https://doi.org/10.55788/ed7ef3d3
“Prolonged cytopenia and infectious complications substantially contribute to the toxicity burden of CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy,” explained Dr Kai Rejeski (LMU Munich, Germany). The CAR-Hematotox score was developed to estimate the risk for haematotoxicity, infections, and poor treatment outcomes after CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy. Whether this tool has utility in patients with relapsed/refractory MM receiving BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy had not yet been established. Dr Rejeski and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis on patients with relapsed/refractory MM receiving either ide-cel or cilta-cel to assess the use of the CAR-Hematotox score in this population (n=113) [1].
HT-high scores at baseline were significantly associated with a poor performance status, high disease activity, prior autologous stem cell transplant, poor renal function, and increased bone marrow infiltration. Also, patients with HT-high scores had an increased risk for prolonged neutropenia compared with patients with HT-low scores (mean 9 vs 3 days; P<0.001). Other haematological toxicities were also more common among patients with HT-high scores (see Figure). Furthermore, the rate of severe infections was significantly higher in patients with HT-high scores than in patients with HT-low scores (40% vs 5%; P<0.0001), mostly driven by an increased rate of bacterial infections (34% vs 3%; P<0.0001). Finally, HT-high scores were linked to poorer PFS (median 5.4 vs 14.9 months; P<0.0001) and OS (median 10.5 vs not reached; P<0.0001) outcomes.
Figure: CAR T-mediated haematotoxicity in HT-high and HT-low patients [1]
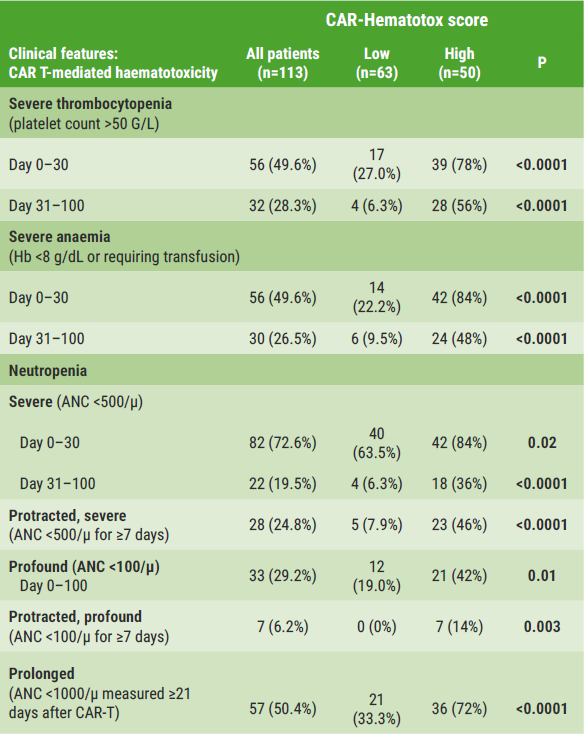
Hb, hemoglobin; ANC, absolute neutrophil count.
- Rejeski K, et al. The CAR-Hematotox Score As a Prognostic Model of Toxicity and Response in Patients Receiving BCMA-Directed CAR-T for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Poster 3343, ASH 64th Annual Meeting, 10–13 December 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Head-to-head: VMP versus Rd in transplant-ineligible MM Next Article
Ultra-sensitive MRD assessment in MM with BloodFlow »
« Head-to-head: VMP versus Rd in transplant-ineligible MM Next Article
Ultra-sensitive MRD assessment in MM with BloodFlow »
Table of Contents: ASH 2022
Featured articles
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
Blinatumomab candidate for standard-of-care in newly diagnosed B-ALL
High-dose methotrexate or standard interim maintenance in young patients with ALL?
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
Excellent results for triplet regimen in FLT3-mutated AML
MRD by qPCR prognostic of outcomes in venetoclax-treated NPM1-mutated AML
Promising results for triplet therapy with magrolimab in AML
Should we use intensive chemotherapy prior to allo-HCT in relapsed/refractory AML?
Chronic Leukaemia
Zanubrutinib wins battle of BTK inhibitors in relapsed or refractory CLL/SLL
Ibrutinib plus venetoclax displays long-term benefits in CLL
Multiple Myeloma
Talquetamab further investigated in heavily pre-treated MM after promising phase 2 data
Promising results of elranatamab for MM in phase 2 MagnetisMM-3 trial
Deep and durable responses for quadruple therapy in smouldering MM
Ultra-sensitive MRD assessment in MM with BloodFlow
CAR-Hematotox score proves useful in relapsed/refractory MM
Head-to-head: VMP versus Rd in transplant-ineligible MM
Lymphoma
Ibrutinib added to ASCT improves clinical outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma
High-dose chemotherapy plus ASCT superior to standard immuno-chemotherapy in primary CNS lymphoma
Odronextamab has considerable anti-tumour effects in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma
Excellent results for AFM13-complexed NK cells in CD30-positive lymphoma
CAR-Hematotox score predicts toxicity, infections, and clinical outcomes in MCL
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Efgartigimod successful in immune thrombocytopenia
INCA033989: novel investigational agent for CALR-mutated MPN
Ruxolitinib mediates clonal evolution of RAS pathway mutations in MPN
Immune Thrombocytopenia
Long-term risk for haematologic disease in persistent, isolated mild thrombocytopenia
Various Topics
C1 inhibitor deficiency linked to thrombosis
Durable responses to gene therapy in haemophilia A
Long-term benefits from beti-cel in transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia
Neutrodiet: non-restricted diet is the preferred option after SCT
Iptacopan offers solution for patients with PNH and residual anaemia after standard-of-care
Novel therapy may replace standard-of-care prophylaxis for GVHD
LMWH does not result in higher live birth rates in women with inherited thrombophilia
Related Articles
February 20, 2023
Neutrodiet: non-restricted diet is the preferred option after SCT
February 20, 2023
C1 inhibitor deficiency linked to thrombosis
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

