Children with Down syndrome (DS) are at high risk of developing myeloid leukaemia (ML-DS). Up to 30% of DS newborns develop a pre-leukaemic transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM), characterised by the accumulation of immature megakaryoblasts of foetal origin. TAM is characterised by GATA1 mutations (GATA1-s) that result in a shorter protein isoform lacking the N-terminal transactivation domain. To understand how trisomy 21 cooperates with GATA1-s in TAM development, the researchers performed a CRISPR/Cas9 screen, targeting the 218 currently annotated coding genes on Hsa21 with 1,090 sgRNAs in both an ML-DS and control cell line.
RUNX1 loss resulted in depletion of ML-DS cells. Additionally, the researchers observed differential RUNX1 isoform expression in acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia (non-DS) and ML-DS primary cells compared with normal haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells or terminally differentiated cells. In a newly established TAM/ML-DS assay, GATA1-s synergised with particular isoforms leading to a hyperproliferative phenotype in vitro and induction of leukaemia in vivo. This was further confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation assays followed by mass spectrometric analysis and DNA sequencing, showing differences in the physical interactions of GATA1/GATA1-s and RUNX1 isoforms as well as at genomic loci in TAM and ML-DS. These results highlight the importance of analysing all isoforms of a gene when studying its function in leukaemogenesis, with relevance for targeted therapies.
1. Gialesaki S, et al. Abstract S146, 24th Congress of the EHA, 13-16 June 2019, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
Posted on
Previous Article
« Positive initial data evaluating the safety and efficacy of IMR-687 for treatment of sickle cell disease Next Article
Residual disease in AML patients prior to stem cell transplant increases relapse risk »
« Positive initial data evaluating the safety and efficacy of IMR-687 for treatment of sickle cell disease Next Article
Residual disease in AML patients prior to stem cell transplant increases relapse risk »
Table of Contents: EHA 2019
Featured articles
Editor Biography
Interview with EHA President Prof. Pieter Sonneveld
Myeloid Malignancies
Residual disease in AML patients prior to stem cell transplant increases relapse risk
Gilteritinib prolongs overall survival in patients with FLT3-mutated relapsed/refractory AML
Initial data on AMV564 in patients with relapsed/refractory AML
