https://doi.org/10.55788/183c9203
Prof. Thomas Deneke (Heart Centre Bad Neustadt, Germany) presented practical advice on the usage of CT and MR for different scenarios in clinical electrophysiology, such as monitoring implanted active devices, before or after AF and VT ablation, and monitoring complications after electrophysiology procedures. This overview aimed to inform electrophysiologists’ decisions on which technology (CT, MR, or both) and specific techniques to use in which clinical setting [1].
A standardised protocol for the inclusion of CT and MR in the planning of catheter ablation procedures was presented: pre-procedural imaging for the acquisition of imaging data, optional post-processing of imaging data, followed by integration in the mapping system by segmentation of imaging data (i.e. automatic, semi-automatic), and finally image integration and registration.
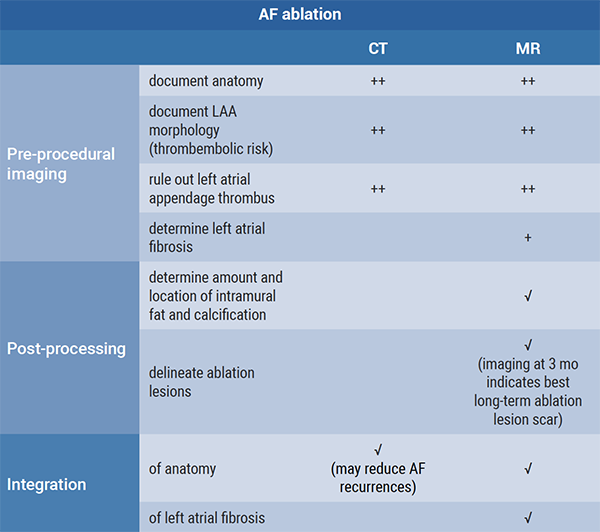
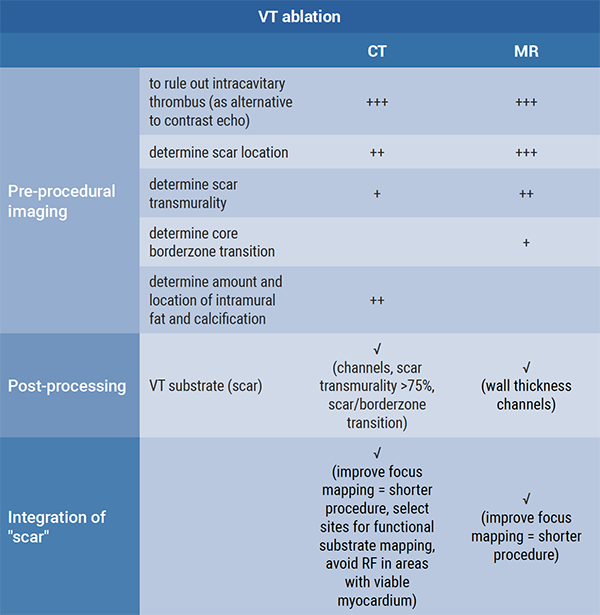
Prof. Deneke further discussed which modality (CT or MR) is ideal for which scenario in AF and VT ablation (see summary in Figure).
Figure: CT and MR imaging for AF ablation and VT ablation [1]
To aid diagnosis of ablation-related complications, CT is suitable for the detection of atrio-oesophageal fistula, oesophageal perforation (i.v. + p.o. water soluble contrast material), vascular complications, and active bleeding. Both CT and MR are suitable for diagnosis of stroke, cerebral ischaemia, and pulmonary vein stenosis.
In summary, MRI is recommended for most workflow procedures and to indicate long-term ablation lesion scars, while CT is the modality of choice in ablation-related complications.
- Deneke T. EHRA practical guide on pre- and postprocedural cardiac imaging in electrophysiology. EHRA 2021 Congress, 23-25 April.
Copyright ©2021 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Novel diagnostic score accurately differentiates between athlete’s heart and ARVC Next Article
Improvements in ischemia and angina common in INOCA, but not correlated »
« Novel diagnostic score accurately differentiates between athlete’s heart and ARVC Next Article
Improvements in ischemia and angina common in INOCA, but not correlated »
Table of Contents: EHRA 2021
Featured articles
Atrial Fibrillation and Direct Oral Anticoagulant
Predictors of young-onset atrial fibrillation
RACE 3 long-term results show fading benefit of targeted therapies in AF and HF
Deep dive into EAST-AFNET 4 results on early rhythm-control in atrial fibrillation
Cryo-FIRST study: improved AF and QoL outcomes with cryoballoon versus drug therapy
STROKESTOP: Benefits of systematic screening for atrial fibrillation
DOACs and bleeding: the role of antidotes
2021 EHRA practical guide: DOACs in pre-operative and bleeding patients
Atrial Ablation
Early rhythm-control ablation: insight from the CHARISMA registry
Personalised pulmonary vein isolation procedure feasible and effective
Pulmonary vein isolation: cryoballoon non-inferior to radiofrequency ablation
Diagnostic Tools
EHRA Practical Guide on cardiac imaging in electrophysiology
Novel diagnostic score accurately differentiates between athlete’s heart and ARVC
The precordial R-prime wave: a discriminator between cardiac sarcoidosis and ARVC
Limited added value of ECG-based mortality prediction in COVID-19 patients using machine learning
Devices
EHRA expert statement on pacemakers and intracardial devices: “watch out for the little old lady”
5-Year efficacy of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator
Specific Populations
Individualised approaches key to success in resynchronisation therapy non-responders
Antiarrhythmic drug treatment in children: evidence-based recommendations
The importance of cardiac imaging in patients with congenital heart disease
Related Articles

June 16, 2021
Letter from the Editor
June 16, 2021
Predictors of young-onset atrial fibrillation
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

