SAkuraSky (NCT02028884) tested satralizumab in combination with baseline immunosuppressants; SAkuraStar (NCT02073279) tested satralizumab as monotherapy. In both placebo-controlled studies, satralizumab reduced the risk of protocol-defined relapse. In a pooled subgroup analysis, efficacy and safety of satralizumab in adults with AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD were assessed [1]. Between-group comparisons were made for time to first relapse, rates of adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, infections, and serious infections that occurred during the double-blind period. To assess safety, data from the overall satralizumab treatment periods were evaluated, including open-label extension periods.
The analysis included 116 adult AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD patients. Compared with placebo, satralizumab significantly reduced protocol-defined relapse risk by 78% in SAkuraSky and by 74% in SAkuraStar. The percentages of patients who were relapse free after 96 weeks were 91.1% in the satralizumab group and 56.8% in the placebo group in SAkuraSky (HR 0.22; 95% CI 0.06–0.82; P=0.014). These percentages were 76.5% and 41.1%, respectively, in SAkuraStar (HR 0.26; 95% CI 0.11–0.63; P=0.001).
In both studies, rates of AEs and serious AEs were similar in the experimental and placebo groups (see Table). Risk of infection or serious infection was not elevated by satralizumab in the double-blind nor in the overall treatment period. Decreases in neutrophil and platelet counts and elevations in liver enzymes were more frequently observed with satralizumab, but were not associated with serious infections or bleeding events.
Table: Adverse event rates in the double-blind and overall treatment periods of the SAkura studies [1]
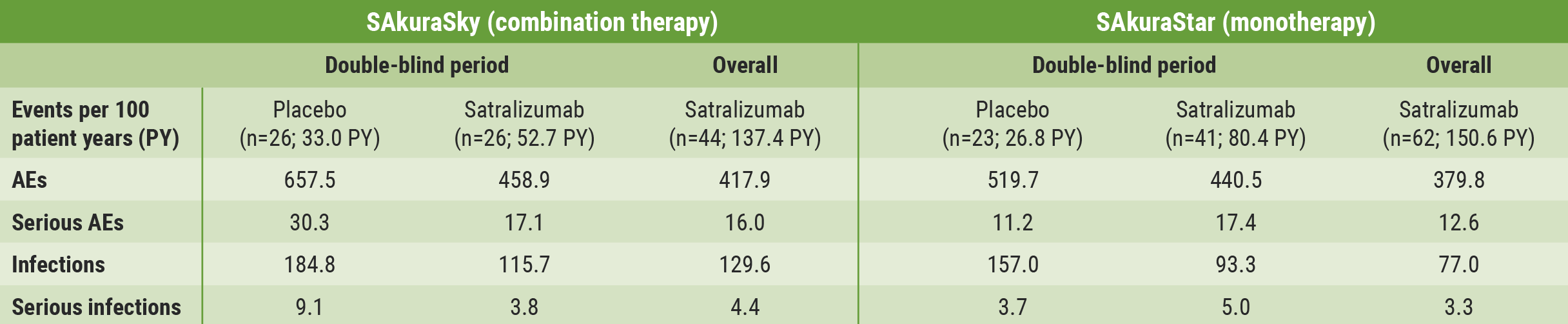
- Bennett J, et al. Satralizumab in adults with AQP4-IgG seropositive NMOSD: Efficacy and safety results from the phase 3 SAkura studies. OPR-163, EAN 2021 Virtual Congress, 19–22 June.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Good long-term safety and efficacy of inebilizumab in NMOSD Next Article
No higher early MS relapse frequency after stopping ponesimod »
« Good long-term safety and efficacy of inebilizumab in NMOSD Next Article
No higher early MS relapse frequency after stopping ponesimod »
Table of Contents: EAN 2021
Featured articles
Letter from the Editor
COVID-19
First evidence of brainstem involvement in COVID-19
Cognitive/behavioural alterations persistent after COVID-19
Neural base of persistent hyposmia after COVID-19
Neurological symptoms and complications of COVID-19 affect outcomes
Cerebrovascular Disease
Intracerebral haemorrhage only slightly increases mortality in COVID-19 patients
Stroke with covert brain infarction indicates high vascular risk
Expanding precision medicine to stroke care
Dexamethasone not indicated for chronic subdural haematoma
Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Severe outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with dementia
Promising diagnostic accuracy of plasma GFAP
Sex modulates effect of cognitive reserve on subjective cognitive decline
Hypersensitivity to uncertainty in subjective cognitive decline
Epilepsy
Minimally invasive device to detect focal seizure activity
‘Mozart effect’ in epilepsy: why Mozart tops Haydn
Migraine and Headache
Factors associated with decreased migraine attack risk
Pregnant migraine patients at higher risk of complications
Occipital nerve stimulation in drug-resistant cluster headache
Rhythmicity in primary headache disorders
Multiple Sclerosis and NMOSD
Typing behaviour to remotely monitor clinical MS status
Alemtuzumab in treatment-naïve patients with aggressive MS
No higher early MS relapse frequency after stopping ponesimod
Good long-term safety and efficacy of inebilizumab in NMOSD
Neuromuscular Disorders
Inability to recognise disgust as first cognitive symptom of ALS
Pathogenic T-cell signature identified in myasthenia gravis
Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel in patients with advanced PD
New Frontier – Navigated Transcranial Ultrasound
Exploring the possibilities
Related Articles
August 18, 2021
Factors associated with decreased migraine attack risk
August 18, 2021
Hypertension pathology visible in white matter lesion volume
August 18, 2021
Good safety and efficacy of cenobamate for focal seizures
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

