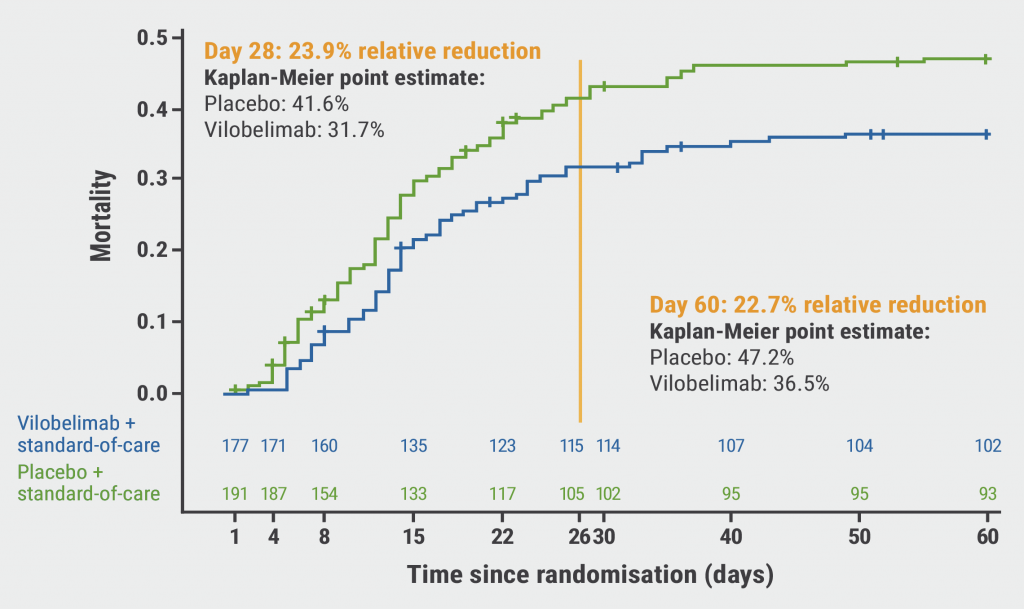
The results displayed a trend towards a reduced risk of all-cause mortality in the vilobelimab arm compared with the placebo arm (31.7% vs 41.6%; see Figure). However, this relative risk reduction of 23.9% was not statistically significant following site-stratified Cox regression (P=0.094), which was the approach recommended by the FDA. In Western-European participants receiving vilobelimab, the observed relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality was 43.0% compared with placebo. In other words, 1 additional life was saved for every 6 participants if they received vilobelimab. Furthermore, participants with more severe disease appeared to benefit more from treatment with vilobelimab than those with less severe disease.
Figure: 28-day mortality rate of vilobelimab- versus placebo-treated COVID-19 patients [4]
In terms of safety, an acceptable safety profile of vilobelimab was reported. The rate of infections and infestations was 62.9% in the intervention arm and 59.3% in the placebo arm.
“A clinically meaningful, but non-significant, benefit was observed for treatment with vilobelimab in this critically-ill population,” said Prof. Vlaar. “The developer aims to present the results to the regulatory authorities.”
- Java A, et al. JCI Insight. 2020;5(15):e140711.
- Carvelli J, et al. Nature. 2020;588:146‒150.
- Vlaar APJ, et al. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(12):e764‒e773.
- Vlaar APJ, et al. Phase 3 RCT of C5a-Specific Vilobelimab in Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. ALERT 3, RCT2881, ERS International Congress 2022, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 September.
Posted on