The new results, presented by Prof. Jeffrey S. Weber (NYU Langone Medical Center, New York City, USA), come from the phase 3 CheckMate 238 trial, which was stopped early owing to benefit. The primary endpoint was recurrence-free survival (RFS) in the intention-to-treat population, with overall survival, safety, side-effect profiles, and RFS relative to tumour PD-L1 expression. Adjuvant nivolumab increased RFS by a significant 35% compared with adjuvant ipilimumab while also reducing the rate of grade ≥3 adverse effects by approximately a third (see Figure).
Figure. Sustained long-term improvement in recurrence-free survival with nivolumab vs ipilimumab as adjuvant treatment for resected stage IIIB/IIIC or IV melanoma.
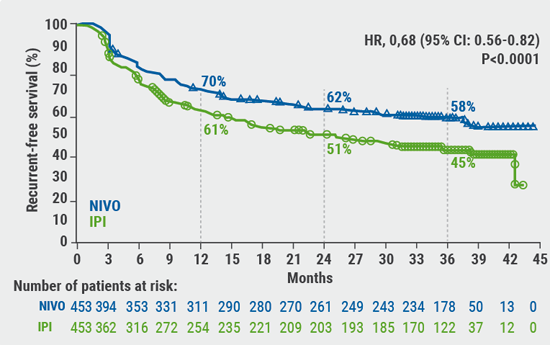
© Jeffrey S. Weber (provided by ESMO).
CheckMate 238 was a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial that included 906 patients who had undergone complete resection for stage IIIB, IIIC, or IV melanoma, who were randomly allocated to receive either nivolumab 3 mg/kg (n=453) every 3 weeks for 4 doses or ipilimumab 10 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 4 doses and then once every 12 weeks (n=453). At 3 years of follow-up, nivolumab continued to demonstrate superior RFS compared with ipilimumab, the active control, with RFS rates of 58% and 45%, respectively (HR 0.68; 95% CI 0.56–0.82; P<0.0001). Distant-metastasis-free survival also continued to be significantly longer for nivolumab, with 36-month rates of 66% and 58%, respectively (HR 0.78; 95% CI 0.62–0.99; P=0.044). Both RFS and distant-metastasis-free survival benefit continued to be observed across key subgroups, including disease stages, BRAF mutation status and PD-L1 expression. No new safety data were generated as part of the 36-month analysis.
- Weber J et al. ESMO Congress 2019. Abstract 1310O.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Frontline ipilimumab/nivolumab improves OS in advanced NCLSC Next Article
Nivolumab improves OS in advanced oesophageal cancer »
« Frontline ipilimumab/nivolumab improves OS in advanced NCLSC Next Article
Nivolumab improves OS in advanced oesophageal cancer »
Table of Contents: ESMO 2019
Featured articles
Interview with ESMO President Prof. Josep Tabernero
Breast Cancer
Triple negative breast cancer gets positive news: KEYNOTE-522 interim results
CDK4/6 inhibitors change landscape of breast cancer treatment: 2 studies
Veliparib-chemo combo prolongs survival without disease progression in some advanced breast cancer patients
Lung Cancer
Improved response rates without survival benefit with pembrolizumab in pretreated mesothelioma
Frontline ipilimumab/nivolumab improves OS in advanced NCLSC
First-line osimertinib significantly lengthens OS in NSCLC
Liquid biopsy to decide the best treatment for NSCLC
Melanoma
Long-term data from CheckMate 067
Adjuvant nivolumab provides benefit
Nivolumab+ipilimumab superior to monotherapy for melanoma brain metastases
GI Cancers
Preoperative chemotherapy for colon cancer
Nivolumab improves OS in advanced oesophageal cancer
Liquid biopsy identifies relapse in patients with colorectal cancer after surgery
In hepatocellular carcinoma, CheckMate 459 misses OS endpoint, but some interesting trends emerge
Heavily pre-treated GIST: ripretinib improves PFS
FGFR2+ cholangiocarcinoma: pemigatinib active as second-line treatment
IDH1+ cholangiocarcinoma: phase 3 results show improved PFS
Advanced colorectal cancer and BRAF mutations: triplet combination improves survival
Genitourinary Cancers
25% reduction in the risk of death in patients with nmCRPC treated with apalutamide
Enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab in advanced bladder cancer: initial results
PARP inhibition in selected patients slows progression on advanced prostate cancer
PFS extension with immunotherapy + chemotherapy in urothelial cancer
Third-line in mCRPC: CARD trial
Prostate cancer: spare radiotherapy after surgery
Novel mode of action for kidney cancer treatment
Gynaecological Cancers
Ovarian cancer patients benefit from combined maintenance therapy
Combination of PARP inhibition plus chemotherapy in ovarian cancer
PFS benefit with niraparib as first-line maintenance in ovarian cancer
CNS Tumours
Ceritinib in ALK+ NSCLC brain metastases
Solid Tumours/Pan-Tumour Data
Mixed data: AMG 510 in tumours with KRASG12C
DNA profiling of carcinoma of unknown primary should inform treatment
Larotrectinib: safe and effective in TRK fusion-positive tumours
Related Articles
November 26, 2019
Liquid biopsy to decide the best treatment for NSCLC
November 26, 2019
Third-line in mCRPC: CARD trial
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

