https://doi.org/10.55788/70fdb2dd
The primary results of KEYNOTE-522 (n=1,174, NCT03036488) demonstrated that neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was superior to chemotherapy and placebo in patients with early-stage TNBC in terms of pCR, and in terms of EFS if the neoadjuvant treatment was followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab [1,2]. With the current, prespecified, exploratory analysis, Prof. Lajos Pusztai (Yale School of Medicine, CT, USA) investigated the EFS by treatment arm, within residual cancer burden categories (RCB), ranging from 0 (no residual disease) to 3 (most residual disease) [3].
In each RCB category, fewer patients with residual disease at surgery received pembrolizumab compared with placebo: RCB-1 8.8% vs 11.5%; RCB-2 18.5% vs 20.3%; RCB-3 5.1% vs 6.7%. According to Prof. Pusztai, this indicates that the addition of pembrolizumab did not only increase the pCR rate (RCB-0) but shifted other RCB categories as well, in favour of pembrolizumab. The 36-month EFS analysis showed that patients with RCB-2 (n=224) might benefit most from pembrolizumab (HR 0.52), suggesting that adjuvant pembrolizumab is beneficial for patients who did not achieve a pCR. The corresponding hazard ratios in patients with RCB-0 (n=716), RCB-1 (n=114), and RCB-3 (n=66) were 0.70, 0.92, and 1.24 (see Figure). Notably, within the RCB-3 stratum, patients on placebo had a higher rate of distant recurrence as first EFS event (53.8% vs 35.0%), whereas patients on pembrolizumab more frequently displayed local recurrence as first EFS event (25.0% vs 7.7%).
Figure: Event-free survival analysis by residual cancer burden subgroup [3]
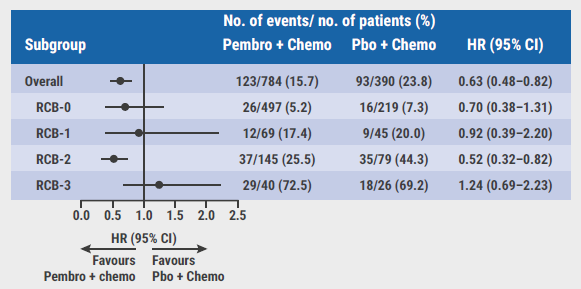
RCB, residual cancer burden; No., number; Pembro, pembrolizumab; Chemo, chemotherapy; Pbo, placebo; HR, hazard ratio.
Dr Erica Michelle Stringer-Reasor (University of Alabama, AL, USA) commented that these results show that RCB is a more detailed biomarker than pCR and offers new insights in the KEYNOTE-522 trial. “We noticed that patients in the RCB-0 and RCB-1 categories performed very well regardless of adjuvant immunotherapy, raising the question whether these patients should receive this treatment. Also, it would be interesting to see whether we can further stratify patients with residual disease, for example with circulating tumour DNA, to refine additional adjuvant therapy even more.”
- Schmid P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:810‒821.
- Schmid P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:556‒567.
- Pusztai L, et al. Event-free survival by residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant pembrolizumab + chemotherapy versus placebo + chemotherapy for early TNBC: Exploratory analysis from KEYNOTE-522. Abstract 503, ASCO 2022 Annual Meeting, 3‒7 June, Chicago, IL, USA.
Copyright ©2022 Medicom Medical Publishers
Posted on
Previous Article
« Contribution of metastatic therapies on mortality reduction in breast cancer Next Article
Metastasis-directed therapy fails in oligometastatic breast cancer »
« Contribution of metastatic therapies on mortality reduction in breast cancer Next Article
Metastasis-directed therapy fails in oligometastatic breast cancer »
Table of Contents: ASCO 2022
Featured articles
Breast Cancer
Sacituzumab govitecan meets primary endpoint
Shaky OS results of palbociclib in ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer
Practice-changing results of T-DXd in HER2-low breast cancer
SET2,3 to inform on chemotherapy decisions in ER-positive breast cancer
Metastasis-directed therapy fails in oligometastatic breast cancer
Analysis by residual cancer burden further clarifies effect of pembrolizumab
Contribution of metastatic therapies on mortality reduction in breast cancer
Radiotherapy may be omitted in breast cancer patients
Promising data for ribociclib after progression on ET plus CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer
7-gene biosignature: Benefits of endocrine therapy and radiotherapy in breast cancer risk groups
Lung Cancer
Additional tiragolumab does not help patients with untreated small cell lung cancer
Success for serplulimab plus chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer
Adagrasib safe and clinically active in non-small cell lung cancer
Long-term benefits of combined immunotherapy over chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
Effect of KRAS mutations and PD-L1 expression on therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer
Melanoma
First results on distant metastasis-free survival in stage II melanoma
Higher response rates for concurrent triple therapy versus sequential therapy in melanoma
Genitourinary Cancers
Exploratory treatment options fail in ccRCC
Adjuvant everolimus did not benefit high-risk renal cell carcinoma
Cabozantinib fails as first-line maintenance therapy in urothelial cancer
177Lu-PSMA-617 is a valid treatment option for PSMA-positive mCRPC
Enzalutamide performs well in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer
Haematologic Malignancies
Autologous stem cell transplantation plus RVd improves PFS in multiple myeloma
Novel first-line treatment option for mantle cell lymphoma
Promising results for novel CAR-T therapy in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
Gastrointestinal Cancers
Panitumumab beats bevacizumab in RAS wildtype left-sided metastatic colorectal cancer
Spectacular results for dostarlimab in mismatch repair deficient rectal cancer
Triplet chemotherapy beats doublet chemotherapy in colorectal cancer liver metastases
To resect or not to resect primary tumours in stage IV colon cancer?
Novel treatment option for KRAS wildtype pancreatic cancer
Gynaecological Cancers
Primary results of rucaparib in ovarian cancer
Trabectedin not superior to chemotherapy in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer
Encouraging results of relacorilant in ovarian cancer
Miscellaneous Topics
Bacterial decolonisation effective against radiation dermatitis
New standard-of-care for cisplatin-ineligible locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Ifosfamide is likely to be the go-to therapy in recurrent Ewing sarcoma
Dabrafenib plus trametinib candidates for standard-of-care in BRAF V600-mutated paediatric low-grade glioma
Related Articles
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

