https://doi.org/10.55788/9a93a95b
Previously, the MINDACT study (NCT00433589) showed that the 70-gene MammaPrint test is able to predict the benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early breast cancer [1,2]. ER-positive patients with a MammaPrint low-risk score do not benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy and are thus preferably treated with an extended endocrine therapy. However, some low-risk patients may be more likely to derive benefits from extended endocrine therapy than others, depending on their risk of late recurrence. Therefore, genomic classifiers that predict the risks of late recurrence may assist with treatment decisions.
In the NSABP-B42 trial (NCT00382070), which compared 5 years of adjuvant letrozole with 10 years of letrozole, only patients with a MammaPrint ‘low but not ultralow’ score had a benefit of 10 years over 5 years of endocrine therapy [3]. To confirm these findings, data from the IDEAL trial (Eudra-CT 2006-003958-16) was analysed. In this trial, no superiority of 5 over 2.5 years (after the first 5 years) of endocrine therapy was observed [4]. Recently, a subgroup analysis was performed based on MammaPrint risk scores. Dr Laura van ‘t Veer (UCLA, CA, USA) presented the results [5].
As expected, patients with a MammaPrint high-risk score did not benefit from extended endocrine therapy. However, in patients with a MammaPrint ‘low but not ultralow risk’ the recurrence-free survival, recurrence-free interval, and breast cancer-free interval were significantly improved with 5 years over 2.5 years of endocrine therapy (HR 0.32, 0.35, and 0.48, respectively; see Figure). This resulted in an absolute benefit of approximately 10 months for each of these endpoints.
Figure: MammaPrint low-risk tumours derive the most extended endocrine therapy benefit [5]
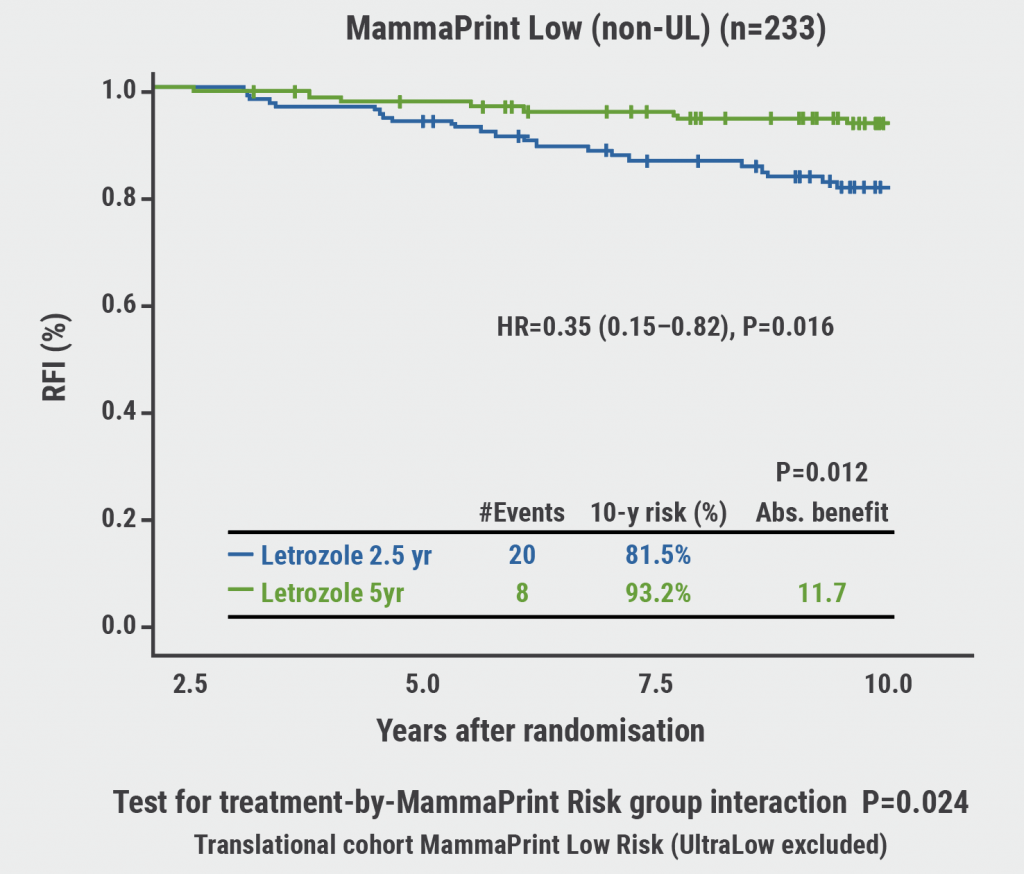
RFI, recurrence-free interval; non-UL, not ultralow.
The latest updates from the TAILOR-X trial (NCT00310180), with 12 years follow-up, also showed the risk of overtreatment [6]. Patients with early ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer with a mid-range Oncotype DX risk score (11–25) were better off skipping chemotherapy.
Based on these results, Dr van ‘t Veer concluded that MammaPrint is predictive of extended endocrine therapy benefits. MammaPrint high-risk patients can avoid extended endocrine therapy overtreatment, while MammaPrint ‘low but not ultralow risk’ patients significantly benefit from extended endocrine therapy.
- Piccart M, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:476–488.
- Lopes Cardozo JMN, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:1335–1345.
- Rastogi P, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(suppl):502.
- Blok EJ, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018;110:40–48.
- Liefers G-J, et al. Utility of the 70-gene MammaPrint test for prediction of extended endocrine therapy benefit in patients with early-stage breast cancer in the IDEAL Trial. Abstract GS5-10, SABCS 2022, 6–10 December, San Antonio, TX, USA.
- Sparano JA, et al. Trial Assigning Individualized Options for TReatment (TAILORx): n update including 12-Year event rates. Abstract GS1-05, SABCS 2022, 6–10 December, San Antonio, TX, USA.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Beyond Moonshot: European Cancer Patients Need Immediate Groundshot Next Article
Anti-PD-1/anti-LAG-3 combination highly effective in HER2-negative breast cancer »
« Beyond Moonshot: European Cancer Patients Need Immediate Groundshot Next Article
Anti-PD-1/anti-LAG-3 combination highly effective in HER2-negative breast cancer »
Table of Contents: SABCS 2022
Featured articles
Miscellaneous
Racial disparity in the tumour microenvironment
Chemo-endocrine therapy worse for cognition than endocrine therapy alone
Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Anti-PD-1/anti-LAG-3 combination highly effective in HER2-negative breast cancer
MammaPrint test predictive for benefit of extended endocrine therapy
HR-positive/HER2-positive Breast Cancer: Trastuzumab-Deruxtecan
Trastuzumab deruxtecan effective in both second-line and neoadjuvant setting
HR-positive/HER2-negative Advanced Metastatic Breast Cancer
Benefit of adjuvant abemaciclib continues to deepen at longer follow-up
First-line ribociclib plus endocrine therapy outperforms combination chemotherapy
Treatment options beyond CDK4/6 inhibition
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Baseline CTC count can guide first-line treatment in HR-positive/HER-negative metastatic breast cancer
ZNF689 deficiency promotes intratumour heterogeneity and resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in TNBC
Oestradiol represses anti-tumoural immune response to promote progression of brain metastases
Basic and Translational Research
Resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is likely due to expansion of pre-existing resistant clones
Germline pathogenic variants for breast cancer also increase contralateral breast cancer risk
Low-dose tamoxifen still prevents recurrence from non-invasive breast cancer
Endocrine interruption to pursue pregnancy does not impact short-term disease in breast cancer
Related Articles
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

