https://doi.org/10.55788/72c32d1f
The efficacy of deucravacitinib for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis was comparable to that of most other biologics, according to a systematic review and network meta-analysis that indirectly compared the efficacy of systemic therapies for psoriasis in Asian patients. Therefore, the oral therapy deucravacitinib appears to be an efficacious and convenient therapy for this population.
“No network meta-analyses comparing systemic therapies for the treatment of Asian patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis have been published to date,” said Prof. Tsen-Fang Tsai (National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan). “Nonetheless, evidence indicates that the comparative efficacy of systemic therapies may be different in Asian populations compared with White patients due to lifestyle differences, patient characteristics, and clinical practice” [1,2]. Therefore, the current study aimed to determine the comparative effectiveness of deucravacitinib relative to other systemic therapies in (East)-Asian patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [2]. The authors selected 20 trials for the network meta-analysis. Prof. Tsai added that bimekizumab, cyclosporine, dimethyl fumarate, and methotrexate were not included as comparators, due to the lack of available data for Asian patients.
After 10–16 weeks, the estimated Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI)75 response was 66% for participants who were treated with deucravacitinib (95% CI 49–80%), which appeared to be higher than the response rate of participants who were being treated with apremilast (24%; 95% CI 12–40), whereas no significant differences were observed between deucravacitinib and TNF-α inhibitors, ustekinumab, and tildrakizumab. The efficacy rates in participants on IL-17 inhibitors, guselkumab, or risankizumab appeared to be somewhat higher (87–98% depending on the agent and dose used; see Figure) than that of deucravacitinib. Similar results were reported for PASI90 responses.
Figure: Estimated PASI75 response rates at weeks 10–16 in an Asian population [2]
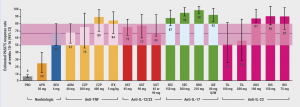
ADM, adalimumab; APR, apremilast; BRO, brodalumab; CZP, certolizumab pegol; DEU, deucravacitinib; GUS, guselkumab; IFX, infliximab; IL, interleukin; IXE, ixekizumab; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PBO, placebo; RIS, risankizumab; SEC, secukinumab; TIL, tildrakizumab; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; UST, ustekinumab.
Prof. Tsai mentioned that few studies that met the inclusion criteria reported long-term endpoints or data on biologic experience. “These data are important for the management of psoriasis and including this information in our network meta-analysis would have improved our understanding of psoriasis management in Asian patients. Nonetheless, oral deucravacitinib appears to be a convenient therapy with comparable efficacy to that of most biologics,” he concluded.
- Yu C, et al. Dermatology and Therapy. 2023;13:187–206.
- Tsai T-F, et al. Indirect comparison of deucravacitinib and other systemic treatments for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in Asian population: A systemic literature review and network meta-analysis. Session Psoriasis 1, WCD 2023, 3–8 July, Singapore, Singapore.
Posted on
« Patients with AA report high long-term regrowth rates with baricitinib Next Article
Knocking out psoriasis with high-dose risankizumab? »
Table of Contents: WCD 2023
Featured articles
Atopic Dermatitis
Rocatinlimab delivers efficacy and safety in atopic dermatitis
Head-to-head: paraffin- versus ceramide-based moisturiser for paediatric AD
Novel JAK1 inhibitor for patients with atopic dermatitis
Can lebrikizumab maintain response rates in atopic dermatitis?
Most patients with AD on dupilumab stick with this drug long-term
Psoriasis
Botulinum toxin A might provide efficacious treatment option for nail psoriasis
POETYK PSO-1 and 2: Long-term efficacy results of deucravacitinib in plaque psoriasis
Encouraging results for first oral IL-23 receptor antagonist in plaque psoriasis
Subcutaneous spesolimab for GPP flare prevention
Knocking out psoriasis with high-dose risankizumab?
Deucravacitinib versus other systemic therapies in Asian patients with psoriasis
Hair Disorders
Patients with AA report high long-term regrowth rates with baricitinib
Can ritlecitinib deliver long-term efficacy in alopecia areata?
TikTok videos on hair disorders lack reliability
Hidradenitis, Acne, and Rosacea
Spesolimab appears successful in hidradenitis suppurativa
Promising results for paroxetine in rosacea
Novel PPARγ modulator reduces acne manifestations
Microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide shifts skin microbiome in rosacea
Other Skin Conditions and Teledermatology
OLYMPIA 2: Positive results for nemolizumab in prurigo nodularis
PRFM or PRP therapy for trophic ulcers due to leprosy?
Large teledermatology project in a remote island in Eastern Indonesia
Can AI-driven teledermatology increase access to healthcare in rural African settings?
Oleogel-S10 shows long-term efficacy and safety in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
Picosecond alexandrite laser safe and effective in benign pigmentary disorders
Gentamicin improves symptoms in paediatric Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis
Related Articles
PRFM or PRP therapy for trophic ulcers due to leprosy?
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

