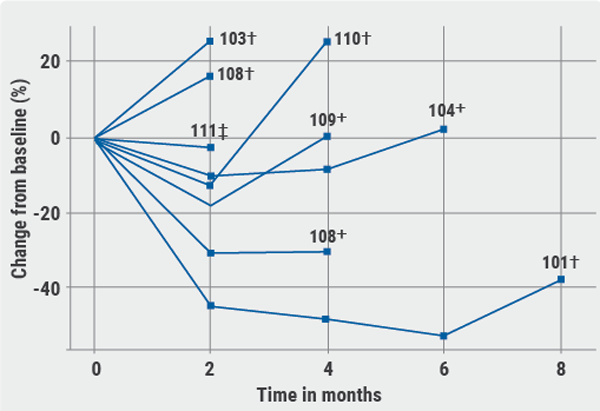
In contrast to targeted therapies, a majority of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors is due to intrinsic resistance. Currently, insights into mechanisms of acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors are limited. It is known that resistance can be mediated by tumour-related intrinsic and extrinsic factors and that for example loss of tumour neoantigens (e.g. chromosomal loss, defects in antigen processing) may mediate resistance in a subset of patients [1].
Various strategies and approaches are being evaluated, such as adding an oncolytic virus to immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in naïve patients or adding a novel agent to immunotherapy in these patients. Combinations of a novel agent and immunochemotherapy in first-line non-small-cell lung cancer treatment in naïve patients is also assessed, as is addition of a targeted agent in treatment-experienced patients, as it is known that targeted therapy can modulate immune cell function. Furthermore, novel agents are thoroughly studies and evaluated to establish their possible role in overcoming resistance (see Table) [2].
Table. Overview of novel agents that may aid in overcoming resistance [2]

- Gainor JF, et al. MS01.01. WCLC 2019.
- Soo R, et al. MS01.03. WCLC 2019.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Novel targets in mesothelioma may aid in developing treatment strategies Next Article
EGFR TKI retreatment effective after earlier discontinuation »
« Novel targets in mesothelioma may aid in developing treatment strategies Next Article
EGFR TKI retreatment effective after earlier discontinuation »
Table of Contents: WCLC 2019
Featured articles
Five-fold increase of OS at 5 years with nivolumab vs docetaxel
Screening, Detection, and Diagnosis
Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Five-fold increase of OS at 5 years with nivolumab vs docetaxel
Promising phase 1 results of novel KRAS-inhibitor in NSCLC
Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) shows durable activity in RET fusion-positive lung cancer
Other Thoracic Malignancies
Immuno-Oncology
Nivolumab + ipilimumab safe first-line treatment for NSCLC patients with comorbidities
Targeted Therapy
Phase 3 Trial Updates
First-line pembrolizumab monotherapy offers durable OS benefit vs chemotherapy in NSCLC patients with high PD-L1 expression
Related Articles
November 8, 2019
Promising phase 1 results of novel KRAS-inhibitor in NSCLC
November 8, 2019
Talazoparib + low-dose temozolomide seems promising in ES-SCLC
November 8, 2019
Durvalumab added to etoposide improves outcomes in ES-SCLC
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

