Bone loss, reflected by low BMD, occurs frequently in patients suffering from AS. Interestingly, it can already be observed at the early stages of the disease. Recent data showed that TNFα blocking therapy has a beneficial effect on BMD, with a 7.2% improvement in lumbar spine BMD and a 2.2% improvement in hip BMD after 4 years of treatment with these agents [2]. Researchers from the Netherlands assessed the effect of 8 years of TNFα blocking therapy on the BMD of the lumbar spine and hip in AS patients. The results of this study were presented by Mark Siderius (University Medical Center Groningen; Medical Center Leeuwarden, the Netherlands).
Of the 131 AS patients included in the study, 73% were male, 83% HLA-B27+, and the mean age was 41.3 years. Patients had received TNFα blocking therapy for at least 8 years, and the use of bisphosphonates at baseline or during follow-up was not permitted. Median symptom duration was 14 years.
During follow-up, which took place at baseline, 1 year, 2 years, and then bi-annually, 27% of patients switched to a second TNFα inhibitor, and disease activity improved significantly during treatment from mean Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS)-C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.8 at baseline to 2.1 after 8 years. With regard to BMD, 34% and 19% of patients had low lumbar spine and hip BMD, respectively, at baseline. The BMD of the lumbar spine and hip BMD Z-scores significantly improved during TNFα blocking therapy at all follow-up visits compared to baseline. Significant improvement compared with the previous timepoint was found in the first year, and scores continued to improve up to 4 years of treatment for the lumbar spine and up to 2 years for the hip. Median percentage of improvement in absolute BMD after 8 years of TNFα blocking therapy compared with baseline was 7.1% for the lumbar spine and 1.6% for the hip (see Figure).
Figure: Bone mineral density improvement in lumbar spine (A) and hip (B) [1]
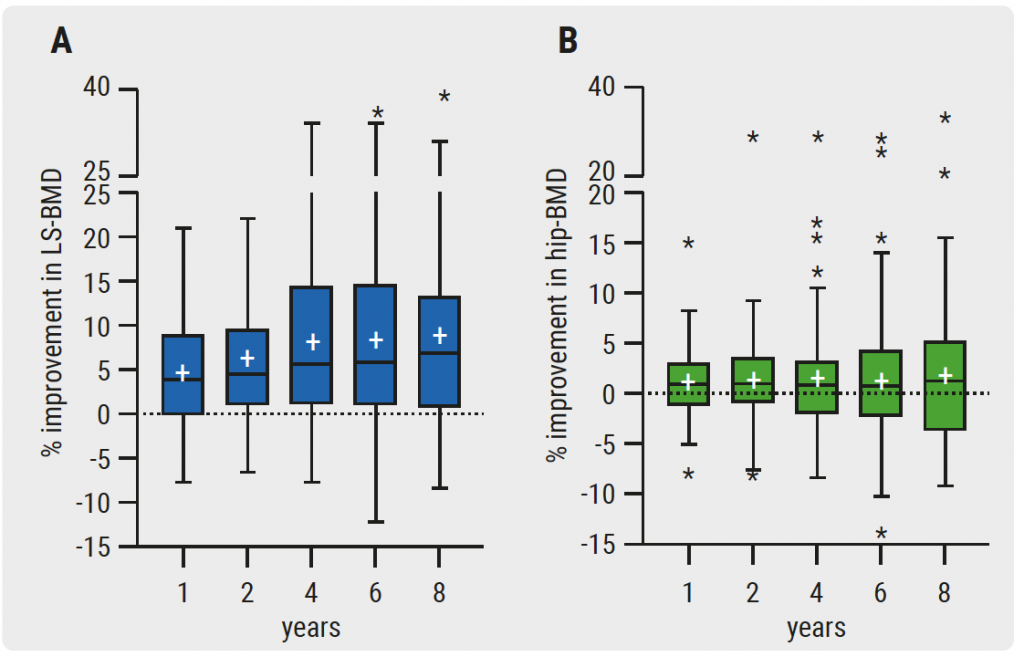
BMD, bone mineral density; LS, lumbar spine. Box-and-whisker plot: Boxes indicate medians with interquartile ranges; + indicates mean; whiskers indicate 1.5 times interquartile distances; * indicate outliers.
- Siderius M, et al. Abstract THU0376. EULAR E-Congress, 3-6 June 2020.
- Beek KJ, et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(6):1041-1048.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Preliminary findings suggest rozibafusp alfa effective and tolerable in RA Next Article
Certolizumab pegol reduces acute anterior uveitis in axial spondyloarthritis »
« Preliminary findings suggest rozibafusp alfa effective and tolerable in RA Next Article
Certolizumab pegol reduces acute anterior uveitis in axial spondyloarthritis »
Table of Contents: EULAR 2020
Featured articles
COVID-19 and inflammatory rheumatic disease: some key issues
Secukinumab monotherapy as efficient as adalimumab
AxSpA real-life remission rates higher on biologics
Olokizumab significantly improves RA features and patient-reported outcomes
Rheumatoid Arthritis
New nanoparticle promising future agent in RA
Olokizumab significantly improves RA features and patient-reported outcomes
Low DAS at 4 months predicts sustained DMARD-free remission
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Reduced maintenance dose of certolizumab pegol can be used in axSpA
Worse response axSpA patients to second TNFi versus first TNFi
AxSpA real-life remission rates higher on biologics
Certolizumab pegol reduces acute anterior uveitis in axial spondyloarthritis
TNF-α inhibitors improve bone mineral density in AS patients
Psoriatic Arthritis
Ixekizumab shows sustained improvements in pain and fatigue at 3 years
Adalimumab added to methotrexate yields better results in PsA than methotrexate escalatio
Upadacitinib provides fast onset of improvement in psoriatic arthritis
Secukinumab monotherapy as efficient as adalimumab
Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
Higher mortality risk with tramadol versus NSAIDs for osteoarthritis patients
Hydroxychloroquine not effective in patients with hand osteoarthritis
Positive effect denosumab on fall risk
Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Anifrolumab achieves rapid and durable BICLA-response
Subclinical myocardial involvement progresses in SSc patients
Composite endpoint CRESS for primary Sjögren’s syndrome
COVID-19
COVID-19 and inflammatory rheumatic disease: some key issues
Related Articles

July 29, 2024
Letter from the Editor
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
HEAD OFFICE
Laarderhoogtweg 25
1101 EB Amsterdam
The Netherlands
T: +31 85 4012 560
E: publishers@medicom-publishers.com

