The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab, which have distinct but complementary mechanisms of action, has shown improved long-term overall survival benefit in advanced NSCLC [1]. In the randomised, phase 3 CheckMate 9LA trial (NCT03215706), first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with 2 cycles of chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival, progression-free survival, and objective response rate versus 4 cycles of chemotherapy alone [2]. Clinical benefit was observed regardless of PD-L1 expression level and histology. This regimen is now approved in the USA and Europe, among others, as first-line treatment for adult patients with metastatic NSCLC and no EGFR or ALK genomic tumour aberrations. Prof. Martin Reck (Lung Clinic Grosshansdorf, Germany) presented updated data with a 2-year minimum follow-up from the CheckMate 9LA study, as well as a post-hoc efficacy analysis in patients who discontinued nivolumab/ipilimumab/chemotherapy due to treatment-related adverse events [3].
At a median follow-up of 30.7 months, patients treated with nivolumab/ipilimumab/chemotherapy continued to derive overall survival benefit compared with chemotherapy alone, with a median overall survival of 15.8 months versus 11.0 months, respectively; 2-year overall survival rates were 38% versus 26% (see Figure). The median progression-free survival with nivolumab/ipilimumab/chemotherapy was 6.7 months versus 5.3 months with chemotherapy. A similar clinical benefit was observed in all randomised patients and across the majority of subgroups, regardless of PD-L1 expression and/or histology.
Figure: Updated overall survival in all randomised patients from CheckMate 9LA [3]
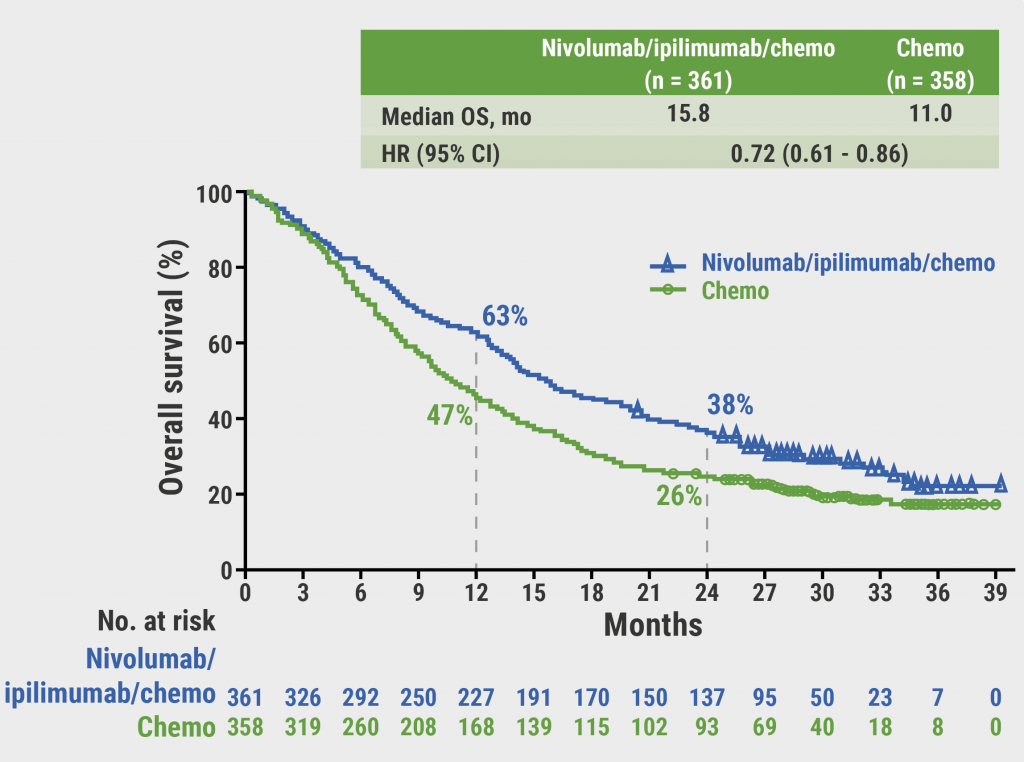
Any grade and grade 3–4 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 92% and 48% of patients in the nivolumab/ipilimumab/chemotherapy arm versus 88% and 38% in the chemotherapy arm, respectively. In patients who discontinued nivolumab/ipilimumab/chemotherapy due to treatment-related adverse events, the median overall survival was 27.5 months (2-year overall survival rate 54%).
