“In Japan, neoadjuvant chemotherapy with CF is the standard-of-care in locally advanced oesophageal cancer,” Dr Ken Kato (National Cancer Center Hospital, Japan) explained.
The current 3-arm, randomised-controlled, phase 3 JCOG1109 trial (UMIN000009482) compared neoadjuvant DCF with neoadjuvant CF and neoadjuvant CF with radiotherapy (CF-RT). In total, 601 patients were randomised 1:1:1 to one of the 3 treatment arms. Subsequently, all patients received transthoracic oesophagectomy with regional lymphadenectomy. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
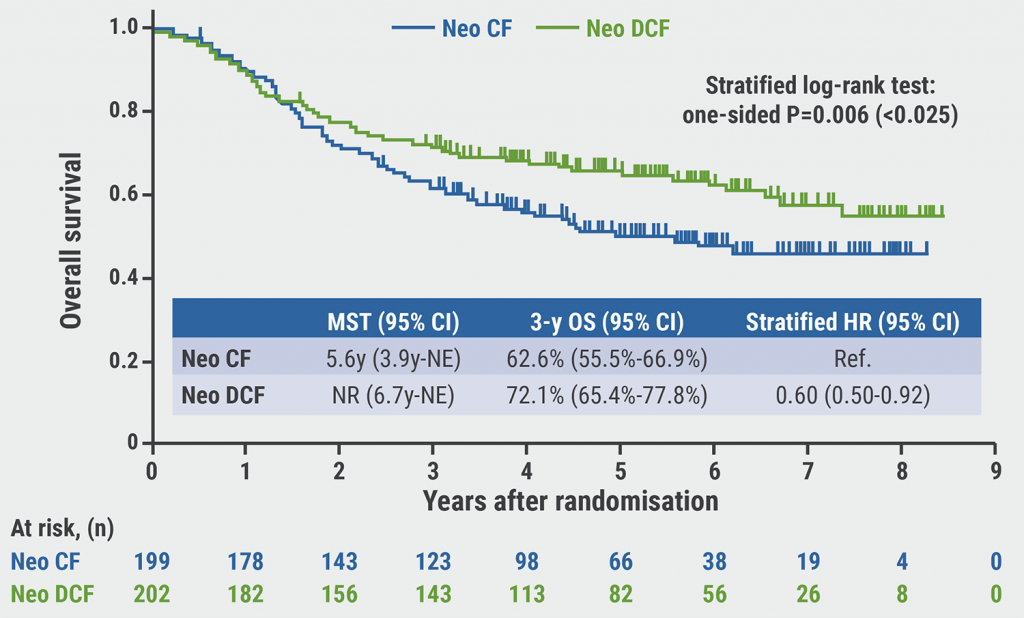
The 3-year OS rates were in favour of the DCF arm compared with the CF arm (72.1% vs 62.6%; HR 0.68; one-sided P=0.006; see Figure). There was no statistically significant OS benefit of CF-RT over CF (68.3% vs 62.6%; HR 0.84; P=0.12). These results were consistent across subgroups. Moreover, the median progression-free survival calculation displayed superior outcomes for the DCF arm compared with the CF arm (not reached vs 2.7 years; HR 0.67).
Figure: Overall survival with DCF vs CF in JCOG1109 [1]
The safety profile of DCF was manageable. In patients treated with DCF, certain grade 3–4 adverse events were more common than in the CF arm: neutropenia (85.2% vs 23.4%), hyponatraemia (26.0% vs 6.2%), febrile neutropenia (16.3% vs 1.0%), and appetite loss (21.4% vs 8.3%). Grade 3–4 oesophagitis was more frequently observed in the CF-RT arm (8.9%) than in the CF or DCF arms (both 1.0%). Furthermore, the intensified DCF regimen did not result in an increase in post-operative complications or post-operative mortality compared with the CF regimen.
Dr Kato concluded that the neoadjuvant DCF regimen represents a new standard treatment in patients with locally advanced oesophageal cancer, given the OS benefit of this treatment and its manageable toxicity profile. More data is needed in the Western population.
- Kato K, et al. A randomized controlled phase 3 trial comparing two chemotherapy regimen and chemoradiotherapy regimen as neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced esophageal cancer, JCOG1109 NExT Oral Abstract Session A, ASCO GI 2022, 20–22 January.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Nivolumab in gastric cancer: Efficacy update and the role of gut microbiome Next Article
The emerging role of AI in gastroesophageal cancer »
« Nivolumab in gastric cancer: Efficacy update and the role of gut microbiome Next Article
The emerging role of AI in gastroesophageal cancer »
Related Articles
February 13, 2024
NETTER-2: Practice-changing results for 177Lu-DOTATATE in GEP-NETs
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

