Prof. Balazs Halmos (Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Medical Center, USA) presented a study on the choice of taxane and KEYNOTE-407 outcomes. His presentation was part of a mini-oral abstract session on real-world considerations in immunotherapy. It focused on an exploratory analysis of data by investigators’ choice of paclitaxel (60.1% of patients) or nab-paclitaxel (39.9% of patients).
KEYNOTE-407 was a phase 3, randomised, double-blind clinical trial in patients with advanced, untreated squamous cell carcinoma [4]. Key eligibility criteria were an ECOG of 0-1, available tissue sample for PD-L1 testing, no symptomatic brain metastasis, and no pneumonitis requiring systemic steroids. Other than a higher percentage of East-Asian patients treated with nab-paclitaxel, baseline characteristics between the two groups were well balanced. They were stratified by choice of taxane, region of enrolment (Eastern Asia vs the rest of the world), and PD-L1 tumour proportion score. OS in the pembrolizumab arm was significantly better than placebo regardless of choice of taxane (see Figure). The HR in the paclitaxel group was 0.67 vs 0.59 in the nab-paclitaxel group. However, Dr Halmos noted that although survival appeared to be numerically better in both arms for the nab-paclitaxel patients, confidence intervals were wide and overlapped.
Figure: Overall survival in an exploratory analysis of taxane choice and KEYNOTE-407 outcomes [4]
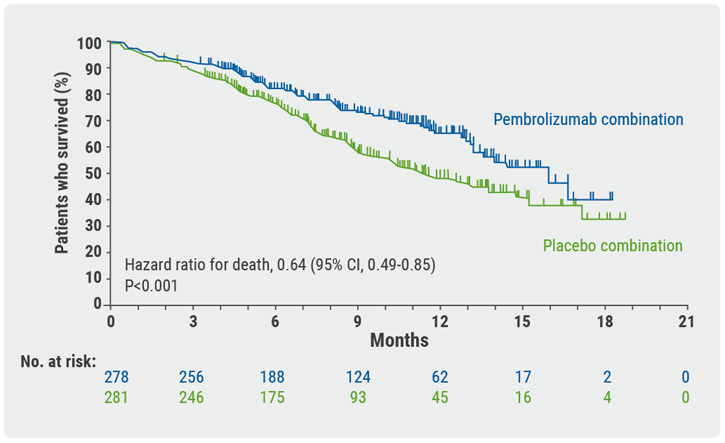
Progression-free survival benefits were also significantly better. The HR was 0.52 in the paclitaxel cohort and 0.65 in the nab-paclitaxel patients. The addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy boosted ORR by about 20% in both groups.
According to Dr Halmos, the findings demonstrate significantly improved overall survival, progression-free survival, response rate, and an acceptable safety profile regardless of taxane choice. “Our data clearly support the addition of pembrolizumab to carboplatin/taxane-based doublet chemotherapy for first-line management of advanced squamous cell NSCLC,” he said.
- Paz-Ares L, et al. N Engl J Med 2018 Sep 25 [Epub ahead of print].
Posted on
Previous Article
« Prognostic value of distant organ-specific metastases in newly diagnosed lung neuroendocrine tumours Next Article
Interview with the IASCL President, Dr. Giorgio Scagliotti »
« Prognostic value of distant organ-specific metastases in newly diagnosed lung neuroendocrine tumours Next Article
Interview with the IASCL President, Dr. Giorgio Scagliotti »
Table of Contents: WCLC 2018
Featured articles
Interview with the IASCL President, Dr. Giorgio Scagliotti
Presidential Symposium – Top 5 abstracts
Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy extends OS in stage 3, unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer
Potential for brigatinib as a first-line treatment option for ALK+ non-small-cell lung cancer
Benefits of chest CT screening
New standard of care in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer
No progression-free survival benefit with nintedanib plus pemetrexed/cisplatin for malignant pleural mesothelioma of epithelial subtype
New Aspects of Immunotherapy
Next generation immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
Combination therapies: Where are we in 2018?
Choice of taxane and addition of pembrolizumab for metastatic squamous non-small-cell lung cancer
New Aspects of Targeted Therapy
PD-L1 expression in untreated EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer and response to osimertinib
Mesothelioma
Unmet needs in surgical management of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Novel Therapies in ROS1 and EGFR
Advances in Small-cell and Neuroendocrine Tumours
Related Articles

November 21, 2018
Next generation immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