“These updated results from CheckMate 9LA continue to support nivolumab/ipilimumab plus 2 cycles of chemotherapy as an efficacious first-line treatment option for patients with advanced NSCLC. In addition, discontinuation due to treatment-related adverse events does not have a negative impact on the long-term benefits seen with this combination,” concluded Prof. Reck.
- Ramalingam SS, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(supl15);abstract 9500.
- Paz-Ares L, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:198-21.
- Reck M, et al. First-line nivolumab (NIVO) plus ipilimumab (IPI) plus two cycles of chemotherapy (chemo) versus chemo alone (4 cycles) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Two-year update from CheckMate 9LA. Abstract 9000, ASCO 2021 Virtual Meeting, 4–8 June.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in TNBC is not superior or non-inferior to capecitabine Next Article
Immune-related adverse events are associated with efficacy of atezolizumab in patients with advanced NSCLC »
« Platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in TNBC is not superior or non-inferior to capecitabine Next Article
Immune-related adverse events are associated with efficacy of atezolizumab in patients with advanced NSCLC »
Table of Contents: ASCO 2021
Featured articles
Downloadable 1-Page Editor-Selected Trial PowerPoint Slides
Breast Cancer
Excellent prognosis for breast cancer patients with ultra-low-risk gene signature
Olaparib benefits early breast cancer patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutation
Platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in TNBC is not superior or non-inferior to capecitabine
Dalpiciclib benefits patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer
Trastuzumab-deruxtecan showed clinical activity in patients with brain metastases
Lung Cancer
Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy improves surgical outcomes in NSCLC
Immune-related adverse events are associated with efficacy of atezolizumab in patients with advanced NSCLC
Sustained efficacy of nivolumab/ipilimumab plus 2 cycles of chemotherapy in NSCLC
Patritumab deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC
Melanoma
Long-term results from ground-breaking melanoma trials
Novel dual checkpoint blockade improves progression-free survival in melanoma
Neoadjuvant therapy with nivolumab plus relatlimab is safe and effective in patients with stage III melanoma
Genitourinary Cancers
VISION trial shows improved survival with 177Lu-PSMA-617 in mCRPC
Abiraterone added to ADT + docetaxel nearly doubles survival in de novo mCSPC
Post-nephrectomy pembrolizumab improves disease-free survival
Glutaminase inhibitor telaglenastat does not improve survival mRCC
Promising efficacy and safety of feladilimab in recurrent/metastatic urothelial carcinoma
Gastrointestinal Cancers
Pembrolizumab benefits survival in MSI-H/dMMR metastastic colorectal cancer
Panitumumab added to 5-FU/LV effective as maintenance therapy in patients with mCRC
Trastuzumab-deruxtecan showed promising activity in patients with HER2-expressing mCRC
Benefit of both I-O/chemo combo and I-O/I-O combo over chemotherapy alone in oesophageal squamous cell cancer
Benefit of I-O/chemo combo over chemotherapy alone in advanced GC/GEJC/EAC
Perioperative chemotherapy and neoadjuvant multimodality therapy appear equally effective
Haematological Cancers
Olutasidenib demonstrates efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory IDH1 mutant AML
Acalabrutinib as effective but better tolerated than ibrutinib in CLL
Gynaecological Cancers
Adjuvant chemotherapy does not improve outcome in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer
Novel drug combination for recurrent ovarian cancer
Dual HER2-blockade shows anti-tumour activity in patients with uterine cancer
Paediatric Cancer
Molecular tumour profiling impacts the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumours
Circulating tumour DNA to evaluate response in children with neuroblastoma
Basic Science
PARP7 inhibitor shows promising results in first-in-human trial
IACS-6274 is well tolerated and biologically active in selected advanced tumours
CYT-0851 shows promising anti-tumour activity across different tumour types
Related Articles

June 24, 2021
ASCO 2021 Highlights Podcast
August 12, 2021
Long-term results from ground-breaking melanoma trials

August 10, 2021
Letter from the Editor
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