Overcoming the “don’t eat me” signal in AML and MDS
Asciminib plus imatinib in patients with heavily pre-treated chronic myeloid leukaemia
Guadecitabine vs treatment of choice in AML
Lymphoid Malignancies
Unmutated IGHV as predictive factor for venetoclax/obinutuzumab benefit in frontline CLL
CAR-T cell therapy in ALL as breakthrough advance
Brentuximab vedotin continues to demonstrate superior clinical activity in classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Infectious complications mild and not common in patients receiving CAR-T therapy for diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Obinutuzumab/polatuzumab in follicular lymphoma
Exciting survival data for ibrutinib vs placebo in treatment-naïve, early-stage CLL
ASCEND study: Acalabrutinib improves progression-free survival in relapsed/refractory CLL
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combination elicits high response rates in CLL
Myeloma
CASSIOPEIA trial: Phase 3 results of daratumumab + bortezomib/thalidomide/dexamethasone in multiple myeloma
Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in multiple myeloma
Higher levels of treatment satisfaction without compromising efficacy: subcutaneous daratumumab in RRMM
Adding isatuximab to pomalidomide and dexamethasone improves PFS and ORR in RRMM
Subcutaneous daratumumab + cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed amyloid light chain amyloidosis
Venetoclax for multiple myeloma: effective but some safety concerns
Benign Haematology
New sickle cell drug voxelotor boosts levels of haemoglobin
Positive initial data evaluating the safety and efficacy of IMR-687 for treatment of sickle cell disease
Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation improves stroke risk in children with sickle cell anaemia
Early trial data shows positive results for treating anaemia in patients with end-stage renal failure
Bench-to-Bedside
Transformation of foetal haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the background of trisomy 21
Treating thalassemia twice, in mice
Haematopoietic stem cells can sense tissue damage in the gut
Promising news for gene therapy for sickle cell disease
Related Articles
August 9, 2019
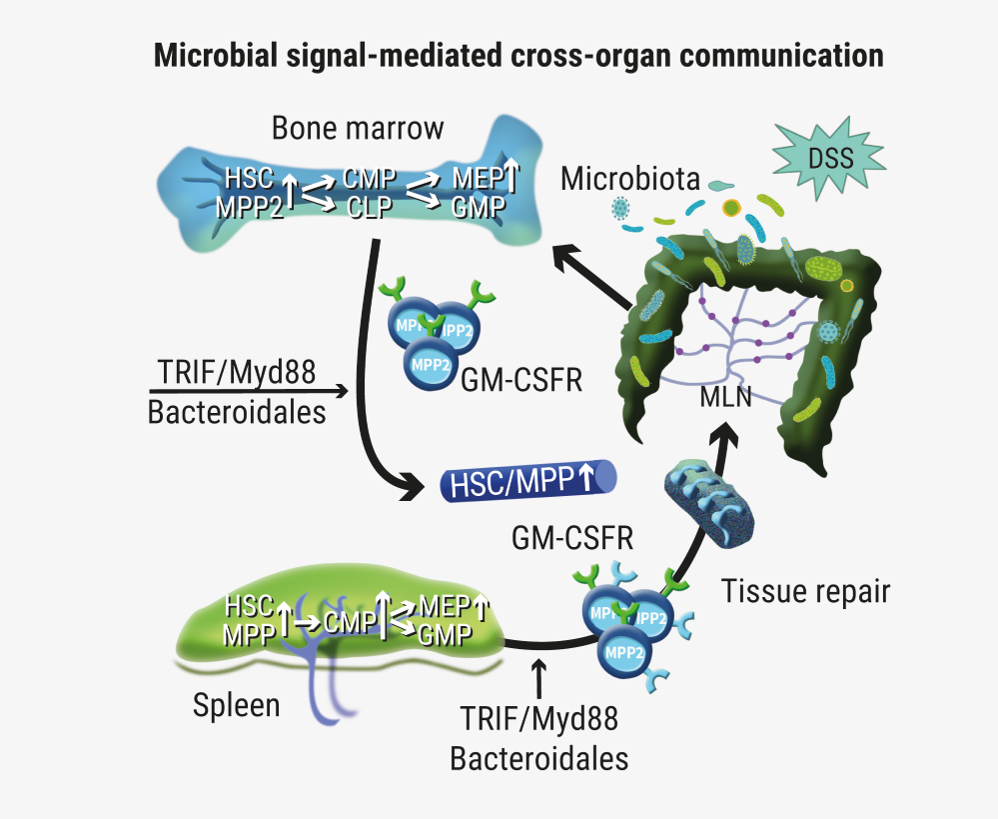
Haematopoietic stem cells can sense tissue damage in the gut
August 9, 2019
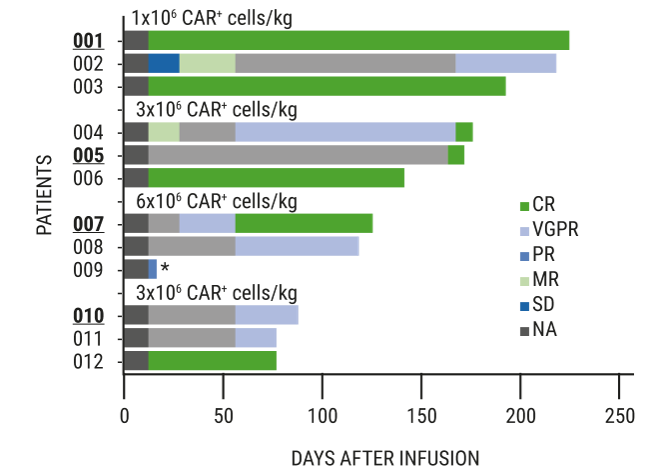
Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in multiple myeloma
© 2024 Medicom Medical Publishers. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy

