The comparative efficacy and safety of recently developed therapies for patients with UC has not been established. A Bayesian network meta-analysis was conducted by Prof. Remo Panaccione (University of Calgary, Canada) and colleagues to compare advanced induction and maintenance therapies for patients with moderately to severely active UC [1]. The study included all therapies with published phase 3 data (i.e. ustekinumab, filgotinib, tofacitinib, infliximab, vedolizumab, adalimumab, golimumab, upadacitinib, and ozanimod). All therapies were compared with placebo.
In biologic-naïve participants, upadacitinib 45 mg induction therapy displayed the largest difference in clinical responsea rates compared with placebo (OR 6.9). Also, filgotinib 200 mg (OR 3.4), tofacitinib (OR 3.1), ustekinumab (OR 3.6), and infliximab 5 mg (OR 3.4) displayed high response rates. Endoscopic improvementb rates confirmed the superior efficacy of upadacitinib induction therapy (OR 6.9), and ozanimod demonstrated high efficacy rates compared with placebo as well (OR 3.6). In biologic-exposed participants, the JAK inhibitors as a class performed well in inducing clinical remission, especially upadacitinib (OR 9.8) and tofacitinib (OR 5.2). In addition, ustekinumab was efficacious in this population, with an OR of 5.9 in inducing clinical remission compared with placebo.
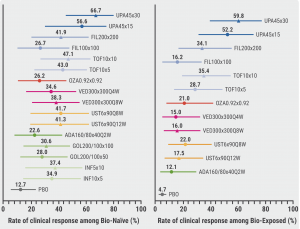
Treat-through analysis in biologic-naïve participants after induction and maintenance therapy showed the highest clinical response rates in participants treated with upadacitinib 45 mg induction and 30 mg maintenance therapy (66.7%), followed by upadacitinib 45 mg induction and 15 mg maintenance therapy (56.6%). This result was confirmed in biologic-experienced participants, with corresponding clinical response rates of 59.8% and 52.2% (see Figure).
Figure: Clinical response rate treat-through analysis in bio-naïve and bio-exposed participants [1]
The safety analysis showed that upadacitinib induction and maintenance therapies were not associated with a higher rate of adverse events than other advanced therapies. The rate of serious adverse events in participants treated with upadacitinib induction therapy and upadacitinib 15 mg or 30 mg maintenance therapy were 3.6%, 4.4%, and 3.8%, respectively.
Prof. Panaccione concluded that upadacitinib induction and maintenance therapies appear to be more efficacious than other advanced therapies regarding clinical response, clinical remission, and endoscopic response rates in both biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced patients with moderately-to-severely UC.
a. Clinical response is defined as a decrease from baseline in full Mayo Score ≥3 points and ≥30% with decrease in rectal bleeding score of ≥1 or absolute rectal bleeding score ≤1
b. Endoscopic improvement is defined as an endoscopic score ≤1.
- Panaccione R, et al. Efficacy and safety of advanced induction and maintenance therapies in patients with moderately to severely active Ulcerative Colitis: An indirect treatment comparison using Bayesian network meta-analysis. OP34, ECCO 2022, 16–19 February.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Subcutaneous infliximab versus subcutaneous vedolizumab in IBD Next Article
Anti-TNFs versus vedolizumab and ustekinumab in Crohn’s disease »
« Subcutaneous infliximab versus subcutaneous vedolizumab in IBD Next Article
Anti-TNFs versus vedolizumab and ustekinumab in Crohn’s disease »
Table of Contents: ECCO 2022
Featured articles
Upadacitinib maintenance therapy delivers sustained improvements in active ulcerative colitis
Novel Treatment Modalities
Guselkumab shows encouraging safety and efficacy in ulcerative colitis
Guselkumab maintenance therapy achieved high efficacy rates in Crohn’s disease
Mirikizumab efficacious for active ulcerative colitis
Risankizumab more efficacious in colonic than in ileal Crohn’s disease
Guselkumab plus golimumab promising combination for ulcerative colitis
Combined endpoint may support personalised medicine in ulcerative colitis
Filgotinib seems promising for perianal fistulising Crohn’s disease
Upadacitinib maintenance therapy delivers sustained improvements in active ulcerative colitis
Upadacitinib counters extraintestinal manifestations in ulcerative colitis
Deucravacitinib does not meet primary endpoint for ulcerative colitis
Head-to-Head Comparisons
Anti-TNFs versus vedolizumab and ustekinumab in Crohn’s disease
Upadacitinib appears to be an efficacious therapy for moderately-to-severely ulcerative colitis
Subcutaneous infliximab versus subcutaneous vedolizumab in IBD
Vedolizumab outperforms anti-TNF in biologic-naïve ulcerative colitis
Short-Term and Long-Term Treatment Results
Ozanimod treatment shows maintained response in ulcerative colitis
Stopping infliximab but not antimetabolites leads to more relapses in Crohn’s disease
Vedolizumab first approved therapy for chronic pouchitis
VEDOKIDS: Vedolizumab seems effective in paediatric IBD
Primary endpoint of 5-hydroxytryptophan for fatigue in IBD not met
Specific Therapeutic Strategies
Positive outcomes with therapeutic drug monitoring during infliximab maintenance therapy
Segmental colectomy beneficial over total colectomy in Chrohn’s disease
Modified 2-stage ileal pouch-anal anastomosis versus 3-stage alternative
Similar results for different corticosteroid tapering protocols in UC
Miscellaneous Topics
Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic for IBD management
AI model distinguishes between histologic activity and remission in ulcerative colitis
Multi-Omic and dietary analysis of Crohn’s disease identifies pathogenetic factors
Novel classification system for perianal fistulising Crohn’s disease
Vaccination tool associated with improved vaccination coverage in IBD
Comparable safety profiles of biological therapies in elderly patients with IBD
Early biologic therapy induces larger effect than delayed treatment in Crohn’s disease
RESTORE-UC: No better outcomes with FMT superdonors than with autologous stools
Related Articles
May 9, 2019
HDAC6 inhibition by CKD-506
August 12, 2021
New GI symptoms common among IBD patients with COVID-19
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

