Pembrolizumab showed anti-tumour activity and manageable safety in metastatic TNBC [1,2].
In addition, results from the phase 1b KEYNOTE-173 trial (NCT02622074) showed that pembrolizumab plus neoadjuvant chemotherapy had promising anti-tumour activity and manageable toxicity in patients with early-stage TNBC [3].
The phase 3 KEYNOTE-522 trial (NCT03036488) evaluated the efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy and pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in patients with early-stage TNBC. A total of 1,174 patients with previously untreated, non-metastatic, centrally confirmed TNBC were randomised 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo, both given with 4 cycles of paclitaxel plus carboplatin, then with 4 cycles of doxorubicin or epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide (neoadjuvant phase). After definitive surgery, patients received pembrolizumab or placebo for 9 cycles or until recurrence or unacceptable toxicity (adjuvant phase). Dual primary endpoints were pathological complete response rate and EFS. The primary analysis showed a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in EFS with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by pembrolizumab [4].
To assess the robustness and consistency of the primary EFS result, pre-specified sensitivity and subgroup analyses for EFS were performed, including 2 that assessed the impact of different censoring rules and 3 that assessed the impact of different event definitions. Treatment effects on EFS were examined in pre-specified patient subgroups defined by nodal involvement (positive or negative), disease stage (1 or 3), menopausal status (premenopausal or postmenopausal), HER2 status (2+ by IHC but FISH- or 0–1+ by IHC), and LDH (>ULN or ≤ULN). Prof. Peter Schmid (Barts Cancer Institute, UK) presented the results of these analyses [5].
After a median follow-up of 39.1 months, the benefit of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab versus neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone was generally consistent with the primary EFS results for all 5 sensitivity analyses and in each subgroup evaluated. Hazard ratio (HR) for the sensitivity analyses varied from 0.63–0.65 (versus 0.63 in the primary analysis). Also, HR for the subgroup analyses was in line with the primary analysis: 0.58–0.73 (see Table).
Table: Hazard Ratio of subgroup analyses [5].
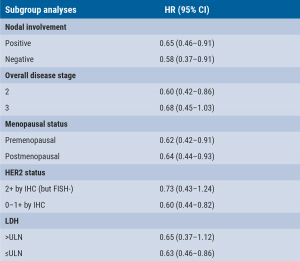
IHC, immunohistochemistry; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ULN, upper limit of normal; HR, hazard ratio.
“These results show a robust treatment benefit of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab for previously untreated non-metastatic TNBC. The EFS benefit was generally consistent across a broad selection of patient subgroups,” concluded Prof. Schmid.
- Adams S, et al. Ann Oncol 2019;30:397–404.
- Adams S, et al. Ann Oncol 2019;30:405–412.
- Schmid P, et al. Ann Oncol 2020;31:569–581.
- Schmid P, et al. N Eng J Med 2020;382:810–821.
- Schmid P, et al. KEYNOTE-522 study of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab + chemotherapy vs placebo + chemotherapy, followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab vs placebo for early-stage TNBC: Event-free survival sensitivity and subgroup analyses. GS1-01, SABCS 2021 Virtual Meeting, 7–10 December.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Early use of ctDNA testing can identify likelihood of relapse in TNBC Next Article
Single-cell spatial analysis can predict response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy »
« Early use of ctDNA testing can identify likelihood of relapse in TNBC Next Article
Single-cell spatial analysis can predict response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy »
Table of Contents: SABCS 2021
Featured articles
Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Aromatase inhibitors outperform tamoxifen in premenopausal women
Concurrent taxane plus anthracycline most beneficial in reducing risk of breast cancer
Reduced risk of recurrence with ovarian suppression plus tamoxifen/exemestane
Metformin does not improve outcomes in patients with early-stage breast cancer
Omitting sentinel lymph node biopsy improves arm symptoms
HR-positive/HER2-negative Breast Cancer
Addition of palbociclib to standard endocrine therapy does not improve outcome in adjuvant treatment
The SERD elacestrant improves outcomes for patients unresponsive to endocrine therapy
Consistent overall survival benefit of ribociclib in advanced breast cancer
Premenopausal women benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy next to endocrine therapy
Promising anti-tumour activity of the CDK7-inhibitor samuraciclib plus fulvestrant
ctDNA is prognostic and predictive for response to ribociclib plus letrozole
Early switch to fulvestrant plus palbociclib beneficial for patients with ESR1 mutation
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Single-cell spatial analysis can predict response to neoadjuvant immunotherapy
Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy benefits event-free survival in TNBC
Early use of ctDNA testing can identify likelihood of relapse in TNBC
Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy benefits patients with combined positive score ≥10
Neratinib plus trastuzumab plus fulvestrant shows encouraging clinical activity
Phase 1–3 Trials
Datopotamab deruxtecan shows promising anti-tumour activity
Trastuzumab deruxtecan outperforms trastuzumab emtansine
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab serve promising dual checkpoint inhibition
Entinostat plus exemestane improves progression-free survival in Chinese patients
Efficacy of pyrotinib plus capecitabine confirmed in previously treated patients
Basic and Translational Research
Using genomics to match treatments improves outcomes
Loss of ASXL1 tumour suppressor promotes resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors
Inducers of ferroptosis are potential drugs to target p53-mutated TNBC cells
MAPK-pathway alterations are associated with resistance to anti-HER2 therapy
Genomic signatures of DCIS define biology and correlate with clinical outcomes
BRCA2 linked to inferior outcomes with CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy
Miscellaneous
Olaparib is well tolerated as an additional treatment
Race effects the likelihood to develop lymphoedema following breast cancer treatment
Sentinel lymph node staging is non-inferior to complete axillary lymph node dissection
One in 7 breast cancers detected during screening are overdiagnosed
Related Articles
January 31, 2022
Omitting sentinel lymph node biopsy improves arm symptoms
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

