The 2-year, phase 3b SURPASS study (NCT03259074) enrolled 859 biologic-naïve patients with active radiographic axSpA and a high risk of radiographic progress, with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) ≥5 mg/L and/or the presence of at least 1 spinal syndesmophyte [1]. The trial design foresaw 3 groups, receiving either adalimumab biosimilar SDZ-ADL 40 mg or secukimumab at 150 mg or 300 mg dosages as study treatment. The primary endpoint was defined as the proportion of patients without radiographic progression at week 104, measured by an mSASSS change from baseline ≤0.5 in the assessment of 3 different central readers.
Baseline demographics showed a mean age of 42.1 and 78.5% of the participants were men. The mean mSASSS was 16.6, the mean hsCRP was 20.4 mg/l, and 73% had ≥1 syndesmophyte. The results revealed similar and non-significant results for the primary endpoint across all groups, with rates of 66.1% (secukinumab 150 mg), 66.9% (secukinumab 300 mg), and 65.9% (SDZ-ADL) of patients not developing radiographic progression up to week 104. Additionally, respective mean values for change from baseline in mSASSS were low, at 0.54, 0.55, and 0.72, respectively, a fact that Prof. Xenofon Baraliakos (Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Germany) highlighted as an important message. In line with these results, also the fractions of patients without new syndesmophytes after 2 years ranging between 53.3% and 56.9% were without significant inter-group differences. The analysis furthermore did not find relevant dissimilarities in the reduction of oedema scores for the spine and sacroiliac joint.
“We did not observe any new safety signals; overall, about 80% of the patients had at least 1 adverse event, the most frequent one was nasopharyngitis,” Prof. Baraliakos stated. For some specific adverse events, the exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EIAR) of secukinumab versus SDZ-ADL differed, among them Crohn’s disease (EIAR 1.0 vs 0.2) and uveitis (EIAR 2.1 vs 1.4).
“This first head-to-head prospective study in axSpA showed that radiographic progression of the spine over 2 years was low, with no significant difference between secukinumab and adalimumab biosimilar and no additional safety aspects as the ones that we know very well,” Prof. Baraliakos summarised.
- Baraliakos X. Effect of secukinumab versus adalimumab biosimilar on radiographic progression in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a randomized phase IIIB study. OP0059, EULAR 2023, 31 May–3 June, Milan, Italy.
Copyright ©2023 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« SSc patients with pre-capillary hypertension benefit from targeted DMARDs Next Article
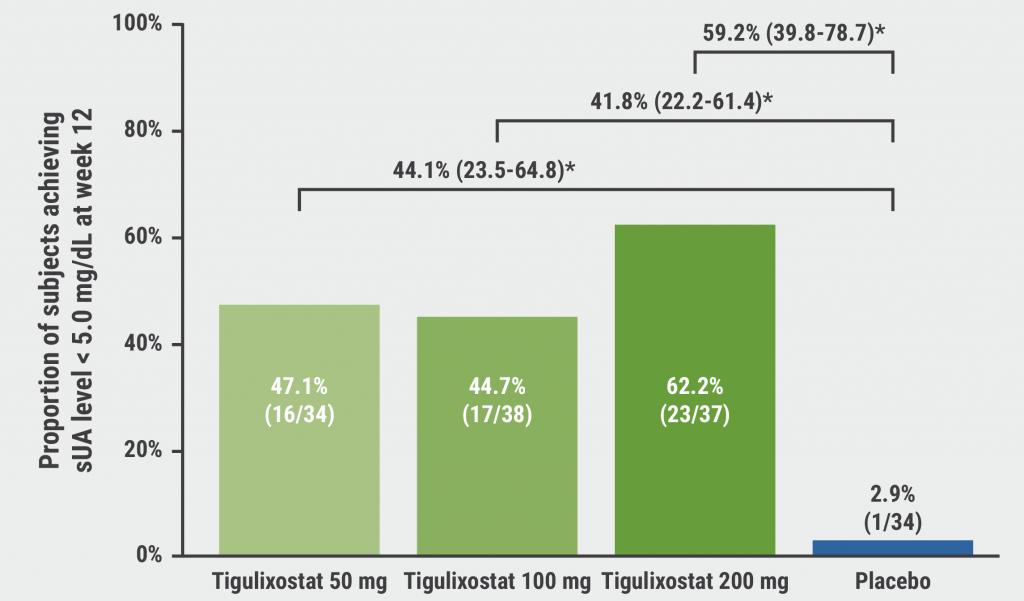
Breakthrough in patients with refractory gout: Novel 2-component infusion therapy controls serum urate levels »
« SSc patients with pre-capillary hypertension benefit from targeted DMARDs Next Article
Breakthrough in patients with refractory gout: Novel 2-component infusion therapy controls serum urate levels »
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy