https://doi.org/10.55788/c54d7eea
“Currently, oral budesonide is the only approved therapy for patients with MC,” said Dr Bram Verstockt (University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium) at the start of his presentation [1]. However, this agent has several limitations, such as a high relapse rate when tapering off of budesonide, treatment resistance, and side effects like osteopenia with long-term exposure. Dr Verstockt and colleagues performed a retrospective case series study to explore the value of biological agents and small molecules in patients with MC (n=98). The population consisted predominantly of women (86.7%) and had a median age at diagnosis of 49.1 years.
TNF inhibitors were used in 77% of the study group, mostly as a first-line advanced therapy option. “This is probably due to the easy access to these agents,” added Dr Verstockt. Vedolizumab was another commonly-used therapy, used in 28% of the included patients, either in first- or second-line. Other biologicals or JAK inhibitors were only administered in a small number of patients. Clinical response and clinical remission rates, and their definitions, are summarised in the Figure; percentages were notably high for JAK inhibitors.
Figure: Clinical response and remission rates at the end of induction therapy [1]
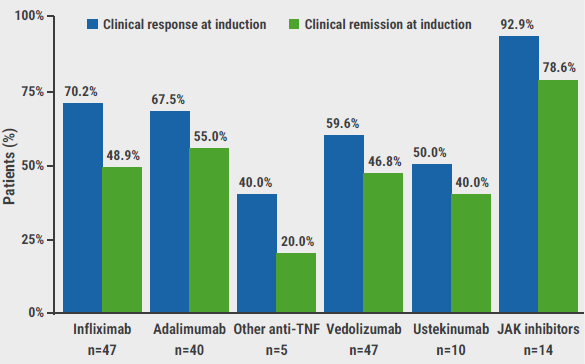
Clinical response: 50% reduction in stool frequency; Clinical remission: <3 stools/day or <1 watery stool/day.
“Although this was a retrospective study, the results imply that advanced therapies can significantly improve the quality-of-life of patients with MC,” concluded Dr Verstockt. “The high response rate, high clinical remission rate, and promising treatment persistence rate among patients treated with JAK inhibitors encourage us to further evaluate the role of these agents in patients with MC.”
- Verstockt B, et al. Promising efficacy of biologicals and small molecules for microscopic colitis: results from a large real-life multicenter cohort. DOP79, 19th Congress of ECCO, 21–24 February 2024, Stockholm, Sweden.
Copyright ©2024 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Ustekinumab as alternative for anti-TNFs in HLA-DQA1*05-positive Crohn’s disease Next Article
PROFILE: Top-down treatment strategy benefits patients with early Crohn’s disease »
« Ustekinumab as alternative for anti-TNFs in HLA-DQA1*05-positive Crohn’s disease Next Article
PROFILE: Top-down treatment strategy benefits patients with early Crohn’s disease »
Table of Contents: ECCO 2024
Featured articles
Meet the Trialist: Dr Yasuharu Maeda on AI-assisted endoscopy
IL-23 Inhibitors on the Rise
VIVID-1: Mirikizumab meets expectations in Crohn’s disease
COMMAND: Long-term efficacy benefits of risankizumab in ulcerative colitis
SEQUENCE: Risankizumab versus ustekinumab across endpoints
QUASAR: Guselkumab improves QoL for patients with ulcerative colitis
Fatigue, urgency, and QoL improvements on mirikizumab in Crohn’s disease
Inspiring Drug Trials and Treatment Strategies
Novel agent VTX002 holds promise in ulcerative colitis
PROFILE: Top-down treatment strategy benefits patients with early Crohn’s disease
Biologicals and JAK inhibitors hold promise in microscopic colitis
Ustekinumab as alternative for anti-TNFs in HLA-DQA1*05-positive Crohn’s disease
How effective is dose escalation of biologicals in IBD?
Make Way for JAK Inhibitors
Promising data for JAK inhibitors in Crohn’s disease from phase 2 trial
U-ENDURE long-term extension: sustained efficacy of upadacitinib in Crohn’s disease
TRIUMPH: Tofacitinib as rescue option for acute severe ulcerative colitis
Focus on Endoscopy, Screening, and Risk Factors
Should we screen for metabolic bone disease at IBD diagnosis?
Predicting relapse in ulcerative colitis with AI-assisted endoscopy
Clear case for NUDT15 genetic testing in Asian patients with IBD
HELIOS: HD-WLE can yield similar neoplasia detection rates as HD-CE
CURE-CD: Capsule endoscopy-guided proactive treatment leads to fewer relapses in Crohn’s disease
Sharp Surgical Solutions
Extended mesenterectomy or mesenteric-sparing surgery in Crohn’s disease?
Similar outcomes for Kono-S and side-to-side anastomosis in Crohn’s terminal ileitis
Risk factors for re-resection in Crohn’s disease revealed
ADMIRE-CD-II: Darvadstrocel does not meet primary endpoint in complex peri-anal fistula
Related Articles
May 9, 2019
Topical review
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

